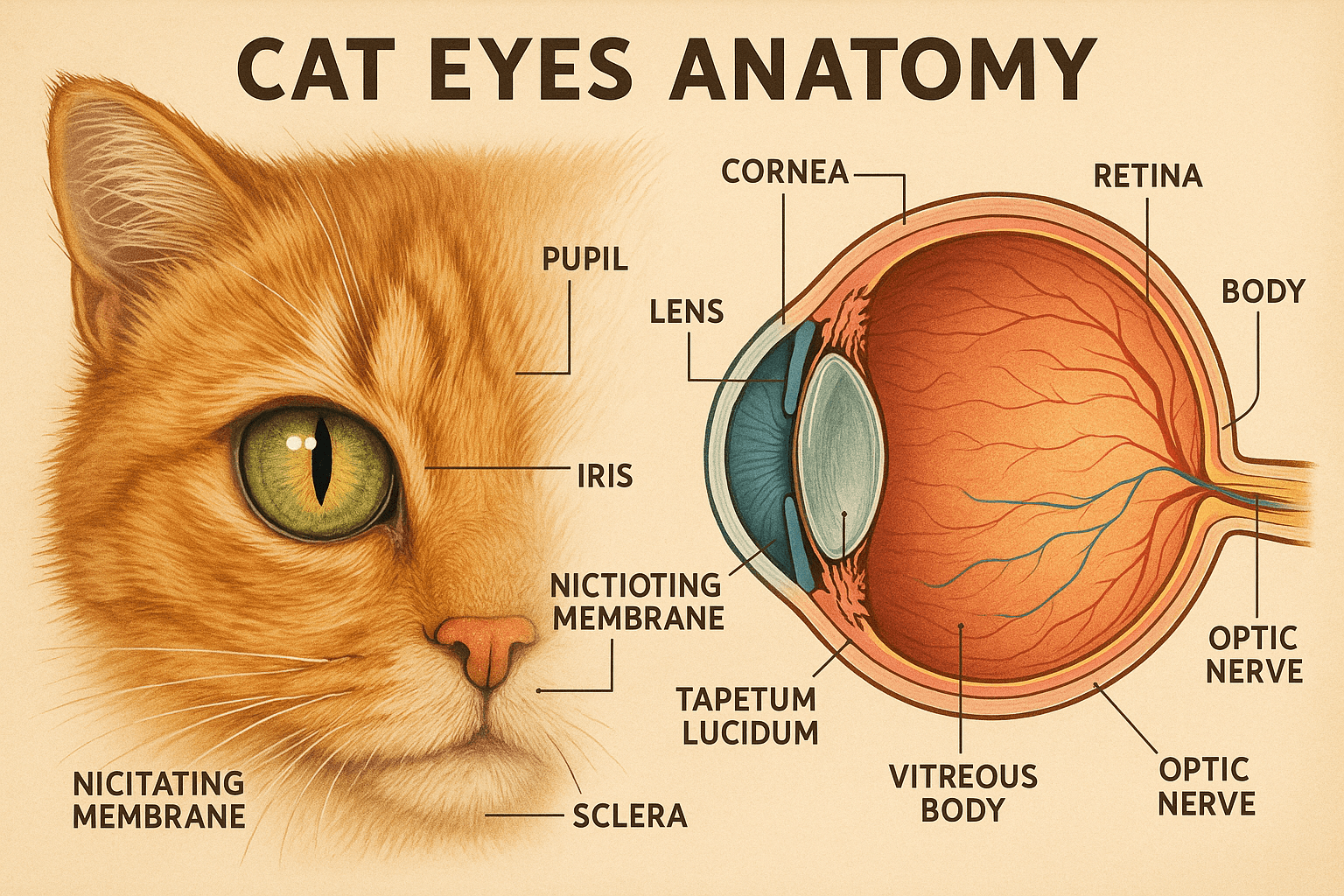
Understanding Cat Eyes Anatomy
Cat eyes are nothing short of mesmerizing, captivating us with their luminous glow and striking colors. But beyond their beauty lies a complex structure finely tuned for survival and adaptation. Cats are nocturnal hunters by nature, and their eyes have evolved to excel in low-light conditions, detect movement, and provide an almost panoramic field of vision. Understanding the anatomy of cat eyes not only deepens our appreciation for these incredible creatures but also helps us better care for their ocular health. In this article, we’ll explore the fascinating components of cat eyes, how they function, and what makes them so uniquely suited to feline life.
Expert Insight: Feline vs. Human Vision
Miller says there are differences in feline and human eye anatomy that make humans a whopping 10 to 12 times better at detecting motion in daylight than cats. But once the sun goes down, it’s cats that have the upper hand.
Key Components of Cat Eye Anatomy
The intricate design of a cat’s eye is what enables its remarkable visual abilities. Let’s break down the primary structures that make up cat eye anatomy and their functions.
Cornea:
The transparent outer layer of the eye, the cornea protects the inner structures while allowing light to enter. It plays a crucial role in focusing vision.Pupil:
The pupil is the black, adjustable opening in the center of the iris. It expands or contracts to control the amount of light entering the eye, adapting to different lighting conditions.Iris:
The colored part of the eye, the iris regulates the size of the pupil. Its flexibility allows cats to adjust rapidly to changes in brightness.Lens:
Located behind the pupil, the lens focuses incoming light onto the retina. It adjusts its shape to help cats see objects clearly at varying distances.Retina:
The retina contains photoreceptor cells (rods and cones) that convert light into electrical signals sent to the brain. Cats have a high density of rods, enhancing their night vision.
These components work together seamlessly, enabling cats to navigate their environment with precision and efficiency, whether in broad daylight or complete darkness.
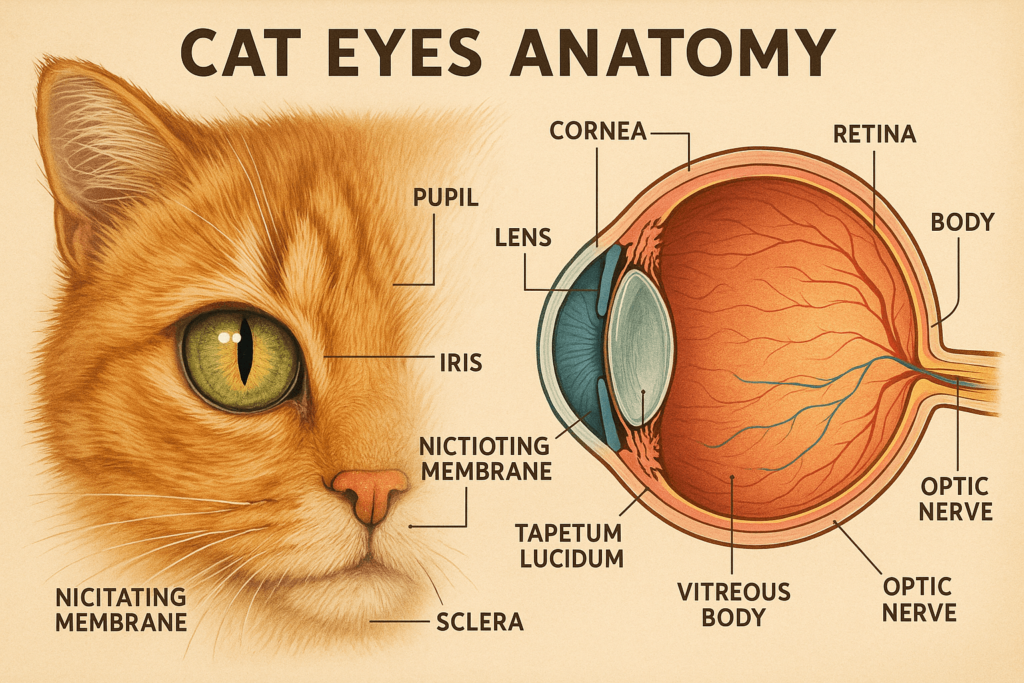
Unique Features of Cat Eyes
Cat eyes possess several distinctive features that set them apart from human eyes and those of other animals. These adaptations are key to their exceptional vision and hunting prowess.
Tapetum Lucidum:
This reflective layer behind the retina enhances night vision by bouncing light back through the photoreceptors, maximizing light absorption. It’s also responsible for the glowing appearance of cat eyes in the dark.Elliptical Pupils:
Unlike humans, cats have vertically slit pupils that can expand widely in low light and contract tightly in bright light, giving them superior light control.Wide Field of Vision:
Cats have a nearly 200-degree field of view, compared to humans’ 180 degrees, allowing them to spot potential threats or prey from multiple angles.High Rod-to-Cone Ratio:
Cats have more rods than cones in their retinas, which boosts their ability to detect motion and see in dim light but limits color perception.Nictitating Membrane:
Also known as the “third eyelid,” this protective membrane helps shield and lubricate the eye without obstructing vision, aiding in self-cleaning and protection.
These unique features highlight why cat eyes are perfectly adapted for their predatory lifestyle and nocturnal habits.
Check this guide 👉Understanding Cat Eye Cataracts: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉How to Clean a Cat Eye Infection: Best 7 Health Tips!
Check this guide 👉Cat Eye Discharge Green: Best 7 Health Tips!
Structure of Cat Eyes | Function/Importance |
|---|---|
Cornea | Protects the eye and focuses light |
Pupil | Controls light entry for optimal vision |
Tapetum Lucidum | Enhances night vision and creates eye glow |
Retina | Converts light into signals for the brain |
Nictitating Membrane | Provides protection and moisture to the eye |
How Cat Eyes Adapt to Light Conditions
One of the most impressive aspects of cat eyes is their ability to adapt to varying light levels. These adaptations ensure they can hunt effectively at dawn, dusk, and nighttime.
Dilation of the Pupil:
In low-light environments, the pupil expands to allow maximum light intake, improving visibility in near-darkness.Constriction in Bright Light:
When exposed to bright light, the pupil narrows to reduce glare and protect the sensitive retina from damage.Role of the Tapetum Lucidum:
This reflective layer amplifies available light, giving cats a significant advantage in dimly lit areas.Rods vs. Cones Balance:
The abundance of rod cells allows cats to detect even the slightest movements in low light, though their color vision is limited.Blinking and Third Eyelid Use:
Cats use their nictitating membrane to shield their eyes from harsh light while maintaining partial vision, ensuring uninterrupted awareness.
These mechanisms demonstrate how cat eyes are engineered for versatility and resilience in diverse lighting scenarios.
Common Eye Issues in Cats
While cat eyes are marvels of evolution, they are not immune to problems. Recognizing common eye issues early can prevent complications and ensure your cat’s long-term health.
Conjunctivitis:
Characterized by redness, swelling, and discharge, conjunctivitis is often caused by infections or irritants.Corneal Ulcers:
Scratches or injuries to the cornea can lead to ulcers, resulting in pain, squinting, and excessive tearing.Glaucoma:
Increased pressure within the eye can cause glaucoma, leading to discomfort, cloudiness, and potential blindness if untreated.Cataracts:
Clouding of the lens impairs vision and may require surgical intervention in severe cases.Third Eyelid Protrusion:
If the nictitating membrane becomes visible, it could indicate underlying illness or injury requiring veterinary attention.
Understanding these conditions empowers cat owners to act promptly and seek professional care when needed.
How to Care for Your Cat’s Eyes
Proper eye care is essential for maintaining your cat’s overall health and preventing potential issues. Here are some practical tips to keep your cat’s eyes clean and healthy.
Inspect Regularly:
Check your cat’s eyes weekly for signs of redness, discharge, or irritation. Early detection can prevent minor problems from worsening.Clean Gently:
Use a damp, soft cloth to wipe away dirt or crust around the eyes. Avoid using harsh chemicals or cotton swabs near the eye area.Trim Facial Hair:
Long-haired breeds may benefit from trimming fur around the eyes to prevent irritation or debris buildup.Provide a Balanced Diet:
Nutrients like taurine and omega-3 fatty acids support eye health and reduce the risk of degenerative conditions.Schedule Vet Visits:
Include regular eye exams during routine check-ups to catch any issues before they escalate.
By following these steps, you can help safeguard your cat’s vision and ensure their eyes remain bright and healthy.
Fun Facts About Cat Eyes
Cat eyes are full of surprises, offering fascinating insights into their behavior and biology. Here are some intriguing facts you might not know.
Eyes Reflect Mood Changes:
A cat’s pupils dilate when they’re excited or frightened and constrict when they’re relaxed or focused.Vertical Slit Evolution:
Scientists believe vertical pupils evolved to help predators judge distance accurately when stalking prey.Color Variations:
Kittens are born with blue eyes, which may change color as they mature due to melanin production.Superior Motion Detection:
Cats can detect rapid movements up to 70% faster than humans, making them excellent hunters.Limited Color Perception:
While cats don’t see vibrant colors, their grayscale and low-light vision compensates for this limitation.
These fun facts reveal just how remarkable and multifaceted cat eyes truly are.
Differences Between Cat and Human Eyes
While cat and human eyes share some similarities, they also exhibit distinct differences tailored to each species’ needs. Exploring these contrasts sheds light on their unique strengths.
Field of Vision:
Cats have a wider field of view (200 degrees vs. 180 degrees), allowing them to spot movement from various angles.Night Vision Capability:
Cats require six times less light than humans to see clearly in the dark, thanks to their high rod count and tapetum lucidum.Color Perception:
Humans have three types of cones for rich color vision, whereas cats have only two, limiting their ability to perceive certain hues.Pupil Shape:
Human pupils are round, while cat pupils are elliptical, enabling greater control over light exposure.Third Eyelid Presence:
Cats possess a nictitating membrane, which humans lack, providing extra protection and moisture to their eyes.
These differences underscore how each species’ eyes have adapted to meet their specific environmental and survival needs.
Frequently Asked Questions About Cat Eyes Anatomy
Why do cat eyes glow in the dark?
The glow is caused by the tapetum lucidum, a reflective layer that enhances night vision by bouncing light back through the retina.
Can cats see in total darkness?
No, cats need some level of ambient light to see, but their night vision is far superior to humans’.
What colors can cats see?
Cats primarily perceive shades of blue and green, with limited ability to distinguish reds and yellows.
How can I tell if my cat has an eye infection?
Signs include redness, swelling, discharge, squinting, or excessive blinking. Consult a vet if you notice any of these symptoms.
Are cat eyes similar to human eyes?
While there are similarities, cat eyes have specialized adaptations like the tapetum lucidum and elliptical pupils that differ significantly from human eyes.
Appreciating the Marvel of Cat Eyes
The anatomy of cat eyes is a testament to nature’s ingenuity, showcasing adaptations that have evolved over millennia to support their survival and success as hunters. From their wide field of vision to the reflective brilliance of the tapetum lucidum, every aspect of their eyes serves a purpose. By understanding how these structures work and recognizing potential health concerns, we can ensure our feline companions enjoy optimal vision throughout their lives. Next time you gaze into your cat’s eyes, take a moment to appreciate the intricate design and functionality that make them truly extraordinary.
Can I Give My Cat Midol? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Learn the risks, symptoms, and safe alternatives to keep your cat healthy and avoid toxic reactions.
Can I Give My Dog Midol? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover the risks, safe alternatives, and expert advice to keep your dog safe from accidental poisoning.
Maximum Weight for Cats on Planes: Best 7 Expert Tips! – Learn airline policies, tips to stay compliant, and ensure safe travels for your feline friend.
Max Weight for Dogs on Planes: Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover airline weight limits, safe travel tips, and solutions for flying with your dog stress-free.