Understanding Dog Radiology: A Vital Tool for Canine Health
Dog radiology, or X-ray imaging, is a cornerstone of veterinary diagnostics, providing invaluable insights into your pet’s internal health. Whether it’s identifying fractures, detecting tumors, or evaluating organ function, radiology helps veterinarians uncover issues that aren’t visible during routine exams. This non-invasive procedure is safe, efficient, and widely used to guide treatment plans for dogs of all ages and breeds. Knowing when and how radiology is used empowers you to make informed decisions about your dog’s healthcare journey.
Common Uses of Radiology in Veterinary Medicine
Radiology plays a pivotal role in diagnosing and monitoring various health conditions in dogs. Veterinarians rely on X-rays to visualize internal structures, helping them identify abnormalities that may not be detectable through physical exams alone. From broken bones to chronic illnesses, radiology provides clarity and precision in treatment planning. Understanding the most common applications of dog radiology ensures you appreciate its importance in modern veterinary care.
- Diagnosing Fractures and Bone Injuries:
X-rays are the gold standard for identifying fractures, dislocations, or other skeletal injuries. They reveal the exact location, severity, and type of damage, guiding surgical or non-surgical interventions. - Detecting Abdominal Abnormalities:
Radiology helps evaluate organs like the liver, kidneys, spleen, and intestines. Conditions such as tumors, obstructions, or fluid accumulation are often diagnosed through abdominal X-rays. - Evaluating Thoracic Conditions:
Chest X-rays are essential for assessing heart size, lung health, and airway function. They are commonly used to diagnose pneumonia, heart disease, or cancerous growths in the chest cavity. - Identifying Dental Issues:
Dental radiology reveals problems below the gum line, such as tooth root abscesses, fractures, or periodontal disease. These issues are often hidden during routine oral exams. - Monitoring Chronic Conditions:
For dogs with arthritis, hip dysplasia, or spinal disorders, radiology tracks disease progression and evaluates the effectiveness of treatments over time.
Radiology’s versatility makes it an indispensable tool in veterinary medicine, offering detailed insights that improve diagnostic accuracy and treatment outcomes.
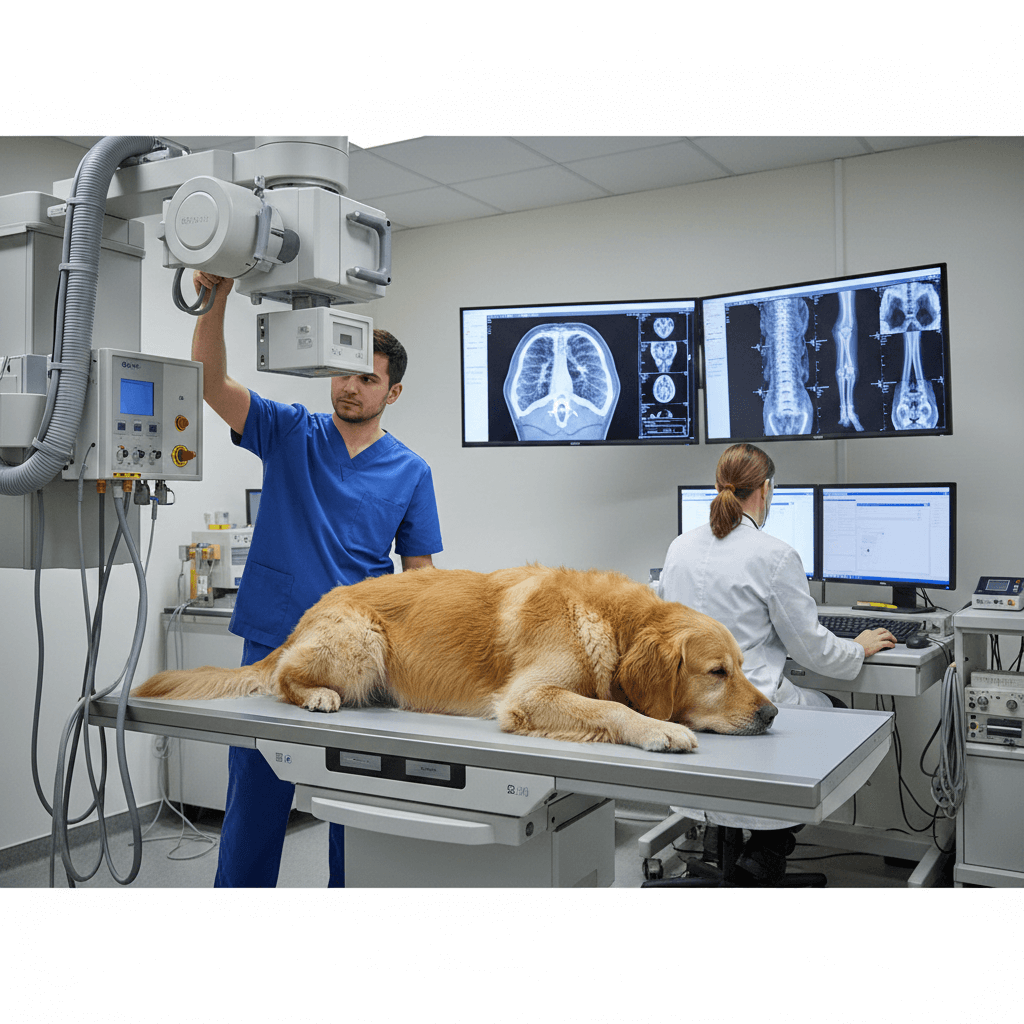
How Dog Radiology Works: The Science Behind X-Rays
Dog radiology uses ionizing radiation to create images of your pet’s internal structures. Understanding the science behind this process helps you appreciate its safety and efficacy. While the technology is advanced, the procedure is straightforward and minimally invasive for your dog.
- Ionizing Radiation and Image Formation:
X-rays pass through soft tissues but are absorbed by denser materials like bones. This contrast creates grayscale images that highlight different structures. - Positioning Your Dog for Imaging:
Technicians position your dog carefully to capture clear images. Sedation may be required for anxious or uncooperative pets but is generally safe when administered by professionals. - Digital vs. Traditional X-Rays:
Modern clinics use digital radiology, which produces higher-quality images faster than traditional film-based methods. Digital X-rays also reduce radiation exposure for both pets and staff. - Interpreting Radiographs:
Veterinarians analyze X-ray images to identify abnormalities. They look for irregular shapes, sizes, or densities that indicate underlying health issues. - Safety Measures During Procedures:
Protective shielding and controlled radiation doses ensure minimal risk to your dog. Technicians follow strict protocols to prioritize safety at all times.
Understanding these technical aspects reassures you that radiology is a safe, effective, and reliable diagnostic tool for your dog’s healthcare needs.
Check this guide 👉How Much Does a Dog Ultrasound Cost? Best 7 Health Tips!
Check this guide 👉Dog Orthodontics: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉Understanding Oncology in Dogs: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Traditional X-Rays | Advanced Imaging Techniques |
|---|---|
Best for skeletal and structural issues | Ideal for soft tissues, organs, and complex structures |
Quick, affordable, and widely available | Provides detailed, high-resolution images |
Minimal preparation required | May involve sedation or longer procedures |
Limited detail for soft tissues | Includes CT scans, MRI, and ultrasound options |
Suitable for routine diagnostics | Used for specialized or hard-to-diagnose cases |
Benefits of Radiology for Dogs
Radiology offers numerous advantages in veterinary diagnostics, making it a preferred choice for many conditions. Its non-invasive nature, combined with high accuracy, ensures rapid identification of health issues without causing significant stress to your pet.
- Non-Invasive and Painless:
Unlike exploratory surgeries, radiology doesn’t require incisions or anesthesia in most cases, reducing recovery time and discomfort. - Quick Results for Immediate Action:
X-rays provide instant images, allowing veterinarians to make timely decisions about treatment plans or further testing. - Cost-Effective Diagnostics:
Compared to advanced imaging techniques like MRI or CT scans, radiology is more affordable while still delivering valuable information. - Wide Range of Applications:
From orthopedic injuries to gastrointestinal blockages, radiology addresses diverse medical concerns, making it versatile and efficient. - Early Detection of Diseases:
Regular X-rays can catch conditions like arthritis, tumors, or organ enlargement early, improving prognosis and treatment success rates.
These benefits highlight why radiology remains a cornerstone of veterinary diagnostics, ensuring comprehensive care for your dog.
Risks and Limitations of Dog Radiology
While radiology is incredibly useful, it’s important to understand its potential risks and limitations. No diagnostic tool is perfect, and being aware of these factors ensures realistic expectations and informed decision-making.
- Limited Soft Tissue Detail:
X-rays excel at visualizing dense structures but may not provide sufficient detail for soft tissues like muscles or ligaments. Additional imaging may be needed. - Radiation Exposure Concerns:
Although minimal, repeated X-rays carry a slight risk of cumulative radiation exposure. Veterinarians weigh this against the diagnostic benefits. - Sedation Risks for Anxious Dogs:
Some dogs require sedation to remain still during imaging, which introduces minor risks, especially for older or medically compromised pets. - Inability to Detect Functional Issues:
Radiology shows structural abnormalities but cannot assess how well organs or systems are functioning. Blood tests or ultrasounds may complement findings. - False Negatives or Ambiguities:
Occasionally, X-rays fail to detect small lesions or early-stage diseases, necessitating further investigation.
Awareness of these limitations ensures you approach radiology as part of a broader diagnostic strategy tailored to your dog’s needs.
Preparing Your Dog for a Radiology Procedure
Proper preparation ensures a smooth and successful radiology session for your dog. By following your veterinarian’s instructions, you minimize stress and maximize the quality of the images obtained.
- Fasting Before the Procedure:
Many vets recommend withholding food for 8–12 hours before abdominal X-rays to reduce gas or food interference with image clarity. - Ensuring Calm Behavior:
Training your dog to remain calm and cooperative during vet visits reduces the need for sedation and speeds up the process. - Providing Medical History Details:
Inform your vet about any preexisting conditions, medications, or recent symptoms to guide their interpretation of the X-rays. - Understanding Sedation Protocols:
If sedation is necessary, ask about the type, dosage, and recovery process to ensure your dog’s safety and comfort. - Staying Calm Yourself:
Your dog picks up on your emotions; staying relaxed reassures them and makes the experience less stressful for everyone involved.
Preparation fosters a positive experience, ensuring accurate results and minimizing complications during the procedure.
Advanced Radiology Techniques for Dogs
Beyond traditional X-rays, advanced radiology techniques offer even greater diagnostic capabilities for complex cases. These methods provide detailed insights into specific areas of concern, enhancing treatment precision.
- Ultrasound Imaging:
Ultrasounds use sound waves instead of radiation to visualize soft tissues, blood flow, and organ function. They’re ideal for evaluating pregnancies, heart conditions, or abdominal masses. - CT Scans (Computed Tomography):
CT scans produce cross-sectional images, offering superior detail for intricate structures like the brain, nasal cavities, or complex fractures. - MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging):
MRIs excel at capturing detailed images of soft tissues, nerves, and the spinal cord, making them invaluable for neurological or musculoskeletal conditions. - Contrast Studies:
Injecting contrast agents highlights specific areas, such as the gastrointestinal tract or urinary system, aiding in the diagnosis of leaks, obstructions, or tumors. - Fluoroscopy for Dynamic Imaging:
This real-time X-ray technique captures moving structures, such as swallowing mechanics or joint mobility, providing functional insights beyond static images.
These advanced techniques expand the scope of radiology, addressing challenges that traditional X-rays cannot resolve.
Post-Radiology Care and Follow-Up Steps
After your dog undergoes radiology, proper aftercare and follow-up are crucial to ensure their continued well-being. Understanding what to expect post-procedure helps you support your dog effectively.
- Monitoring Sedation Recovery:
If sedated, monitor your dog closely for grogginess, disorientation, or difficulty walking. Most dogs recover fully within a few hours. - Observing for Behavioral Changes:
Watch for signs of discomfort, pain, or worsening symptoms that might indicate underlying issues revealed by the X-rays. - Discussing Results with Your Vet:
Schedule a follow-up appointment to review findings and discuss next steps, whether it’s medication, surgery, or lifestyle adjustments. - Implementing Treatment Plans:
Adhere to prescribed therapies, diets, or medications to address conditions identified through radiology and prevent further complications. - Scheduling Regular Check-Ups:
For chronic conditions, regular monitoring through repeat X-rays or other diagnostics ensures ongoing management and early detection of changes.
Post-radiology care ensures your dog receives the full benefits of the procedure, promoting long-term health and recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions About Dog Radiology
Is dog radiology safe?
Yes—modern X-rays use low radiation doses and strict safety protocols, making them safe for most dogs.
How long does a radiology procedure take?
Most X-rays are completed within 15–30 minutes, though advanced techniques like CT or MRI may take longer.
Does my dog need sedation for an X-ray?
Sedation depends on your dog’s temperament and the complexity of the procedure; calm, cooperative dogs may not require it.
Are there alternatives to radiology?
Yes—ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans may be used depending on the condition being diagnosed.
How much does dog radiology cost?
Costs vary by location and technique, ranging from $100–$300 for X-rays to $1,000+ for advanced imaging like MRI.
A Lifeline in Every Diagnostic Journey
Dog radiology is more than just a diagnostic tool—it’s a window into your pet’s health, offering clarity and direction when uncertainty looms. Whether detecting fractures, tumors, or chronic conditions, radiology empowers veterinarians to provide precise, effective care tailored to your dog’s unique needs. By understanding its benefits, limitations, and applications, you become an active participant in your dog’s healthcare journey. Remember, early detection and informed decisions pave the way to better outcomes and happier, healthier lives. With radiology as part of your toolkit, you’re equipped to face any challenge alongside your loyal companion.
Poodle Water Dog: Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how Poodles excel in water activities, from swimming to training, and unlock their aquatic potential today.
Salt Poisoning in Cats: Best 7 Expert Tips! – Learn the dangers of salt toxicity, spot symptoms early, and discover how to keep your cat safe from this serious health risk.
Salt Poisoning in Dogs: Best 7 Expert Tips! – Learn the dangers of salt toxicity, recognize symptoms, and discover life-saving steps to protect your dog.
Can Too Much CBD Kill a Cat? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover the risks, safe dosages, and signs of CBD toxicity to keep your cat safe and healthy.




