Megaesophagus in Dogs: Understanding the Symptoms and Challenges
Megaesophagus is a condition that affects a dog’s ability to swallow and move food from the esophagus to the stomach. This disorder can lead to serious health complications if not properly managed, making it crucial for pet owners to recognize the symptoms early. While the exact cause of megaesophagus can vary—from congenital issues to acquired conditions—the impact on a dog’s quality of life is significant. In this blog post, we’ll explore the key symptoms of megaesophagus, discuss its implications, and provide practical tips for managing this challenging condition. By understanding the signs and treatment options, you can ensure your furry friend receives the care they need to thrive despite this diagnosis.
Common Symptoms of Megaesophagus in Dogs
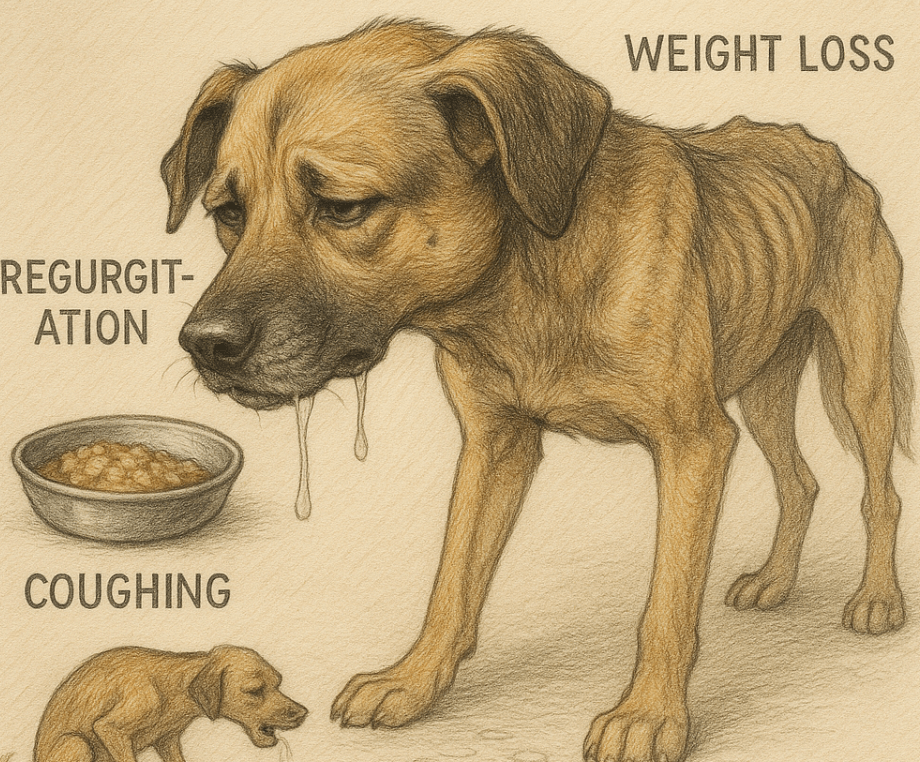
Recognizing the symptoms of megaesophagus is the first step toward ensuring timely intervention and proper care. These signs often indicate that your dog is struggling to process food effectively.
Regurgitation:
Unlike vomiting, regurgitation involves undigested food being expelled effortlessly from the esophagus without nausea or retching.Weight Loss:
Due to the inability to properly digest food, dogs with megaesophagus may experience significant weight loss over time.Excessive Drooling:
Increased saliva production is a common symptom, as the esophagus struggles to move food downward.Coughing and Gagging:
Food or liquid trapped in the esophagus can irritate the throat, leading to persistent coughing or gagging.Foul Breath (Halitosis):
Undigested food lingering in the esophagus can cause bad breath, signaling an underlying issue.
Understanding these symptoms allows pet owners to seek veterinary care promptly, improving their dog’s chances of effective management.
Potential Causes of Megaesophagus in Dogs
Megaesophagus can arise from a variety of causes, both congenital and acquired. Identifying the underlying reason is essential for determining the best course of treatment.
Congenital Megaesophagus:
Some dogs are born with an underdeveloped or malfunctioning esophagus, which becomes apparent shortly after weaning.Neuromuscular Disorders:
Conditions like myasthenia gravis or Addison’s disease can disrupt the nerve signals needed for normal esophageal function.Trauma or Injury:
Physical damage to the esophagus or surrounding nerves can impair its ability to contract and move food.Idiopathic Causes:
In some cases, the exact cause of megaesophagus remains unknown, making diagnosis and treatment more challenging.Secondary to Other Health Issues:
Certain cancers, infections, or systemic diseases can contribute to the development of megaesophagus.
By working closely with your veterinarian, you can pinpoint the cause and tailor a treatment plan to your dog’s specific needs.
Check this guide 👉Dog Stomach Ultrasound Cost: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉Dog Stomach Pain and Shaking: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉Dog Stomach Gurgling: Best 7 Health Tips!
Symptoms of Megaesophagus | Management Strategies |
|---|---|
Regurgitation | Feeding from an elevated position |
Weight loss | Providing small, frequent meals |
Excessive drooling | Using a Bailey chair for feeding |
Coughing and gagging | Monitoring hydration levels closely |
Foul breath (halitosis) | Regular dental cleanings and checkups |
Managing Megaesophagus at Home
Caring for a dog with megaesophagus requires lifestyle adjustments to ensure their comfort and well-being. Here are some strategies to help manage the condition at home.
Elevated Feeding:
Position your dog in an upright posture while eating and drinking to allow gravity to assist food movement into the stomach.Small, Frequent Meals:
Divide meals into smaller portions throughout the day to reduce the strain on the esophagus.Use of a Bailey Chair:
A specially designed chair keeps your dog upright during and after meals, minimizing the risk of regurgitation.Blended or Soft Foods:
Offering food in liquid or mushy form makes it easier for your dog to swallow and digest.Monitor Hydration:
Ensure your dog stays hydrated by offering water frequently, but always in small amounts to prevent aspiration.
Implementing these strategies can significantly improve your dog’s quality of life and reduce complications associated with megaesophagus.
Complications Associated with Megaesophagus
If left untreated, megaesophagus can lead to several serious complications that may jeopardize your dog’s health. Being aware of these risks underscores the importance of proactive management.
Aspiration Pneumonia:
Inhalation of regurgitated food or liquid into the lungs can cause pneumonia, a potentially life-threatening condition.Malnutrition:
Chronic difficulty in digesting food can result in malnutrition, weakening your dog’s immune system and overall health.Dehydration:
Difficulty swallowing liquids increases the risk of dehydration, especially if regurgitation occurs frequently.Esophageal Damage:
Prolonged exposure to undigested food can irritate or damage the lining of the esophagus, worsening the condition.Decreased Quality of Life:
Persistent discomfort and health challenges can diminish your dog’s happiness and energy levels.
Addressing these complications early through proper care and veterinary guidance is essential for maintaining your dog’s health.
Tips for Diagnosing Megaesophagus
Diagnosing megaesophagus requires thorough evaluation by a veterinarian. Here are some steps and tests involved in confirming the condition.
Physical Examination:
Your vet will assess your dog’s overall health and look for signs of regurgitation or weight loss.Radiographs (X-rays):
Imaging helps identify an enlarged esophagus and rule out other potential causes of symptoms.Fluoroscopy:
This real-time X-ray shows how the esophagus functions during swallowing, providing a clearer diagnosis.Blood Tests:
Screening for underlying conditions like myasthenia gravis or hormonal imbalances is crucial for identifying acquired cases.Endoscopy:
A camera inserted into the esophagus allows direct visualization of any structural abnormalities.
Early and accurate diagnosis sets the stage for effective treatment and long-term management.
Dietary Adjustments for Dogs with Megaesophagus
Feeding a dog with megaesophagus requires creativity and patience to ensure they receive adequate nutrition. These dietary adjustments can make a significant difference.
Liquidized Meals:
Blending food into a smooth consistency reduces the risk of regurgitation and aids digestion.High-Calorie Supplements:
Adding supplements ensures your dog receives sufficient nutrients despite limited food intake.Homemade vs. Commercial Diets:
Both options can work; consult your vet to determine the best balance for your dog’s needs.Avoid Dry Kibble:
Hard, dry foods are difficult to swallow and increase the likelihood of regurgitation.Experiment with Textures:
Some dogs tolerate thicker “meatballs” of food better than thin liquids, so trial and error may be necessary.
Finding the right diet can dramatically improve your dog’s ability to eat comfortably and stay nourished.
Preventing Aspiration Pneumonia in Dogs with Megaesophagus
Aspiration pneumonia is one of the most serious risks associated with megaesophagus. Taking preventive measures is vital to protect your dog’s respiratory health.
Upright Feeding Positions:
Always feed your dog in an upright position and keep them elevated for 15-30 minutes afterward to minimize aspiration risk.Regular Vet Check-Ups:
Routine examinations help catch early signs of pneumonia before it becomes severe.Monitor Breathing Patterns:
Watch for changes in breathing, such as wheezing or rapid panting, which could indicate respiratory issues.Limit Water Intake During Meals:
Too much water during feeding increases the chance of liquid entering the lungs.Prompt Treatment for Infections:
Address any signs of infection quickly to prevent secondary complications.
By staying proactive, you can greatly reduce the likelihood of aspiration pneumonia and safeguard your dog’s health.
Frequently Asked Questions About Megaesophagus in Dogs
What is the life expectancy of a dog with megaesophagus?
With proper care and management, many dogs can live happy lives, though individual outcomes depend on the severity and underlying cause.
Can megaesophagus be cured?
Congenital cases are typically lifelong, but some acquired forms may improve with treatment of the underlying condition.
How do I know if my dog has aspiration pneumonia?
Symptoms include coughing, fever, lethargy, and labored breathing; immediate veterinary attention is critical.
Are certain breeds more prone to megaesophagus?
Yes, breeds like German Shepherds, Great Danes, and Irish Setters have a higher predisposition.
What should I feed my dog with megaesophagus?
Blended, high-calorie diets or specialized formulas are ideal for easy digestion and nutrient absorption.
Supporting Your Dog Through Megaesophagus
Living with a dog diagnosed with megaesophagus can be challenging, but with dedication and proper care, it’s possible to provide them with a fulfilling and comfortable life. Recognizing the symptoms early, implementing effective management strategies, and staying vigilant about potential complications are key to ensuring your dog’s well-being. Remember, you’re not alone—your veterinarian and support groups can offer valuable guidance and encouragement along the way. By prioritizing your dog’s unique needs, you can create a nurturing environment where they can thrive despite the challenges posed by megaesophagus.
Do Cats Have Taste Buds? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how cats experience flavors and why their taste is so unique.
Do Dogs Have Taste Buds? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how dogs experience taste, their preferences, and what it means for their diet and health.
Can Cats Taste Sweet? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover why cats can’t taste sweetness, how it affects their diet, and tips to keep them healthy and happy.
Can Dogs Taste Sweet? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how dogs perceive sweetness, which foods are safe, and tips to manage their sweet cravings responsibly.