Understanding Keratitis in Dogs
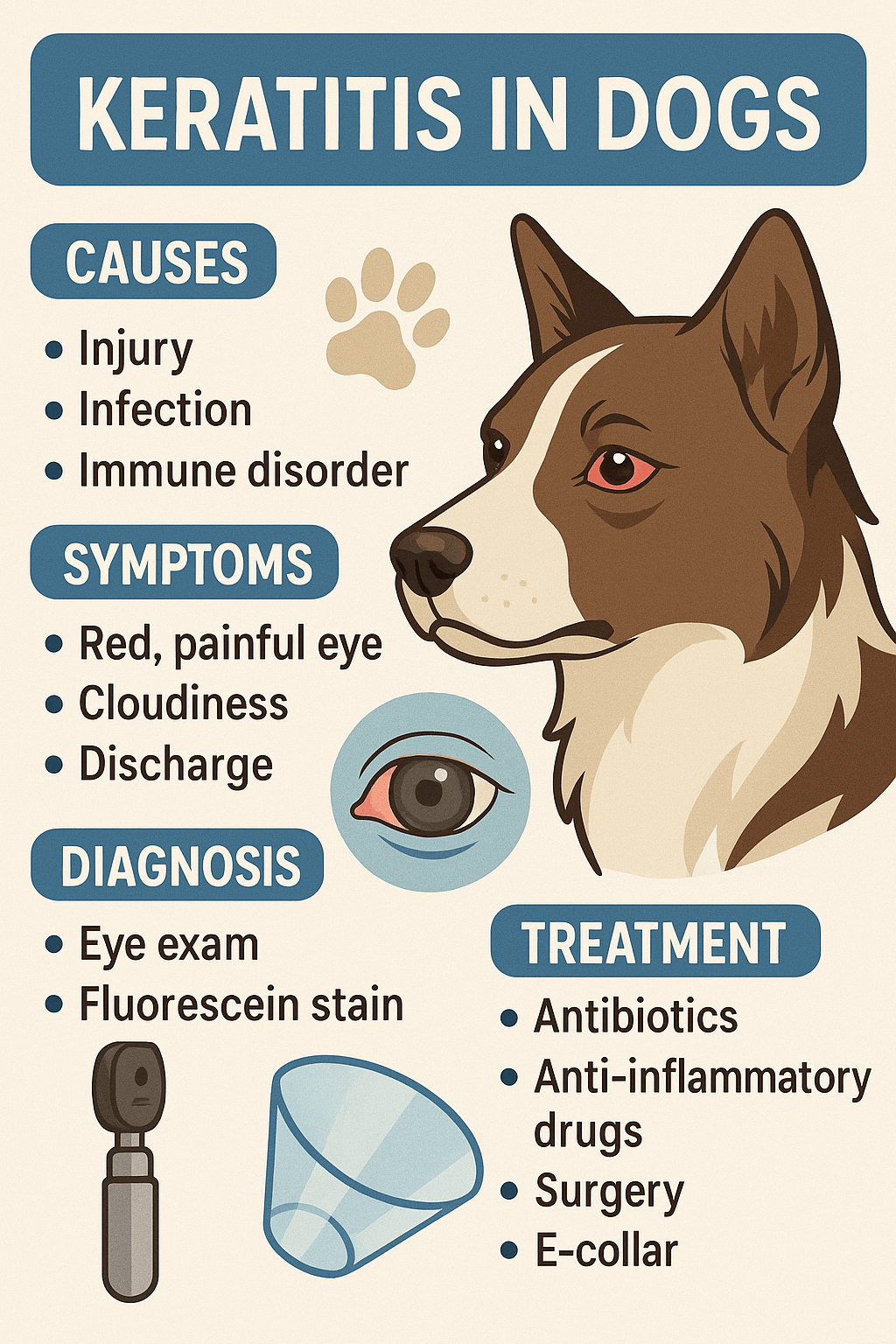
Keratitis is a condition that affects the cornea of a dog’s eye, leading to inflammation and discomfort. While it may sound alarming, understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help you address this issue effectively. Whether your furry friend is showing signs of redness, cloudiness, or excessive tearing, recognizing keratitis early can make a significant difference in their recovery. This blog post dives into everything you need to know about keratitis in dogs, from identifying the warning signs to managing the condition with care and compassion.
Expert Insight on Keratitis in Dogs
“Acute non-ulcerative keratitis may not involve any obvious changes to the cornea at first, but in some cases it may be possible to notice a subtle cloudiness or haziness to the eye. When the condition becomes more chronic, buildup of dark pigmentation on the cornea begins. In contrast, ulcerative keratitis involves a disruption in the top layer of the cornea, which may or may not be visible with the naked eye and is diagnosed by your veterinarian.”
Common Causes of Keratitis in Dogs
Keratitis can stem from various factors, ranging from infections to environmental irritants. Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Bacterial or Viral Infections:
Bacteria or viruses can invade the cornea, leading to inflammation and infection-related keratitis.Trauma or Injury:
Scratches, foreign objects, or blunt force trauma to the eye can damage the cornea, triggering keratitis.Immune-Mediated Disorders:
Some dogs develop keratitis due to an overactive immune response attacking the corneal tissue.Dry Eye (Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca):
Insufficient tear production can leave the cornea vulnerable to irritation and infection, resulting in keratitis.Genetic Predisposition:
Certain breeds, such as Boxers and Bulldogs, are more prone to chronic superficial keratitis due to genetic factors.
By pinpointing the root cause, veterinarians can tailor treatment plans to address your dog’s specific needs and promote faster healing.
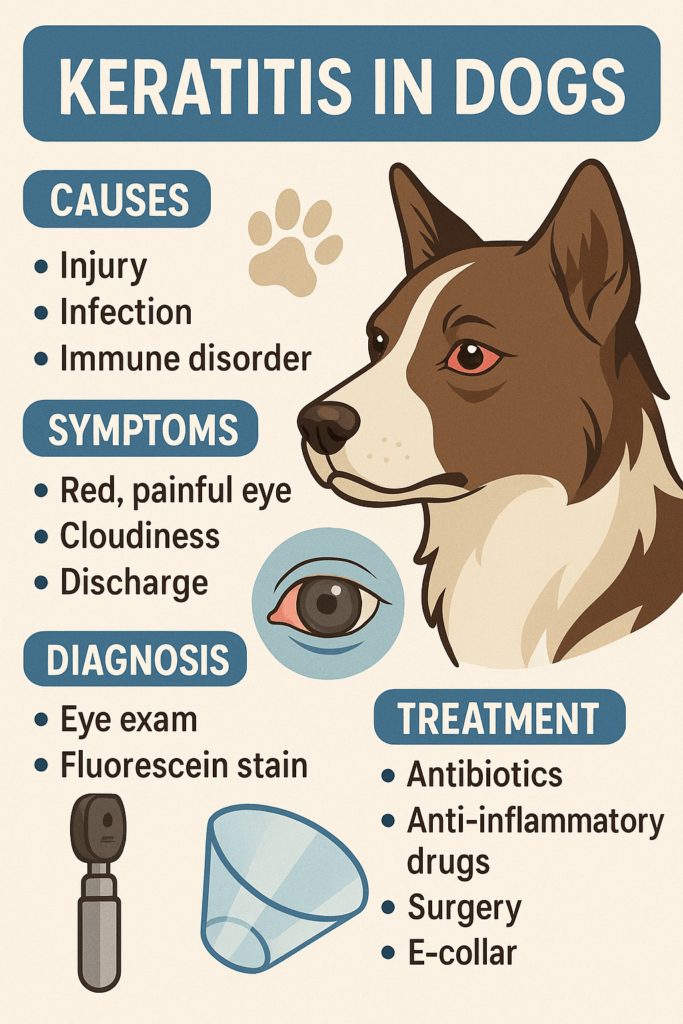
Signs and Symptoms of Keratitis in Dogs
Recognizing the symptoms of keratitis is essential for early intervention. These signs often manifest in visible changes to your dog’s eyes or behavior.
Redness and Swelling:
The white part of the eye may appear bloodshot, and the surrounding area might swell.Cloudy or Hazy Cornea:
A cloudy or opaque appearance in the eye is one of the hallmark signs of keratitis.Excessive Tearing or Discharge:
Watery eyes or abnormal discharge can indicate irritation or infection in the cornea.Squinting or Pawing at the Eye:
Dogs may squint frequently or paw at their eyes due to discomfort or pain.Sensitivity to Light:
Keratitis can make your dog’s eyes sensitive to bright light, causing them to avoid well-lit areas.
If you notice any of these symptoms, consult your veterinarian promptly to prevent further complications.
Check this guide 👉Dog Eye Injury Treatment: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉Dog Eye Blood Vessel Burst: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉Dog Eye Watering: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Types of Keratitis | Treatment Options |
|---|---|
Ulcerative Keratitis | Antibiotics, pain relief medications |
Infectious Keratitis | Antiviral or antibacterial treatments |
Chronic Superficial Keratitis | Topical corticosteroids, immune modulators |
Pigmentary Keratitis | Tear stimulants, surgical removal of pigmentation |
Traumatic Keratitis | Anti-inflammatory drugs, protective collars |
Diagnosing Keratitis in Dogs
Proper diagnosis is key to treating keratitis effectively. Veterinarians use a combination of clinical assessments and diagnostic tools to identify the condition accurately.
Physical Examination:
The vet will inspect your dog’s eyes for visible signs of inflammation, cloudiness, or injury.Fluorescein Stain Test:
A special dye is applied to detect corneal ulcers or abrasions that might not be visible to the naked eye.Schirmer Tear Test:
This test measures tear production to determine if dry eye is contributing to the condition.Intraocular Pressure Measurement:
Checking the pressure inside the eye helps rule out glaucoma or other related conditions.Biopsy or Culture:
In severe cases, a biopsy or culture may be performed to identify specific pathogens causing the infection.
Accurate diagnosis ensures targeted treatment, improving your dog’s chances of a full recovery.
Preventing Keratitis in Dogs
While not all cases of keratitis can be prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk of your dog developing this condition.
Regular Eye Checkups:
Schedule routine veterinary visits to monitor your dog’s eye health and catch potential issues early.Protective Eyewear:
For active or working dogs, consider using protective goggles during outdoor activities to shield their eyes.Maintain Good Hygiene:
Clean your dog’s face regularly to remove dirt, debris, or irritants that could harm their eyes.Monitor for Foreign Objects:
Keep an eye out for grass seeds, dust, or other particles that could lodge in your dog’s eyes.Address Underlying Conditions:
Treat conditions like dry eye or allergies promptly to minimize the risk of secondary complications.
Taking preventive steps can significantly lower the likelihood of keratitis and ensure your dog’s eyes stay healthy.
Managing Chronic Superficial Keratitis
Chronic superficial keratitis, also known as pannus, requires careful management to prevent progression. Understanding how to address this condition can improve your dog’s quality of life.
Use of Topical Steroids:
Corticosteroid eye drops help reduce inflammation and slow the progression of the disease.Immunosuppressive Medications:
Drugs like cyclosporine can suppress the immune response attacking the cornea.UV Protection:
Limit exposure to direct sunlight, as UV rays can worsen pannus symptoms.Regular Monitoring:
Frequent checkups are necessary to adjust treatment as the condition evolves.Lifelong Management:
Pannus is a lifelong condition, so consistent care is essential for maintaining eye health.
With dedication and proper treatment, dogs with chronic superficial keratitis can live comfortably.
Home Care Tips for Dogs with Keratitis
Providing supportive care at home can enhance your dog’s recovery from keratitis. These tips ensure a safe and healing environment.
Administer Medications as Directed:
Follow your vet’s instructions carefully when applying eye drops or ointments.Create a Calm Space:
Minimize stress by keeping your dog in a quiet, comfortable area during recovery.Prevent Rubbing or Scratching:
Use an Elizabethan collar to stop your dog from pawing at their eyes.Keep the Environment Clean:
Reduce exposure to dust, smoke, or allergens that could irritate the eyes.Offer Nutritious Food:
A balanced diet supports overall health and aids in healing.
Home care plays a vital role in speeding up recovery and preventing recurrence.
When to Seek Emergency Veterinary Care
Some eye conditions require immediate attention to prevent permanent damage. Knowing when to act quickly can save your dog’s vision.
Severe Pain or Squinting:
If your dog shows extreme discomfort or keeps their eye shut, seek help immediately.Profuse Bleeding or Discharge:
Unusual amounts of blood or pus indicate a serious problem needing urgent care.Sudden Vision Loss:
Any abrupt change in your dog’s ability to see warrants an emergency visit.Foreign Object Lodged in the Eye:
Never attempt to remove deeply embedded objects yourself; let professionals handle it.Aggressive Behavior Due to Pain:
If your normally gentle dog becomes aggressive, it may signal intense eye pain.
Timely intervention can prevent complications and protect your dog’s eye health.
Frequently Asked Questions About Keratitis in Dogs
Can keratitis lead to blindness in dogs?
If left untreated, severe cases of keratitis can result in vision loss or blindness. Early treatment is critical.
Is keratitis painful for dogs?
Yes, keratitis can cause discomfort or pain, especially if there’s an ulcer or infection present.
How long does it take to treat keratitis?
Treatment duration varies depending on the type and severity of keratitis but typically ranges from a few weeks to several months.
Are certain breeds more prone to keratitis?
Breeds with short noses, such as Pugs and Bulldogs, are more susceptible due to their eye anatomy.
Can I use human eye drops for my dog’s keratitis?
No, human eye drops may contain ingredients harmful to dogs. Always consult your vet for appropriate treatments.
Caring for Your Dog’s Eyes: A Path to Recovery
Keratitis in dogs may seem daunting, but with prompt diagnosis, proper treatment, and ongoing care, most cases can be managed successfully. By staying vigilant for signs of eye trouble and taking preventive measures, you can safeguard your dog’s vision and overall well-being. Remember, your veterinarian is your best ally in navigating this condition—don’t hesitate to seek professional guidance whenever needed. With love and attention, you can help your furry companion overcome keratitis and enjoy a lifetime of clear, healthy eyes.
Do Cats Have Taste Buds? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how cats experience flavors and why their taste is so unique.
Do Dogs Have Taste Buds? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how dogs experience taste, their preferences, and what it means for their diet and health.
Can Cats Taste Sweet? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover why cats can’t taste sweetness, how it affects their diet, and tips to keep them healthy and happy.
Can Dogs Taste Sweet? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how dogs perceive sweetness, which foods are safe, and tips to manage their sweet cravings responsibly.