Where Are Dog Chips Placed?
How Microchips Are Implanted in Dogs
- Standard Placement Location:
The microchip is inserted subcutaneously between the shoulder blades, just beneath the skin. This location is chosen because it’s easily accessible and minimizes discomfort during implantation. - Why the Shoulder Blade Area Is Ideal:
Placing the chip here ensures it stays securely in place, as the area experiences minimal movement compared to other parts of the body. It also reduces the risk of migration, where the chip might shift to another location over time. - Procedure Details:
The microchip is implanted using a specialized needle slightly larger than those used for vaccinations. The process takes only a few seconds and is similar to administering a routine shot, making it quick and painless for most dogs. - No Anesthesia Required:
Unlike surgical procedures, microchipping doesn’t require anesthesia. However, many veterinarians choose to implant the chip during spaying or neutering to combine tasks and reduce stress for the dog. - Post-Implantation Care:
After the procedure, there’s no special care needed. The site may be slightly tender for a short period, but complications like infection or irritation are exceedingly rare.
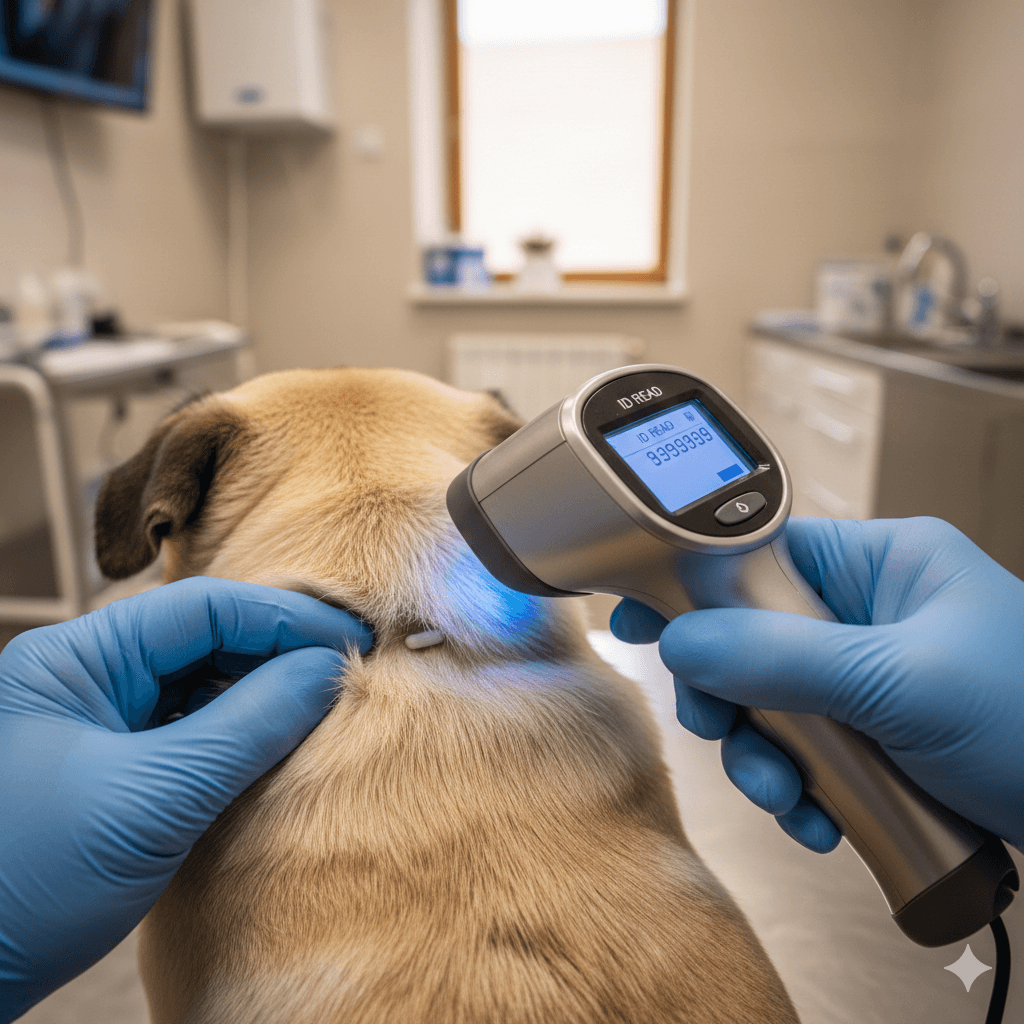
Benefits of Microchipping Your Dog
- Permanent Identification:
Unlike collars, which can fall off or be removed, microchips remain embedded under the skin for life, ensuring continuous identification. - Quick and Reliable Scanning:
Shelters, veterinarians, and animal control officers use universal scanners to read microchip information. This makes it easy to identify a lost dog and contact their owner promptly. - Increased Recovery Rates:
Studies show that microchipped dogs are reunited with their owners at much higher rates than non-microchipped dogs, especially in cases where they’re found far from home. - Affordable and Accessible:
The cost of microchipping is relatively low, often ranging from $25 to $50, and many shelters include it as part of adoption fees. Some communities even offer free or discounted microchipping events. - Peace of Mind for Owners:
Knowing your dog carries a permanent ID provides reassurance, especially if you live in an area prone to natural disasters or have an escape-prone pet.
Check this guide 👉Tracking Chips for Dogs: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉Is Microchipping a Dog Safe? Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉Reasons Not to Microchip Your Dog: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Microchip | Collar Tags |
|---|---|
Implanted subcutaneously between the shoulder blades | Attached to the collar and visible externally |
Permanent identification for the dog’s lifetime | Can fall off, break, or become unreadable over time |
Requires a scanner to read the ID number | Displays contact info directly, no equipment needed |
Minimal maintenance; only registration updates required | Needs regular replacement due to wear and tear |
Ideal for long-term safety and permanent ID | Best for quick visual identification in everyday situations |
How to Register and Update Microchip Information
- Initial Registration Process:
After implantation, the microchip company sends a registration form or online link. You must provide your contact details, including your name, address, phone number, and email. - Importance of Up-to-Date Information:
If you move, change phone numbers, or transfer ownership, update the microchip registry immediately. Outdated information renders the chip useless in locating the owner. - Multiple Registration Options:
Most microchip companies allow online, phone, or mail-in updates. Some even offer mobile apps for easy management of your pet’s profile. - Annual Check-Ups:
Make it a habit to review your microchip registration annually, such as during your dog’s yearly vet visit, to confirm all details remain accurate. - Transferring Ownership:
When rehoming a dog, notify the microchip company of the new owner’s information. Failure to do so can lead to confusion if the dog ever gets lost.
Common Concerns About Microchipping Dogs
- Is Microchipping Painful?
The sensation is similar to a routine vaccination. Most dogs tolerate the procedure well, showing little to no reaction during or after implantation. - Can the Chip Migrate?
While rare, migration can occur if the chip isn’t properly inserted. Choosing a qualified veterinarian reduces this risk significantly. - Are There Health Risks?
Complications like infections or tumors are extremely uncommon. Millions of dogs worldwide have been safely microchipped without adverse effects. - Does the Chip Contain GPS?
Microchips do not track your dog’s location. They store only an identification number that links to your contact information in a database. - What Happens If the Chip Fails?
Chip failure is rare, but having backup identification methods (like a collar tag) adds an extra layer of security.
How Shelters and Veterinarians Use Microchips
- Universal Scanners:
Modern scanners can read multiple microchip frequencies, ensuring compatibility regardless of the brand used. This eliminates confusion during identification. - Immediate Owner Contact:
Once scanned, the chip’s ID number retrieves the owner’s contact information from the manufacturer’s database. This allows swift communication to arrange the dog’s return. - Handling Unregistered Chips:
If a chip lacks updated registration, shelters conduct additional efforts, such as searching local databases or posting found pet alerts online. - Routine Scanning Protocols:
Many shelters and clinics scan every incoming animal automatically, even if brought in for unrelated reasons, to check for existing chips. - Educating Pet Owners:
Veterinarians often explain the importance of microchipping during wellness visits, encouraging proactive measures before an emergency arises.
What to Do If Your Dog’s Microchip Isn’t Detected
- Verify the Scanning Process:
Ask the veterinarian or shelter to use a different scanner or try again later, as operator error or equipment malfunctions can sometimes cause missed readings. - Check for Migration:
If the chip has migrated from its original placement, request a full-body scan to locate it. This is uncommon but possible in some cases. - Contact the Microchip Company:
Reach out to the manufacturer to verify the chip’s status and troubleshoot potential issues with registration or functionality. - Consider Reimplantation:
If the chip cannot be located or confirmed functional, discuss reimplanting a new one with your veterinarian. Many companies offer replacements at reduced costs. - Document Everything:
Keep records of the chip’s ID number, implantation date, and any correspondence with the microchip provider for future reference.
Alternatives to Microchipping for Dog Identification
- Collar Tags:
Personalized tags display your dog’s name and contact information visibly, making it easier for finders to reach you directly without needing a scanner. - Tattooing:
Some owners opt for tattoos placed inside the ear or on the inner thigh. While less common today, they remain a visible and permanent option. - GPS Trackers:
Wearable GPS devices attach to collars and provide real-time location tracking via smartphone apps. These require batteries and cellular service but offer active monitoring. - QR Code Collars:
Modern collars feature QR codes linked to online profiles containing your dog’s information. Anyone with a smartphone can scan the code to access details. - Combination Approach:
Using multiple methods—such as a collar tag, GPS tracker, and microchip—creates layers of protection, maximizing the chances of recovery in case one method fails.
Frequently Asked Questions About Dog Microchipping
Where exactly is a dog microchip placed?
The microchip is implanted subcutaneously between the shoulder blades, just beneath the skin. This location ensures it stays secure and is easy to scan.
Does the microchip contain GPS tracking?
No, microchips do not have GPS capabilities. They store only an identification number linked to your contact information in a database.
Is microchipping painful for my dog?
The procedure is similar to a routine vaccination and causes minimal discomfort. Most dogs tolerate it well without any lasting effects.
Can the microchip move or migrate within the body?
While rare, migration can occur if improperly inserted. Choosing a qualified veterinarian minimizes this risk significantly.
How do I update my dog’s microchip information?
Contact the microchip company online, by phone, or via mail to update your contact details. Many providers also offer mobile apps for easy management.
A Lifeline Beneath the Skin
Pemphigus Erythematosus in Cats: Best 7 Expert Tips! – Learn to recognize symptoms, manage flare-ups, and improve your cat’s quality of life.
Pemphigus Erythematosus in Dogs: Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover causes, symptoms, and treatment options to manage this autoimmune skin condition effectively.
Cat Tympanic Membrane: Best 7 Expert Tips! – Learn how to protect your cat’s eardrum, spot issues early, and ensure lifelong auditory health.
Dog Tympanic Membrane: Best 7 Expert Tips! – Learn how to protect your dog’s eardrum, spot issues early, and ensure lifelong ear health with expert advice.