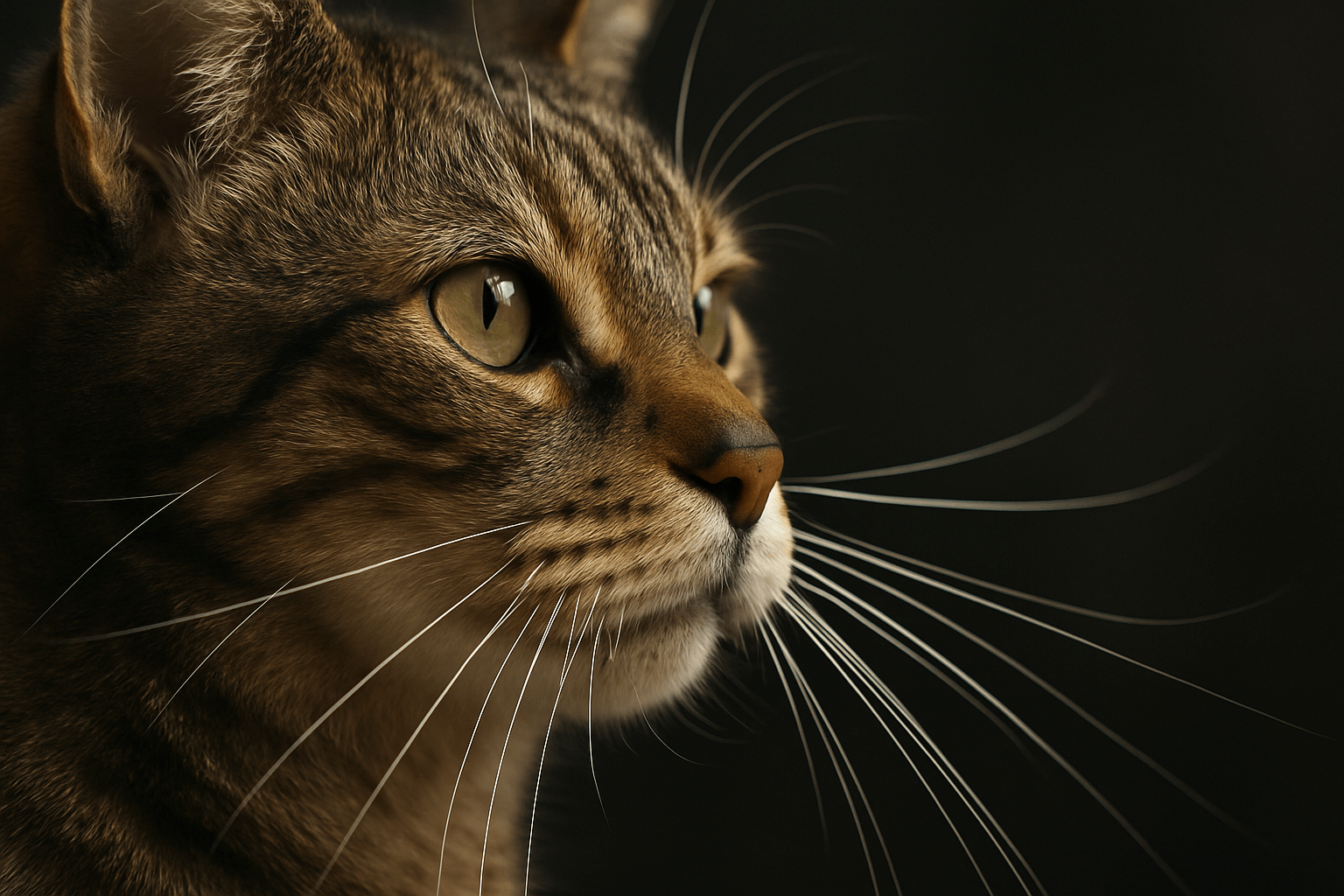
How Do Cat Whiskers Work? The Secret Sensory System Every Owner Should Know
Cat whiskers aren’t just facial hair—they’re highly specialized sensory organs. More than just a charming feature, they’re the key to your cat’s spatial awareness, navigation, and survival. When you see your cat’s whiskers twitching in the dark, you’re witnessing a living, breathing radar system at work. Understanding how cat whiskers work transforms how you see your feline companion—and why you should never cut them.
The Biological Design Behind Whiskers
Cat whiskers, or vibrissae, are far more complex than ordinary fur. Each one is deeply rooted and wired directly into the nervous system. Here’s what makes them extraordinary:
Deep Follicle Anchoring:
Each whisker grows from a follicle rich with blood vessels and nerves—up to three times more sensitive than regular hair follicles.Muscle Control at the Base:
Special muscles allow cats to move their whiskers independently, adjusting their position to gather precise environmental data.Tactile Sensitivity:
The tip of each whisker contains mechanoreceptors that detect even the faintest air currents or physical contact.Length Proportional to Body Width:
A cat’s whiskers typically span the width of its body, acting as a natural ruler to judge if they can fit through tight spaces.Constant Neural Feedback:
Whiskers send real-time data to the brain’s somatosensory cortex, creating a detailed 3D map of the cat’s immediate surroundings.
Whiskers are not passive hairs—they’re active sensors, constantly communicating with your cat’s brain. To ignore them is to misunderstand a core part of your cat’s perception.
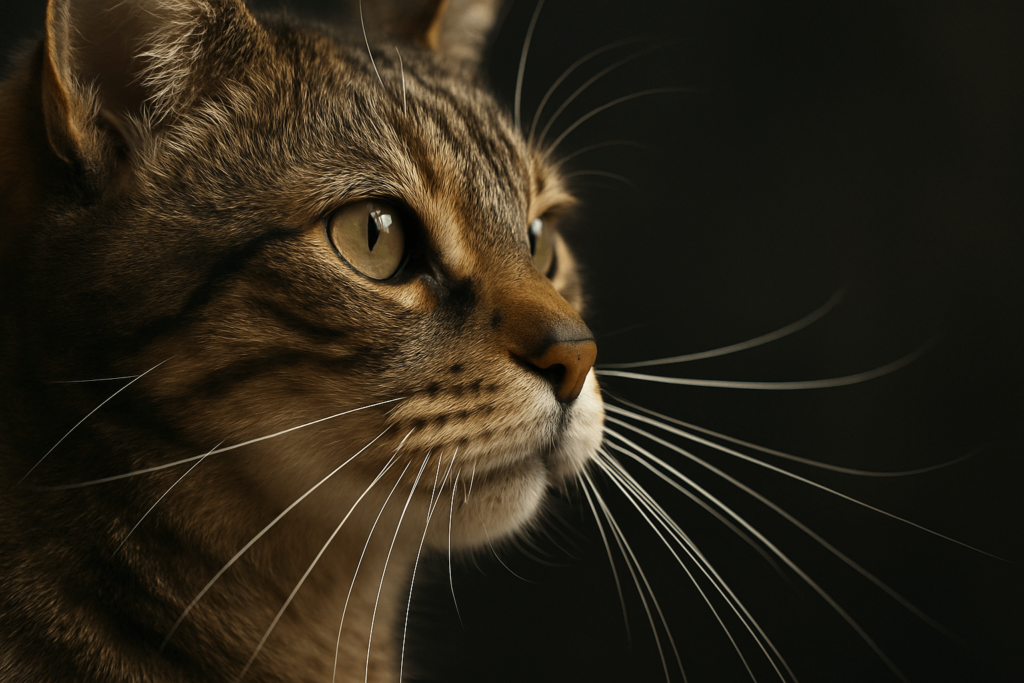

The Five Primary Functions of Cat Whiskers
Whiskers do far more than help cats “feel” their way around. They’re essential tools for survival, communication, and daily function. Here’s how they serve your cat:
Spatial Awareness:
Whiskers act like a built-in measuring tape, helping cats determine if an opening is wide enough to pass through—critical for hunting and escaping predators.Nighttime Navigation:
In total darkness, whiskers detect subtle air movements caused by nearby objects, allowing cats to move with precision even without sight.Hunting Precision:
When a cat catches prey, whiskers help locate the exact position of the animal’s body, especially when it’s too close to see clearly.Emotional Expression:
Whisker position reflects mood—forward and alert when curious, pinned back when scared or threatened, relaxed when at ease.Environmental Mapping:
Whiskers sense changes in air pressure and temperature, alerting cats to approaching storms, drafts, or hidden obstacles.
These functions aren’t optional extras—they’re survival mechanisms honed over millions of years. Without whiskers, your cat would be disoriented, anxious, and vulnerable.
Check this guide 👉Crimped Cat Whiskers: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉Understanding Cat Whisker Fatigue: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉Cat Whiskers Position Meaning: Best 7 Expert Tips!
| Whisker Function | Real-World Impact |
|---|---|
| Measuring space and width | Prevents cats from getting stuck in narrow gaps or boxes |
| Detecting air currents | Enables navigation in complete darkness or low-light conditions |
| Sensing nearby movement | Helps detect prey, predators, or sudden changes in environment |
| Relaying emotional state | Signals fear, curiosity, or aggression to other animals and humans |
| Assisting in close-range hunting | Guides precise bite placement when capturing prey |
Why Cutting Cat Whiskers Is Dangerous
It’s a heartbreaking myth that trimming whiskers is harmless—like a haircut. In reality, it’s akin to blinding someone in one sensory dimension. Here’s why you must never cut them:
Disorientation and Anxiety:
Without whiskers, cats lose their spatial map. They may bump into walls, misjudge jumps, or appear confused in familiar rooms.Impaired Hunting Ability:
Even indoor cats rely on whiskers to detect prey movement. Trimming them reduces their confidence and coordination.Increased Stress Levels:
Whiskers are tied to emotional regulation. Their loss can trigger chronic stress, hiding, or even aggression.Difficulty Eating:
Some cats struggle to locate food bowls without whisker feedback, leading to reduced appetite or messy eating.Long Recovery Period:
Whiskers grow back slowly—weeks to months—and during that time, your cat lives in a world of uncertainty.
Whiskers are not decorative. They are vital. Never trim, pluck, or tug them—even if they look “messy.”
What Happens When Whiskers Fall Out Naturally
Whiskers, like all hairs, have a life cycle. They grow, rest, and shed—naturally. But this process is often misunderstood.
Normal Shedding:
It’s common to find one or two whiskers on the floor. This is part of their renewal cycle—no cause for alarm.No Pain or Discomfort:
Whiskers shed painlessly. If your cat seems distressed during shedding, look for other signs of illness.Regrowth Is Guaranteed:
New whiskers will emerge from the same follicle, usually within 2–3 months.Uneven Growth Is Normal:
Whiskers don’t all shed at once. You may notice asymmetry, but this is typical and temporary.Sudden Mass Loss Is a Red Flag:
If multiple whiskers fall out rapidly or the follicles appear inflamed, consult your vet—it could signal skin disease, infection, or hormonal imbalance.
Natural shedding is quiet and uneventful. Sudden or excessive loss is not—and should never be ignored.
Whisker Fatigue: The Hidden Problem in Modern Cat Care
Even if you never cut your cat’s whiskers, they can still be overstimulated. Enter “whisker fatigue”—a condition caused by constant, unnecessary pressure on the vibrissae.
Tight Food Bowls:
Deep ceramic bowls that press against whiskers during eating can cause sensory overload and stress.Frequent Face Rubbing:
Cats who constantly rub their faces against furniture or walls may be trying to relieve whisker discomfort.Signs of Discomfort:
Refusing to eat from bowls, pawing at food, or eating only from the edge of the bowl are classic indicators.Solution: Use Wide, Shallow Dishes:
Ceramic, stainless steel, or glass plates with low sides give whiskers room to move freely.Avoid Plastic Bowls:
They can harbor bacteria and may cause allergic reactions that irritate the sensitive skin around whiskers.
Whisker fatigue isn’t widely known—but it’s incredibly common in domestic cats. A simple change in bowl design can dramatically improve your cat’s eating experience.
How Whiskers Help Cats Navigate the World
Your cat doesn’t just see the world—they feel it. Whiskers create a tactile image of their environment that complements—and sometimes surpasses—vision.
Detecting Obstacles in Darkness:
Even in pitch-black rooms, whiskers sense nearby furniture, walls, or people by detecting air displacement.Judging Distance for Jumps:
Before leaping, cats use whiskers to gauge the gap, ensuring they land safely—critical for climbing and hunting.Avoiding Collisions:
In tight spaces like hallways or under furniture, whiskers act as bumper sensors, preventing head-on impacts.Sensing Prey Movement:
When a mouse rustles in a corner, whiskers pick up the air current before the cat even sees it.Navigating in Crowded Spaces:
Multi-cat households or busy homes can be overwhelming. Whiskers help cats avoid accidental collisions with other pets or people.
Think of whiskers as your cat’s version of a 3D scanner—constantly mapping, updating, and reacting to their surroundings in real time.
Myths and Misconceptions About Cat Whiskers
There’s no shortage of misinformation. Let’s debunk the most common myths once and for all.
Myth: Whiskers are just for balance.
False. While they assist with spatial awareness, balance is primarily controlled by the inner ear.Myth: All cats have the same number of whiskers.
Most have 12 per side (24 total), but some have more. The number varies by breed and genetics.Myth: Whiskers grow back if cut.
Yes—but the damage during regrowth is real. Cats suffer during the process.Myth: Whiskers only work on the face.
No. Cats also have whiskers above their eyes, on their chin, and on the backs of their front legs—called carpal whiskers.Myth: A cat with short whiskers is less capable.
Not true. Whisker length varies naturally. What matters is their sensitivity, not their length.
Understanding the truth helps you protect your cat’s sensory world—not accidentally harm it.
FAQ: How Do Cat Whiskers Work?
Can a cat’s whiskers grow back if they break?
Yes. Whiskers regenerate naturally over several weeks. Never pull or trim them—let nature take its course.
Do whiskers help cats see in the dark?
Not directly. But they detect air movement and nearby objects, allowing cats to navigate safely when vision is limited.
Why do some cats have curly whiskers?
Certain breeds, like the Devon Rex, have naturally curly whiskers due to genetic mutations. This doesn’t impair function.
Can whiskers sense temperature?
Indirectly. Whiskers detect air currents caused by temperature changes, helping cats locate warm or cool spots.
Is it normal for a cat to lose whiskers after surgery?
Sometimes. Stress or anesthesia can temporarily disrupt the hair cycle. If whiskers don’t regrow within 3 months, consult your vet.
Respect the Sensory Gift
Your cat’s whiskers are not an accessory. They are a gift from evolution—a living, breathing network of nerves that lets your feline friend perceive the world in ways we can only imagine. To cut them is to silence a voice your cat never learned to speak. To ignore them is to miss the quiet poetry of their daily navigation—the way they glide through shadows, land perfectly on narrow ledges, and sense your presence before you even move.
The next time you see your cat’s whiskers twitching as they explore a new room, pause.
That’s not just hair.
That’s their sixth sense.
And it’s working—perfectly, precisely, beautifully.
Canned Pumpkin for Cat Diarrhea: Best 7 Expert Tips! Natural remedy to firm stools, soothe upset bellies, and support gut health safely.
Can a Cat Give You Scabies? Best 7 Expert Tips! Discover the truth about feline mites, human skin risks, and how to protect yourself—without panic.
Cat Flea vs Human Flea: Best 7 Expert Tips! Discover the truth about bites, species, and how to eliminate infestations for good.
Weird Cat Behaviors: Best 7 Expert Tips! Discover why cats do strange things—and how to understand, not punish, their instincts for a happier home.