Small Dog Syndrome: Understanding and Managing Behavioral Challenges
Small dog syndrome is a term used to describe a collection of behavioral issues commonly observed in smaller dog breeds. These behaviors, such as excessive barking, jumping, or aggression, often stem from a lack of proper training, overindulgence, or misunderstandings about their needs. While small dogs are undeniably adorable, their size doesn’t exempt them from the rules and boundaries necessary for harmonious living. In this blog post, we’ll explore what small dog syndrome is, its causes, and how to address it effectively. By understanding these challenges and implementing positive training techniques, you can help your pint-sized pup become a well-behaved and happy companion.
Common Signs of Small Dog Syndrome
If you’re unsure whether your dog exhibits signs of small dog syndrome, here are some common behaviors to watch for:
Excessive Barking:
Small dogs may bark excessively to assert dominance or demand attention.Jumping on People:
Many small dogs jump up to greet people, often because they’ve never been taught not to.Aggressive Behavior:
Growling, snapping, or lunging at strangers or other animals can indicate a lack of socialization.Ignoring Commands:
Small dogs with this syndrome often disregard basic commands like “sit” or “stay.”Guarding Behavior:
Some small dogs may guard food, toys, or even their owners aggressively.
Recognizing these signs early can help you address the root causes and prevent small dog syndrome from escalating into more serious behavioral problems.
Causes of Small Dog Syndrome
Small dog syndrome doesn’t develop overnight; it’s often the result of specific factors in a dog’s environment or upbringing. Here are the most common causes:
Lack of Training:
Owners may assume small dogs don’t need formal training because of their size, leading to unaddressed behavioral issues.Overindulgence:
Spoiling small dogs by letting them get away with undesirable behaviors can reinforce those actions.Inadequate Socialization:
Failing to expose small dogs to different people, animals, and environments can make them fearful or reactive.Owner Misunderstandings:
Some owners mistakenly view bad behavior as “cute” or harmless due to their dog’s small stature.Fear-Based Aggression:
Small dogs may act out aggressively if they feel threatened or overwhelmed by larger dogs or humans.
Understanding these causes is the first step toward addressing small dog syndrome and fostering a healthier relationship with your pet.
Check this guide 👉Understanding the Shrinking Dog Syndrome: Best 7 Expert Tips
Check this guide 👉Understanding Littermate Syndrome in Dogs: Best 7 Tips!
Check this guide 👉Can a Dog Have Down Syndrome? Best 7 Expert Tips!
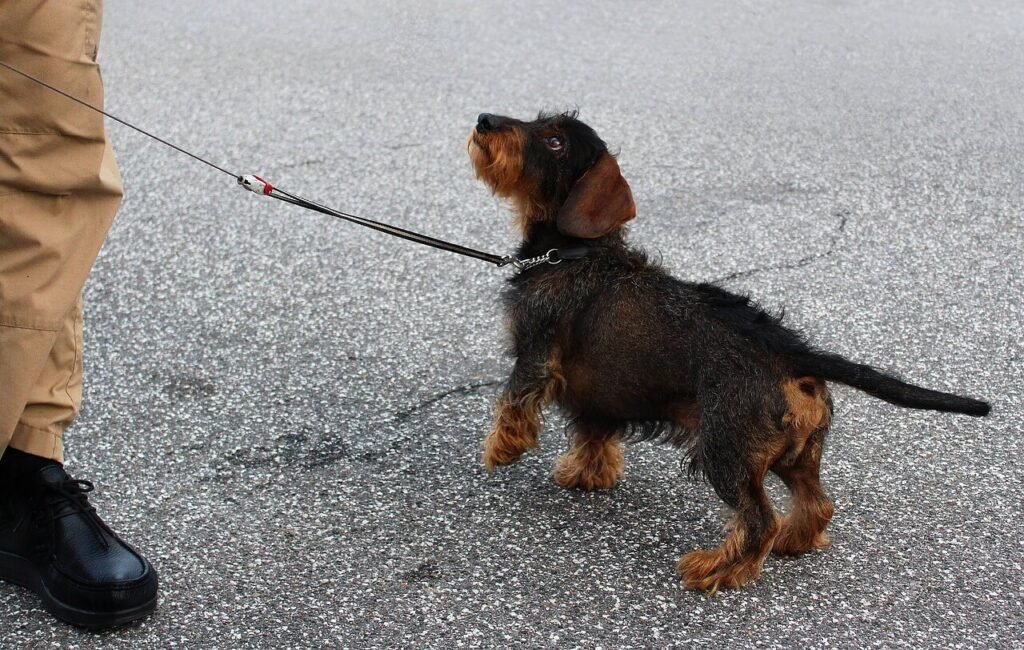

Behavioral Issue | How to Address It |
|---|---|
Excessive Barking | Teach the “quiet” command and reward calmness. |
Jumping on People | Ignore jumping and reward all four paws on the ground. |
Aggressive Behavior | Work with a trainer to desensitize triggers. |
Ignoring Commands | Use consistent reinforcement during training. |
Guarding Behavior | Practice sharing items calmly and use positive rewards. |
Tips for Preventing Small Dog Syndrome
Prevention is always better than correction when it comes to behavioral issues. Here are some tips to help you avoid small dog syndrome altogether:
Start Training Early:
Begin obedience training as soon as you bring your puppy home to establish good habits early.Set Clear Boundaries:
Be consistent with rules and enforce them gently but firmly to show your dog what’s expected.Socialize Regularly:
Expose your dog to various environments, people, and animals to build confidence and reduce fear-based reactions.Avoid Overindulgence:
Resist the urge to let your dog do whatever they want just because they’re small.Reward Good Behavior:
Use treats, praise, and affection to reinforce positive actions consistently.
By taking proactive steps, you can ensure your small dog grows up to be a well-adjusted and respectful companion.
Effective Training Techniques for Small Dogs
Training a small dog requires patience, consistency, and positivity. Here are some techniques to help you manage and correct small dog syndrome effectively:
Use Positive Reinforcement:
Reward desired behaviors with treats, toys, or verbal praise to encourage repetition.Keep Sessions Short:
Limit training sessions to 5-10 minutes to maintain your dog’s focus and enthusiasm.Practice Basic Commands:
Focus on teaching essential commands like “sit,” “stay,” and “come” to establish control.Redirect Unwanted Behaviors:
Provide alternative activities, such as chewing on a toy, to distract from undesirable actions.Be Consistent:
Ensure everyone in the household uses the same commands and enforces the same rules.
With these techniques, you can transform your small dog’s behavior while strengthening your bond.
Signs Your Dog May Have Small Dog Syndrome
If you’re unsure whether your small dog is exhibiting signs of small dog syndrome, here are some subtle and not-so-subtle behaviors to watch for. These indicators can help you identify potential issues early on:
Demanding Attention:
Your dog may bark or whine incessantly until you pet them or give them attention.Refusing to Move:
Some small dogs will stubbornly refuse to walk or move unless carried, showing a lack of obedience.Resource Guarding:
They might growl or snap when someone approaches their food, toys, or even you.Overexcitement Around Guests:
Jumping, barking, or nipping at visitors is a common sign of uncontrolled energy.Ignoring Recall Commands:
If your dog consistently ignores your calls, it could indicate a lack of training or respect for boundaries.
Recognizing these behaviors early allows you to address them proactively and prevent them from escalating into more serious problems.
How to Build Confidence in Small Dogs
Many behaviors associated with small dog syndrome stem from insecurity or fear. Building your dog’s confidence can help reduce these issues significantly. Here are some ways to foster confidence in your small dog:
Positive Reinforcement:
Reward calm and obedient behavior with treats, praise, or playtime to boost their self-assurance.Controlled Exposure to New Experiences:
Gradually introduce your dog to new environments, people, and animals to desensitize them to unfamiliar situations.Teach Basic Commands:
Mastering simple commands like “sit” or “stay” gives your dog a sense of structure and accomplishment.Encourage Independent Play:
Provide toys and activities that allow your dog to entertain themselves, reducing clinginess and dependency.Avoid Coddling Fearful Behavior:
Instead of comforting your dog when they’re scared, calmly encourage them to face their fears in a safe way.
By nurturing your dog’s confidence, you’ll help them feel more secure and less likely to act out due to anxiety or fear.
Mistakes Owners Make That Worsen Small Dog Syndrome
Even well-meaning owners can unintentionally reinforce small dog syndrome through certain actions. Avoiding these mistakes can make a significant difference in your dog’s behavior:
Letting Them Get Away with Bad Behavior:
Ignoring jumping, barking, or nipping because “they’re small” only reinforces the unwanted behavior.Carrying Them Everywhere:
Constantly carrying your dog prevents them from learning how to behave confidently on their own.Using Punishment-Based Training:
Yelling or scolding can increase fear and aggression, worsening behavioral issues over time.Neglecting Exercise Needs:
Assuming small dogs don’t need much exercise can lead to pent-up energy and destructive behavior.Inconsistent Rules:
Allowing certain behaviors one day and punishing them the next creates confusion and frustration for your dog.
By avoiding these common pitfalls, you’ll create a stable and supportive environment that encourages good behavior and discourages small dog syndrome.
Frequently Asked Questions About Small Dog Syndrome
What is small dog syndrome?
Small dog syndrome refers to behavioral issues like aggression, barking, or disobedience that often arise in small breeds due to improper training or indulgence.
Can small dog syndrome be corrected?
Yes, with consistent training, patience, and professional guidance if needed, small dog syndrome can be managed effectively.
Why do small dogs act out more than large dogs?
Small dogs are often treated differently, such as being allowed to misbehave due to their size, which can lead to behavioral problems.
At what age should I start training my small dog?
Training should begin as early as 8-12 weeks old to establish good habits from the start.
Is small dog syndrome caused by genetics?
While genetics can influence temperament, most cases of small dog syndrome result from environmental factors and owner behavior.
Final Thoughts: Building a Harmonious Relationship with Your Small Dog
Small dog syndrome may present challenges, but it’s entirely manageable with the right approach. By recognizing the signs, understanding the causes, and implementing effective training techniques, you can transform your small dog into a well-behaved and joyful companion. Remember, consistency, patience, and love are key to overcoming behavioral issues and fostering a strong bond with your furry friend. With dedication and effort, you’ll create a harmonious living environment where both you and your small dog can thrive. Embrace the journey—it’s worth every wagging tail and happy bark!
Do Cats Have Taste Buds? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how cats experience flavors and why their taste is so unique.
Do Dogs Have Taste Buds? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how dogs experience taste, their preferences, and what it means for their diet and health.
Can Cats Taste Sweet? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover why cats can’t taste sweetness, how it affects their diet, and tips to keep them healthy and happy.
Can Dogs Taste Sweet? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how dogs perceive sweetness, which foods are safe, and tips to manage their sweet cravings responsibly.