The Scottish Wildcat: A Symbol of Wilderness and Resilience
The Scottish wildcat, often referred to as the “Highland Tiger,” is one of Britain’s most elusive and iconic predators. With its striking tabby coat, fierce independence, and mysterious nature, this rare feline has captured the imagination of wildlife enthusiasts for centuries. However, habitat loss, hybridization with domestic cats, and human interference have pushed the Scottish wildcat to the brink of extinction. Today, conservationists are working tirelessly to protect this magnificent creature and preserve its role in the ecosystem. In this blog post, we’ll explore the history, characteristics, challenges, and efforts to save the Scottish wildcat—a true symbol of Scotland’s untamed wilderness.
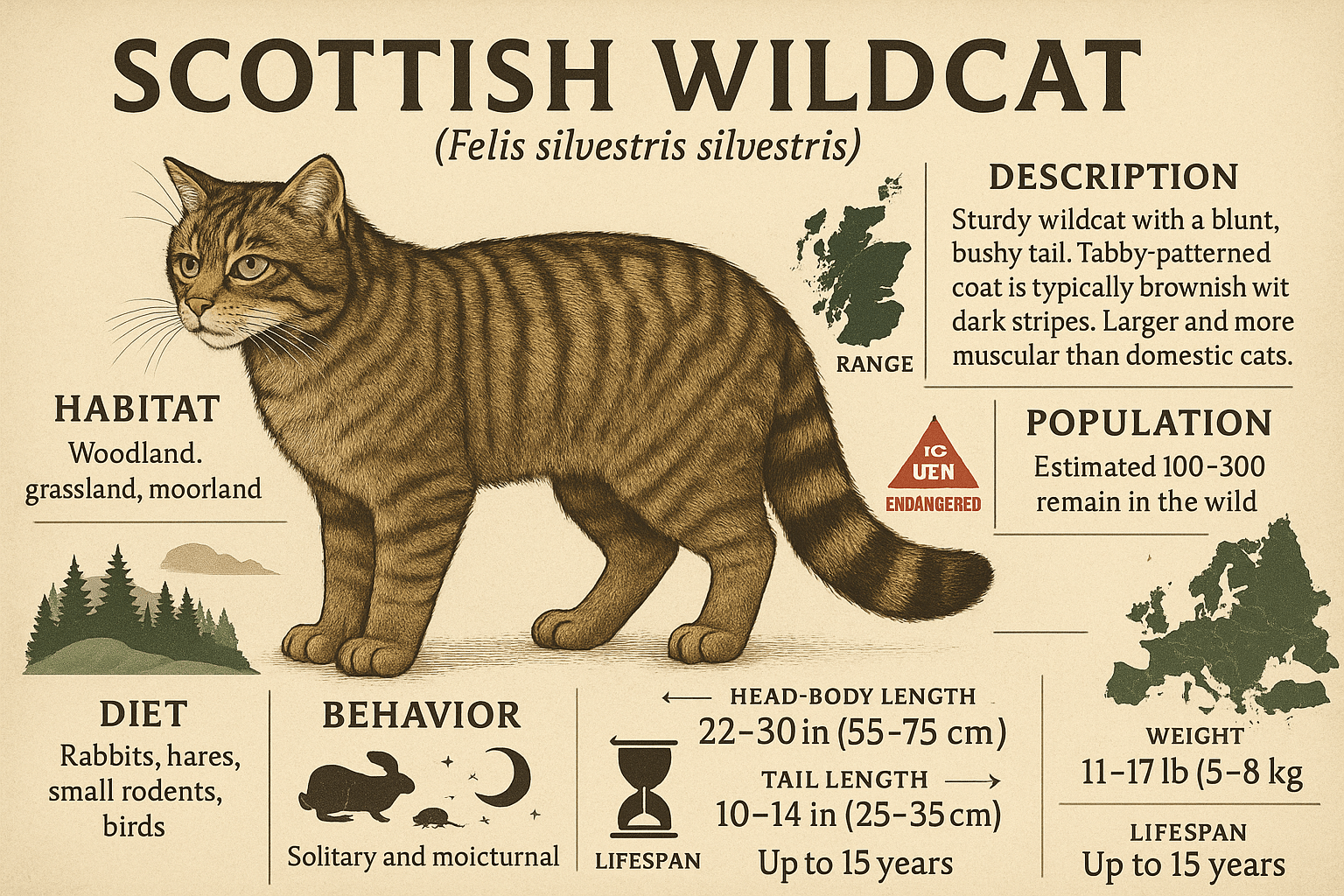
Key Characteristics of the Scottish Wildcat
The Scottish wildcat stands out from its domestic counterparts in several ways. Its unique physical traits and behaviors make it a fascinating subject of study and admiration.
Distinctive Coat Pattern:
The Scottish wildcat features a thick, bushy tail with a black tip, along with bold, unbroken stripes running down its flanks—traits rarely seen in domestic cats.Robust Build:
Larger and stockier than domestic cats, wildcats have powerful muscles designed for hunting and survival in rugged terrain.Solitary Nature:
Unlike domestic cats, Scottish wildcats are highly territorial and prefer to live alone, marking their territory with scent markings and vocalizations.Nocturnal Hunting Habits:
Wildcats are primarily nocturnal hunters, preying on small mammals like rabbits and rodents to sustain themselves.Independent Spirit:
Known for their fierce independence, Scottish wildcats avoid human contact and rely solely on their instincts to survive.
These defining traits highlight what makes the Scottish wildcat such a remarkable and resilient species, perfectly adapted to its natural environment.

Challenges Facing the Scottish Wildcat
Despite its resilience, the Scottish wildcat faces numerous threats that have severely impacted its population. Understanding these challenges is crucial to ensuring its survival.
Hybridization with Domestic Cats:
Interbreeding with domestic cats dilutes the genetic purity of the Scottish wildcat, making it harder to identify true wildcats in the wild.Habitat Loss:
Deforestation and agricultural expansion have reduced the wildcat’s natural habitat, forcing them into smaller, fragmented areas.Persecution by Humans:
Historically, wildcats were hunted due to misconceptions about their threat to livestock, further decimating their numbers.Competition for Food:
The introduction of invasive species and changes in prey availability have made it harder for wildcats to find sufficient food.Climate Change Impact:
Rising temperatures and shifting ecosystems pose additional challenges to the wildcat’s survival in its native range.
Addressing these issues requires urgent action and collaboration among conservationists, policymakers, and local communities.
Check this guide 👉Pallas Cat Lifespan: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉Somali Tabby Cat: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉Silver Smoke Maine Coon: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Scottish Wildcat Traits | Conservation Efforts |
|---|---|
Distinctive striped coat | Genetic testing to identify pure wildcats |
Solitary and territorial behavior | Protected areas and wildlife corridors |
Nocturnal hunting habits | Public awareness campaigns |
Independent and elusive nature | Neutering programs for feral cats |
Adapted to rugged Highland landscapes | Breeding programs to boost populations |
How You Can Help Protect the Scottish Wildcat
While professional conservationists play a vital role in saving the Scottish wildcat, individuals can also contribute to these efforts. Here are some practical ways to get involved.
Support Conservation Organizations:
Donate to or volunteer with groups dedicated to protecting the Scottish wildcat and its habitat.Report Sightings Responsibly:
If you believe you’ve spotted a Scottish wildcat, report it to local wildlife authorities without disturbing the animal.Participate in Feral Cat Neutering Programs:
Reducing the number of feral cats helps prevent hybridization and protects wildcat genetics.Spread Awareness:
Educate others about the importance of conserving the Scottish wildcat and the threats it faces.Respect Wildlife Habitats:
When visiting wildcat territories, follow guidelines to minimize your impact on their environment.
Every small effort counts toward securing a future for this incredible species.
Myths and Misconceptions About the Scottish Wildcat
Misunderstandings about the Scottish wildcat have contributed to its decline over the years. Dispelling these myths is essential for fostering greater appreciation and support for the species.
Myth: They’re Just Large Domestic Cats:
Unlike domestic cats, Scottish wildcats are genetically distinct and possess unique adaptations suited to life in the wild.Myth: Wildcats Pose a Threat to Livestock:
While they may occasionally hunt poultry, wildcats primarily target small mammals and pose little risk to larger livestock.Myth: All Tabby Cats Are Wildcats:
Many tabby-patterned cats resemble wildcats but lack their specific markings and genetic makeup.Myth: Wildcats Are Aggressive Toward Humans:
Wildcats avoid humans and rarely interact with people unless provoked.Myth: Their Extinction Wouldn’t Matter:
Losing the Scottish wildcat would disrupt ecosystems and diminish biodiversity in Scotland’s Highlands.
Clarifying these misconceptions helps build a stronger case for protecting this endangered species.
The Role of Genetics in Wildcat Conservation
Genetics plays a critical role in identifying and preserving pure Scottish wildcats. Advances in science have provided tools to differentiate true wildcats from hybrids, aiding conservationists in their mission.
DNA Testing:
Scientists use DNA samples to determine whether an individual cat carries wildcat-specific genes.Hybrid Identification:
Hybrids exhibit mixed traits, making genetic analysis essential for distinguishing them from pure wildcats.Breeding Programs:
Captive breeding initiatives focus on pairing genetically pure wildcats to strengthen the population.Database Creation:
Researchers maintain databases of wildcat genetics to track lineage and monitor diversity.Long-Term Monitoring:
Ongoing genetic studies ensure that reintroduced wildcats remain free from hybridization risks.
Genetic research offers hope for restoring the Scottish wildcat population while maintaining its purity.
Adapting to Life in the Highlands
The Scottish wildcat’s ability to thrive in harsh environments is a testament to its adaptability. These adaptations allow it to survive in challenging conditions where other species might struggle.
Thick Fur for Cold Weather:
Their dense coats provide insulation against Scotland’s cold and wet climate.Keen Sense of Hearing:
Exceptional hearing allows wildcats to detect prey even in dense underbrush.Stealthy Movements:
Wildcats move silently through their terrain, avoiding detection by both predators and prey.Strong Jaw Muscles:
Powerful jaws enable them to deliver quick, lethal bites to their prey.Territorial Marking:
Scent marking deters rivals and establishes boundaries within their expansive territories.
These adaptations underscore the wildcat’s remarkable ability to endure in the rugged Highlands.
Cultural Significance of the Scottish Wildcat
The Scottish wildcat holds a special place in Scottish folklore and culture, symbolizing freedom and untamed beauty. Its cultural significance reinforces the need to protect this iconic species.
Symbol of Independence:
The wildcat represents Scotland’s rebellious spirit and resistance to oppression.Celtic Mythology:
Ancient Celts revered wildcats as symbols of courage and ferocity.Modern Iconography:
The wildcat appears in logos, crests, and emblems, celebrating its enduring legacy.Tourism Appeal:
Wildlife tourism centered around the wildcat draws visitors eager to glimpse this rare predator.Inspiration for Art:
Artists and writers continue to draw inspiration from the wildcat’s mystique and allure.
By honoring its cultural value, we deepen our commitment to safeguarding the Scottish wildcat for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Scottish Wildcat
What does a Scottish wildcat look like?
Scottish wildcats have bold, unbroken stripes, a bushy tail with a black tip, and a robust build compared to domestic cats.
Where do Scottish wildcats live?
They inhabit remote areas of Scotland’s Highlands, including forests, moorlands, and rocky terrains.
Why are Scottish wildcats endangered?
Habitat loss, hybridization with domestic cats, and persecution by humans are major factors contributing to their decline.
Can I adopt a Scottish wildcat?
No, Scottish wildcats cannot be kept as pets; they are wild animals requiring specialized care and protection.
How can I identify a true wildcat?
Look for distinctive features like unbroken stripes, a thick tail with a black tip, and behavioral traits such as extreme shyness around humans.
Preserving the Legacy of the Scottish Wildcat
The Scottish wildcat embodies the spirit of Scotland’s rugged wilderness—a symbol of strength, independence, and resilience. Yet, its future hangs precariously in the balance due to human activity and environmental changes. By raising awareness, supporting conservation efforts, and taking meaningful action, we can help ensure that this majestic creature continues to roam the Highlands for generations to come. Let us honor the legacy of the Highland Tiger by working together to protect its place in the wild.
How Do I Know If My Cat Died Peacefully? Best 7 Expert Tips! Discover the quiet signs of a peaceful feline passing and find comfort in their final moments.
How Do I Know If My Cat Died Peacefully? A Gentle Guide for Heartbroken Owners Losing a cat is not just …
Why Do Abyssinian Cat Colors Matter? Best 7 Expert Tips! Discover the genetics, rare hues, and care secrets behind Abyssinian coat colors for a healthier, happier cat.
Cat Enrichment Activities: Best 7 Expert Tips! Unlock your cat’s natural instincts with proven strategies for mental stimulation, physical health, and lasting happiness.