Understanding Dog Prostate Cancer Symptoms: Early Detection Saves Lives
Prostate cancer in dogs is a serious condition that primarily affects older, unneutered male dogs. While it’s relatively rare compared to other canine cancers, its symptoms can mimic less severe urinary or reproductive issues, making early detection challenging but crucial. Recognizing the signs of dog prostate cancer symptoms is the first step toward ensuring your furry companion receives timely veterinary care. In this blog post, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options for prostate cancer in dogs. By understanding this disease, you can take proactive steps to protect your dog’s health and provide them with the best possible quality of life.
Common Symptoms of Dog Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer in dogs often presents with subtle signs that may initially be mistaken for other conditions. However, being vigilant about these symptoms can help you catch the disease early. Here are the most common signs to watch for:
Difficulty Urinating
Straining to urinate or producing only small amounts of urine can indicate prostate enlargement or blockage caused by cancer.Blood in Urine or Semen
Hematuria (blood in urine) or bloody discharge during mating is a red flag that requires immediate veterinary attention.Constipation or Straining to Defecate
An enlarged prostate can press on the rectum, making bowel movements painful or difficult.Lethargy and Weakness
Dogs with prostate cancer may appear unusually tired, lose interest in activities, or struggle with mobility.Abdominal Pain or Swelling
Discomfort in the abdomen or noticeable swelling can signal an underlying issue with the prostate.
If you notice any combination of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult your veterinarian promptly. Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve outcomes for dogs with prostate cancer.
Causes and Risk Factors of Prostate Cancer in Dogs
While the exact cause of prostate cancer in dogs isn’t fully understood, certain factors increase the likelihood of its development. Understanding these risks can help you take preventive measures and monitor your dog more closely.
Age
Prostate cancer typically affects older dogs, particularly those over the age of eight.Unneutered Status
Intact male dogs are at a higher risk due to prolonged exposure to testosterone, which can stimulate abnormal cell growth.Breed Predisposition
Larger breeds, such as Doberman Pinschers and German Shepherds, may have a slightly higher incidence of prostate cancer.Chronic Prostatitis
Long-term inflammation of the prostate gland can increase the risk of malignant changes over time.Genetic Factors
A family history of cancer or reproductive disorders may predispose some dogs to prostate cancer.
By identifying these risk factors, you can work with your veterinarian to create a tailored health plan for your dog. Regular check-ups and early neutering can reduce the chances of developing this devastating disease.
Check this guide 👉Understanding a Swollen Prostate in Dogs: Best 7 Tips!
Check this guide 👉Signs Your Dog Needs Anal Glands Expressed: Best 7 Tips
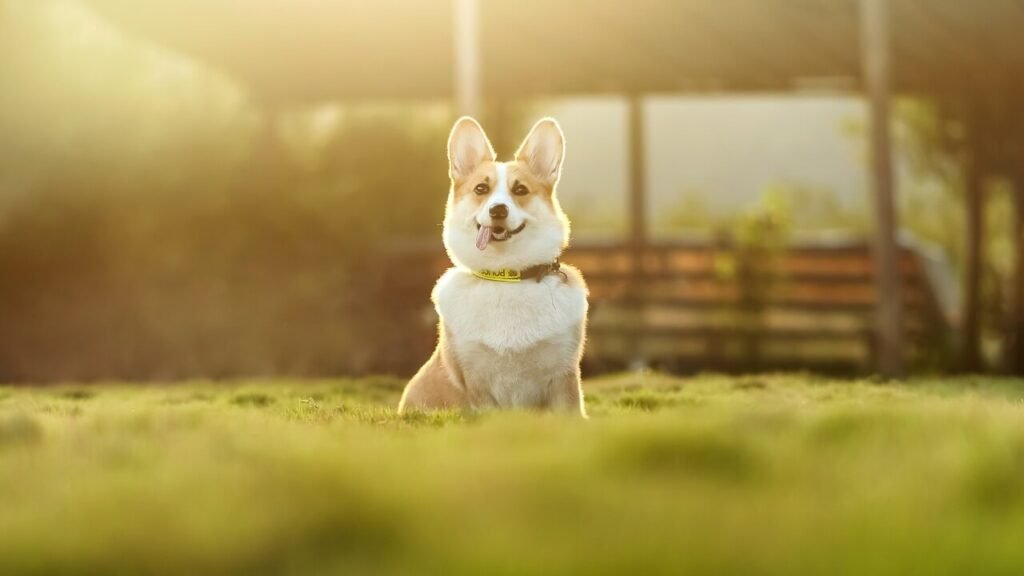

Symptoms of Dog Prostate Cancer | Preventive Measures |
|---|---|
Difficulty urinating | Neuter your dog early. |
Blood in urine or semen | Schedule regular vet exams. |
Constipation or straining | Monitor for urinary/reproductive issues. |
Lethargy and weakness | Maintain a healthy weight and diet. |
Abdominal pain or swelling | Address chronic inflammation promptly. |
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Dog Prostate Cancer
Once prostate cancer is suspected, your veterinarian will conduct a series of tests to confirm the diagnosis and determine the best course of action. Here’s what to expect during the diagnostic and treatment process:
Physical Examination
Your vet will palpate the abdomen to assess the size and shape of the prostate gland.Ultrasound Imaging
An ultrasound provides detailed images of the prostate, helping identify tumors or abnormalities.Biopsy
A tissue sample from the prostate is analyzed to confirm whether the growth is benign or malignant.Surgical Intervention
If the cancer is localized, surgical removal of the prostate may be an option, though it carries significant risks.Chemotherapy and Radiation
For advanced cases, chemotherapy or radiation therapy may be recommended to slow tumor growth and alleviate symptoms.
Early detection plays a critical role in determining treatment success. Work closely with your veterinarian to explore all available options and make informed decisions about your dog’s care.
How to Support Your Dog During Treatment
Caring for a dog with prostate cancer requires patience, compassion, and a willingness to adapt to their changing needs. Here are some ways to support your furry friend throughout their treatment journey:
Provide a Comfortable Environment
Create a calm, stress-free space where your dog can rest and recover comfortably.Adjust Their Diet
Offer nutrient-rich foods that support overall health and boost their immune system during treatment.Monitor Symptoms Closely
Keep track of any changes in behavior, appetite, or symptoms to report to your veterinarian promptly.Administer Medications as Directed
Follow your vet’s instructions carefully when giving medications or supplements to manage pain and inflammation.Offer Emotional Support
Spend quality time with your dog, providing reassurance and affection to help them feel safe and loved.
Your dedication and care can make a world of difference in your dog’s quality of life. Remember, you’re not alone—lean on your vet and support network for guidance and encouragement.
Alternative Therapies to Support Dogs with Prostate Cancer
While traditional treatments like surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation are often the primary options for prostate cancer in dogs, alternative therapies can complement these approaches and improve your dog’s quality of life. Here are some supportive therapies to consider:
Acupuncture
Acupuncture may help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation caused by prostate cancer, providing relief for your dog.Herbal Supplements
Certain herbs, such as turmeric or milk thistle, are believed to have anti-inflammatory and immune-boosting properties that support overall health.Physical Therapy
Gentle exercises and stretches can help maintain mobility and muscle strength, especially if your dog is experiencing weakness.Massage Therapy
Massage can reduce stress, improve circulation, and provide comfort to dogs dealing with cancer-related discomfort.Dietary Adjustments with Natural Ingredients
Adding omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and other natural ingredients to your dog’s diet may help combat inflammation and support recovery.
These alternative therapies should always be discussed with your veterinarian to ensure they’re safe and appropriate for your dog’s specific condition. When used alongside conventional treatments, they can enhance your dog’s well-being and comfort.
Ways to Improve Your Dog’s Mental Health During Treatment
Cancer treatment can take a toll not only on your dog’s physical health but also on their mental and emotional well-being. Keeping your dog mentally engaged and happy is essential during this challenging time.
Interactive Toys
Puzzle toys and treat-dispensing games can stimulate your dog’s mind and provide a sense of accomplishment.Short Play Sessions
Even brief playtimes with their favorite toy or a gentle game of fetch can boost their mood and energy levels.Training Exercises
Teaching simple commands or tricks using positive reinforcement keeps their brain active and strengthens your bond.Outdoor Time
If your dog feels up to it, short walks or time spent in the yard can provide mental stimulation and fresh air.Routine and Structure
Maintaining a consistent daily routine helps reduce anxiety and gives your dog a sense of stability.
By focusing on your dog’s mental health, you can help them stay positive and engaged, even during difficult times. Small efforts can make a big difference in their overall happiness.
Signs That Your Dog’s Prostate Cancer May Be Progressing
Monitoring your dog’s condition closely is crucial to identify any progression of prostate cancer. Recognizing these signs early allows you to adjust treatment plans and provide additional support.
Increased Pain or Discomfort
If your dog seems more reluctant to move or shows signs of pain, it could indicate the cancer is advancing.Loss of Appetite
A sudden refusal to eat or significant weight loss may signal worsening health.Changes in Behavior
Increased lethargy, irritability, or withdrawal from family members can suggest your dog is struggling.Frequent Urinary Accidents
Difficulty controlling urination or increased accidents indoors may point to worsening urinary symptoms.Labored Breathing or Weakness
These symptoms could indicate the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, requiring immediate attention.
Being vigilant about these warning signs ensures you can act quickly to address your dog’s needs. Early intervention can help manage symptoms and improve their quality of life, even as the disease progresses.
FAQ
Is prostate cancer common in dogs?
Prostate cancer is relatively rare in dogs but tends to occur more frequently in older, unneutered males.
Can neutering prevent prostate cancer in dogs?
Yes, neutering reduces the risk of prostate cancer by eliminating testosterone, which can contribute to abnormal cell growth.
What are the first signs of prostate cancer in dogs?
Early signs include difficulty urinating, blood in urine or semen, constipation, lethargy, and abdominal swelling.
How is prostate cancer diagnosed in dogs?
Diagnosis involves physical exams, ultrasounds, biopsies, and sometimes X-rays or blood tests to confirm the presence of cancer.
Are there treatments available for dog prostate cancer?
Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and palliative care to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Stay Vigilant for Your Dog’s Health
Prostate cancer in dogs is a challenging diagnosis, but recognizing dog prostate cancer symptoms early can make all the difference in your pet’s prognosis. By staying informed about the signs, causes, and treatment options, you empower yourself to advocate for your dog’s well-being. Regular veterinary check-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and preventive measures like neutering can go a long way in reducing the risk of this disease. Above all, remember that your love and dedication are invaluable sources of strength for your dog during difficult times. Together, you and your veterinarian can navigate this journey and ensure your loyal companion lives their best life.
Do Cats Have Taste Buds? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how cats experience flavors and why their taste is so unique.
Do Dogs Have Taste Buds? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how dogs experience taste, their preferences, and what it means for their diet and health.
Can Cats Taste Sweet? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover why cats can’t taste sweetness, how it affects their diet, and tips to keep them healthy and happy.
Can Dogs Taste Sweet? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how dogs perceive sweetness, which foods are safe, and tips to manage their sweet cravings responsibly.