Understanding Hyperthyroidism in Dogs
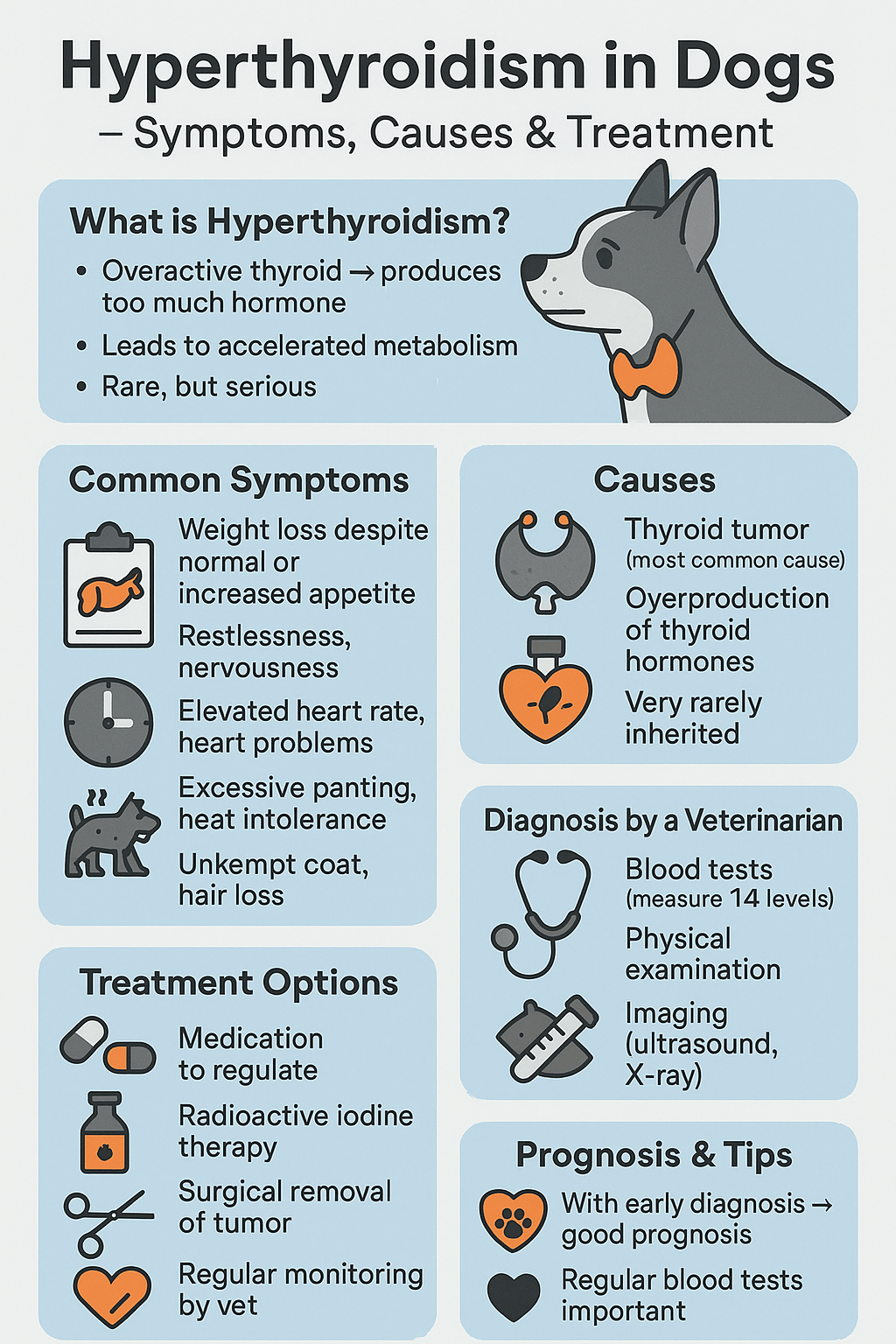
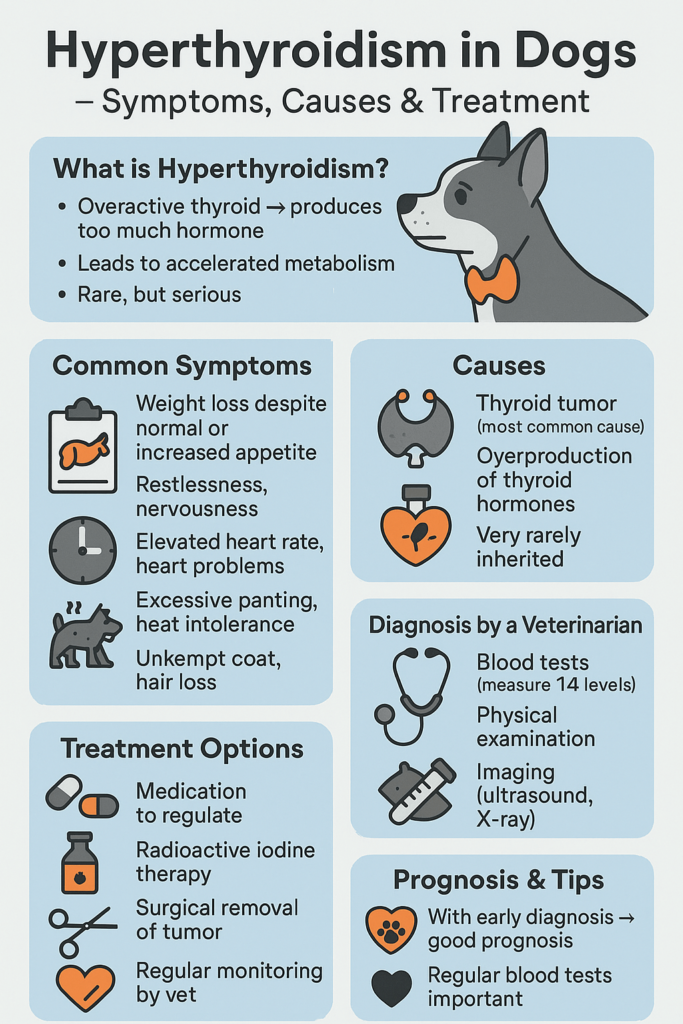
Hyperthyroidism in dogs is a relatively rare condition compared to its prevalence in cats, but it can still pose significant health challenges for affected pets. This hormonal disorder occurs when the thyroid gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, leading to a range of symptoms that can impact your dog’s overall well-being.
While hyperthyroidism is often associated with weight loss, increased appetite, and restlessness, early detection and treatment are crucial for managing the condition effectively. In this blog post, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options for hyperthyroidism in dogs, empowering you to provide the best care for your furry companion.
Expert Insight on Hyperthyroidism in Dogs
“Hyperthyroidism is a rare condition caused by the overproduction of hormones made by the thyroid gland found in the neck region. This condition is most often caused by a cancerous tumor within the thyroid, but a benign thyroid mass, diet, and certain supplements can also be contributing factors.”
Common Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism in Dogs
Recognizing the signs of hyperthyroidism is the first step toward ensuring your dog receives timely medical attention. These symptoms can vary in severity and may overlap with other health issues, so professional diagnosis is essential.
Weight Loss Despite Normal or Increased Appetite:
One of the hallmark signs of hyperthyroidism is unexplained weight loss, even when your dog continues to eat normally or more than usual.Increased Thirst and Urination:
Dogs with hyperthyroidism often drink more water and urinate more frequently, which can sometimes indicate underlying kidney issues as well.Restlessness and Hyperactivity:
Excessive energy levels, pacing, or difficulty settling down may signal an overactive thyroid.Vomiting or Diarrhea:
Gastrointestinal upset, including vomiting or diarrhea, can occur due to the body’s heightened metabolic state.Rapid Heart Rate or Panting:
A racing heart or persistent panting, even at rest, may be linked to the effects of excess thyroid hormones on the cardiovascular system.
If your dog exhibits any of these symptoms, consult your veterinarian promptly to rule out or confirm hyperthyroidism and begin appropriate treatment.
Causes of Hyperthyroidism in Dogs
While hyperthyroidism in dogs is less common than in cats, understanding its potential causes can help pet owners take preventive measures and seek timely veterinary care.
Thyroid Tumors:
The most frequent cause of hyperthyroidism in dogs is a benign or malignant tumor in the thyroid gland, known as a thyroid adenoma or carcinoma.Excessive Iodine Intake:
Consuming diets or supplements high in iodine can sometimes overstimulate the thyroid gland, though this is rare.Medications or Treatments:
Certain medications or treatments targeting other conditions may inadvertently affect thyroid function, leading to hyperthyroidism.Genetic Predisposition:
Some breeds may have a higher susceptibility to thyroid disorders, although research on this topic is ongoing.Environmental Factors:
Exposure to environmental toxins or chemicals may disrupt thyroid function, though direct links are not yet fully understood.
Identifying the underlying cause of hyperthyroidism can guide veterinarians in developing an effective treatment plan tailored to your dog’s needs.
Check this guide 👉Dog Thyroid Medication Side Effects: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉Euthyroid Sick Syndrome in Dogs: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉Understanding Dog Thyroid Cancer: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism | Treatment Options for Dogs |
|---|---|
Weight loss | Medication to regulate hormone levels |
Increased thirst and urination | Surgical removal of thyroid tumors |
Restlessness and hyperactivity | Radioactive iodine therapy |
Vomiting or diarrhea | Dietary adjustments |
Rapid heart rate or panting | Regular monitoring and follow-ups |
Diagnosing Hyperthyroidism in Dogs
Accurate diagnosis is critical for addressing hyperthyroidism effectively. Veterinarians use a combination of physical exams, lab tests, and imaging techniques to confirm the condition.
Blood Tests:
Measuring thyroid hormone levels (T3 and T4) in the blood is the primary method for diagnosing hyperthyroidism. Elevated levels indicate an overactive thyroid.Urinalysis:
A urinalysis helps assess kidney function, as hyperthyroidism can sometimes mask underlying renal issues.Physical Examination:
Your vet will check for physical signs like an enlarged thyroid gland, abnormal heart rhythms, or muscle weakness.Imaging Studies:
Ultrasound or X-rays may be used to identify thyroid tumors or abnormalities in the gland.Monitoring Other Health Indicators:
Additional tests may evaluate liver function, electrolyte balance, and overall metabolic health to ensure a comprehensive diagnosis.
A thorough diagnostic process ensures that your dog receives the most appropriate and effective treatment plan.
Managing Hyperthyroidism Through Diet and Lifestyle
In addition to medical treatments, dietary and lifestyle adjustments can play a supportive role in managing hyperthyroidism in dogs. These changes aim to improve overall health and minimize symptoms.
Balanced Nutrition:
Feeding a high-quality, balanced diet helps maintain optimal body weight and supports thyroid function. Avoid excessive iodine-rich foods unless advised by your vet.Regular Exercise:
Controlled physical activity can help manage stress and promote healthy metabolism, reducing the risk of complications.Hydration:
Ensure your dog has constant access to fresh water to prevent dehydration caused by increased thirst and urination.Stress Reduction:
Minimizing stress through a calm environment and predictable routines can positively impact your dog’s overall well-being.Routine Vet Check-Ups:
Regular follow-ups allow your vet to monitor hormone levels and adjust treatment plans as needed.
By combining medical interventions with supportive care, you can enhance your dog’s quality of life and manage hyperthyroidism more effectively.
Complications of Untreated Hyperthyroidism
Untreated hyperthyroidism can lead to serious health complications, making early intervention crucial for your dog’s long-term well-being. Understanding these risks underscores the importance of prompt veterinary care.
Heart Disease:
Excess thyroid hormones can strain the heart, leading to conditions like hypertension or congestive heart failure.Kidney Damage:
Hyperthyroidism may exacerbate pre-existing kidney issues or contribute to new renal problems over time.Muscle Weakness:
Chronic overproduction of thyroid hormones can result in muscle wasting and decreased mobility.Behavioral Changes:
Dogs may become increasingly anxious or aggressive due to hormonal imbalances affecting their mood and behavior.Shortened Lifespan:
Without treatment, hyperthyroidism can significantly reduce your dog’s life expectancy and overall quality of life.
Addressing hyperthyroidism early helps mitigate these risks and ensures your dog remains healthy and happy.
Alternative Therapies for Hyperthyroidism
While conventional treatments are the gold standard, some pet owners explore complementary therapies to support their dog’s recovery. These options should always be discussed with your veterinarian before implementation.
Herbal Supplements:
Certain herbs, such as bugleweed or lemon balm, are believed to have mild thyroid-regulating properties, though scientific evidence is limited.Acupuncture:
Acupuncture may help alleviate symptoms like muscle pain or restlessness by promoting relaxation and improving circulation.Homeopathy:
Some holistic practitioners recommend homeopathic remedies to address hormonal imbalances, though results vary widely.Massage Therapy:
Gentle massage can reduce stress and improve muscle tone, providing comfort for dogs with hyperthyroidism.Environmental Enrichment:
Creating a stimulating yet calming environment can help manage behavioral symptoms associated with the condition.
Alternative therapies should complement—not replace—traditional veterinary care for optimal outcomes.
Preventive Measures for Hyperthyroidism
While not all cases of hyperthyroidism can be prevented, certain steps can reduce your dog’s risk of developing this condition. Proactive measures contribute to overall health and longevity.
Regular Veterinary Visits:
Annual check-ups allow your vet to detect early warning signs of thyroid dysfunction before it progresses.Balanced Diet:
Feeding a nutritionally complete diet tailored to your dog’s age, breed, and activity level supports thyroid health.Avoiding Toxins:
Limit exposure to harmful chemicals, pesticides, and pollutants that could disrupt endocrine function.Weight Management:
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces strain on the body’s systems, including the thyroid gland.Monitoring Senior Dogs:
Older dogs are more susceptible to thyroid disorders, so increased vigilance is key during their golden years.
Preventive care empowers you to safeguard your dog’s health and catch potential issues early.
Frequently Asked Questions About Hyperthyroidism in Dogs
Is hyperthyroidism common in dogs?
No, hyperthyroidism is relatively rare in dogs compared to cats, but it can still occur, especially in older dogs.
What is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism in dogs?
Thyroid tumors, either benign or malignant, are the primary cause of hyperthyroidism in dogs.
How is hyperthyroidism treated?
Treatment options include medication, surgery, radioactive iodine therapy, and dietary adjustments based on the dog’s specific needs.
Can hyperthyroidism be cured?
In many cases, yes, especially if the underlying cause is addressed, such as surgical removal of a tumor.
Are certain breeds more prone to hyperthyroidism?
While no breed is definitively predisposed, larger breeds like Golden Retrievers and Boxers may have a slightly higher risk.
Providing the Best Care for Dogs with Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism in dogs, though uncommon, requires careful attention and proactive management to ensure your pet’s health and happiness. By recognizing symptoms early, working closely with your veterinarian, and implementing supportive care strategies, you can effectively manage this condition and improve your dog’s quality of life. Remember, every dog is unique, and tailoring treatment to their individual needs is key to success. With love, patience, and informed care, you can help your furry friend thrive despite the challenges posed by hyperthyroidism.
Do Cats Have Taste Buds? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how cats experience flavors and why their taste is so unique.
Do Dogs Have Taste Buds? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how dogs experience taste, their preferences, and what it means for their diet and health.
Can Cats Taste Sweet? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover why cats can’t taste sweetness, how it affects their diet, and tips to keep them healthy and happy.
Can Dogs Taste Sweet? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how dogs perceive sweetness, which foods are safe, and tips to manage their sweet cravings responsibly.