High Liver Enzymes in Cats: What You Need to Know
When your veterinarian mentions that your cat has elevated liver enzymes, it can be concerning. High liver enzymes in cats are not a disease in themselves but rather an indicator of an underlying issue affecting the liver or other parts of the body. The liver plays a vital role in digestion, detoxification, and overall health, so any abnormality demands attention. Understanding what causes elevated liver enzymes, how they are diagnosed, and what steps to take can help you ensure your feline friend receives the care they need. Let’s explore this important topic to empower you as a proactive and informed cat owner.
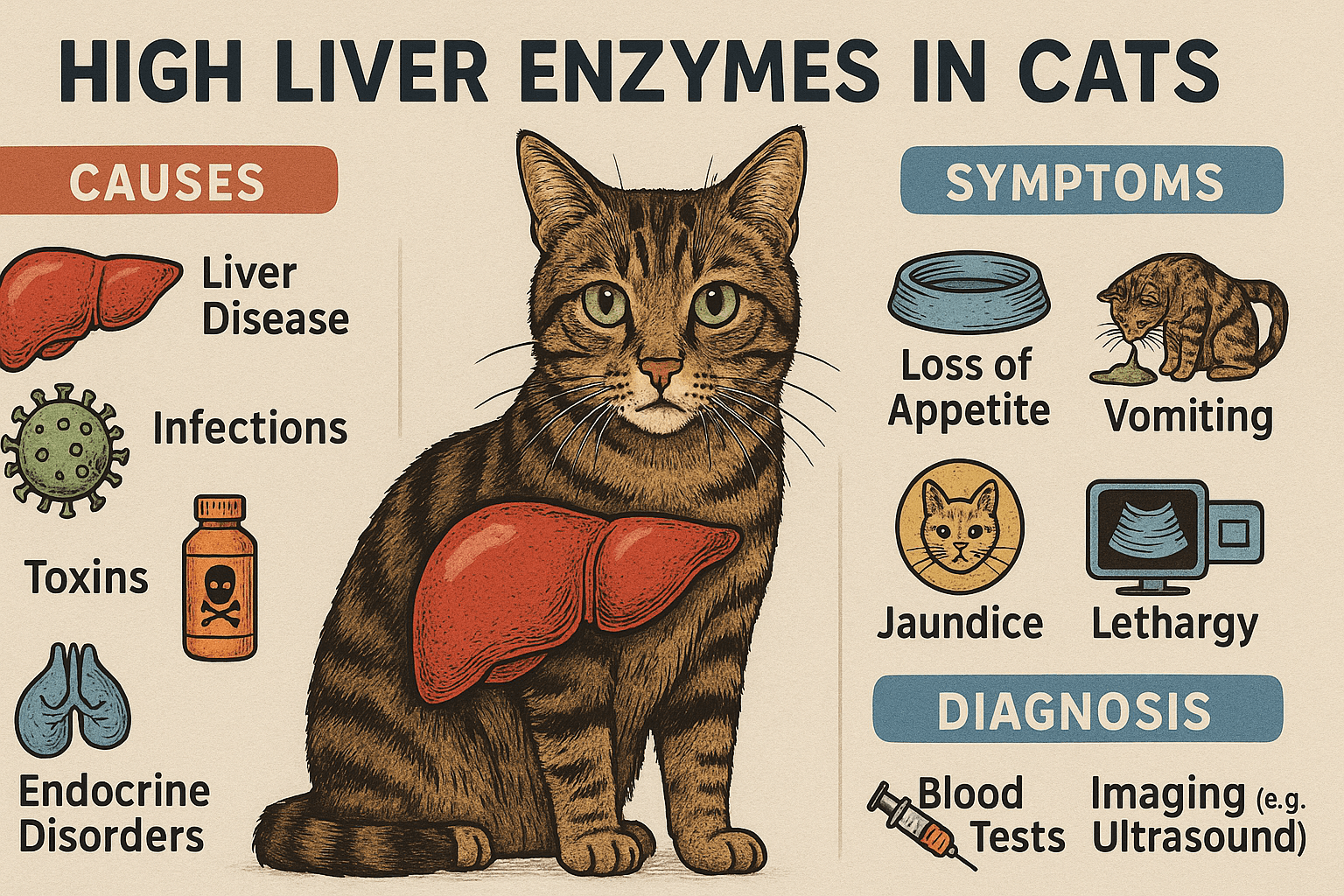
Common Causes of High Liver Enzymes in Cats
Elevated liver enzymes in cats can stem from a variety of conditions, ranging from mild to severe. Identifying the root cause is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment plan.
Hepatic Lipidosis (Fatty Liver Disease):
This condition occurs when fat accumulates in the liver, often due to prolonged anorexia or rapid weight loss. It’s one of the most common liver disorders in cats.Infections or Inflammation:
Bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections can inflame the liver, leading to increased enzyme levels. Feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) is one example.Toxin Exposure:
Cats are sensitive to toxins like certain medications, plants, or household chemicals, which can damage liver cells and elevate enzyme levels.Cancer or Tumors:
Liver tumors, whether benign or malignant, can disrupt normal liver function and result in high enzyme readings.Cholangiohepatitis:
This inflammatory condition affects the bile ducts and liver tissue, commonly seen in cats and often linked to bacterial infections.
Understanding these potential causes helps veterinarians narrow down diagnostic possibilities and develop targeted treatment strategies.
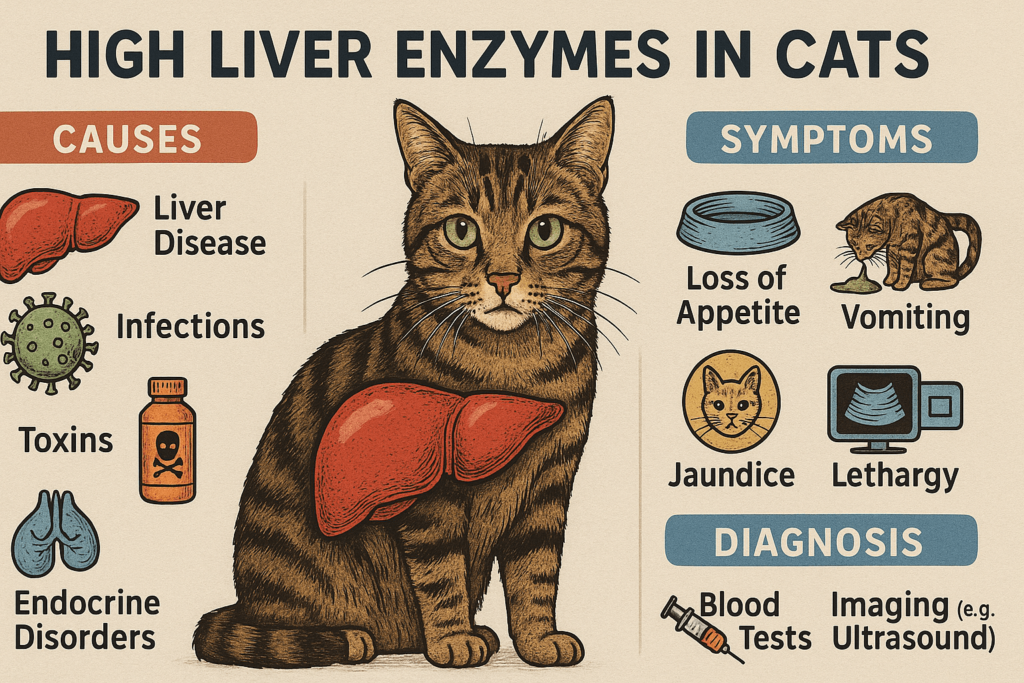
Symptoms of Elevated Liver Enzymes in Cats
While high liver enzymes are typically detected through blood tests, some symptoms may alert you to potential liver issues in your cat. Recognizing these signs early can lead to prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Lethargy and Weakness:
Cats with liver problems often appear unusually tired or uninterested in their surroundings.Loss of Appetite:
A sudden refusal to eat is a common symptom of liver-related issues, particularly hepatic lipidosis.Jaundice (Yellowing of Skin or Gums):
Jaundice occurs when bilirubin builds up in the bloodstream, causing yellow discoloration of the skin, gums, or whites of the eyes.Vomiting or Diarrhea:
Digestive upset, including vomiting or diarrhea, can indicate liver dysfunction.Increased Thirst and Urination:
Excessive drinking and urination may signal liver or kidney involvement, requiring further investigation.
If you notice any of these symptoms, schedule a vet visit promptly to assess your cat’s liver health.
Check this guide 👉Liver Failure in Cats: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉Cat Kidney Stone Treatment: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉How Long Can a Cat Live with Kidney Disease? Best 7 Tips!
Causes of High Liver Enzymes in Cats | Treatment Options |
|---|---|
Hepatic lipidosis | Feeding tube placement, nutritional support |
Infections or inflammation | Antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications |
Toxin exposure | Removing toxin source, supportive care |
Liver tumors or cancer | Surgery, chemotherapy, or palliative care |
Cholangiohepatitis | Steroids, antibiotics, dietary adjustments |
Diagnostic Tests for High Liver Enzymes
To determine the cause of high liver enzymes in your cat, veterinarians rely on a combination of diagnostic tests. These evaluations help pinpoint the underlying issue and guide treatment decisions.
Complete Blood Count (CBC):
A CBC checks for signs of infection, anemia, or other abnormalities that may relate to liver function.Serum Biochemistry Profile:
This test measures specific liver enzymes, such as ALT, AST, ALP, and bilirubin, to assess liver health.Ultrasound Imaging:
An abdominal ultrasound provides detailed images of the liver, helping identify structural changes, masses, or blockages.Urinalysis:
Examining urine can reveal additional clues about liver function and rule out other conditions like kidney disease.Liver Biopsy:
In some cases, a biopsy is necessary to diagnose specific liver diseases, such as cancer or chronic inflammation.
These diagnostic tools work together to provide a comprehensive picture of your cat’s liver health.
Preventing Liver Problems in Cats
While not all liver issues are preventable, taking proactive steps can significantly reduce the risk of high liver enzymes and related complications.
Provide a Balanced Diet:
Feed your cat high-quality food formulated for their age and health needs to support optimal liver function.Prevent Obesity:
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of fatty liver disease and other metabolic conditions.Limit Toxin Exposure:
Keep toxic plants, medications, and household chemicals out of reach to protect your cat’s liver.Schedule Regular Vet Check-Ups:
Routine exams and bloodwork can detect early signs of liver issues before they become severe.Encourage Hydration:
Ensure your cat drinks enough water to support liver and kidney health, especially if they eat dry food.
By adopting these preventive measures, you can help safeguard your cat’s liver and overall well-being.
Supporting a Cat with Liver Disease
Managing a cat with liver disease requires ongoing care and attention. Here are practical tips to help you support your cat during this challenging time.
Feed Small, Frequent Meals:
Smaller portions throughout the day can be easier for a cat with liver issues to digest and absorb nutrients.Choose Liver-Friendly Foods:
Opt for diets rich in high-quality protein and low in carbohydrates, tailored to your cat’s specific needs.Monitor Weight Changes:
Regularly weigh your cat to track any fluctuations, as significant weight loss or gain can impact liver health.Administer Medications as Prescribed:
Follow your vet’s instructions carefully to ensure your cat receives the full benefit of prescribed treatments.Create a Stress-Free Environment:
Minimize stress by providing a calm, predictable routine and safe spaces for your cat to rest.
With consistent care and monitoring, you can help your cat thrive despite liver challenges.
Understanding Liver Enzyme Levels
Interpreting liver enzyme levels can be confusing, but knowing what each enzyme indicates can provide valuable insights into your cat’s health.
ALT (Alanine Aminotransferase):
Elevated ALT levels suggest acute liver cell damage or injury.AST (Aspartate Aminotransferase):
High AST levels may indicate liver or muscle damage, requiring further testing to differentiate.ALP (Alkaline Phosphatase):
Increased ALP often points to bile duct obstruction, bone growth, or steroid use.GGT (Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase):
Elevated GGT is associated with bile flow issues or liver inflammation.Bilirubin:
High bilirubin levels indicate impaired liver function or red blood cell breakdown.
Understanding these markers helps demystify blood test results and guides discussions with your vet.
When to Seek Emergency Care
Some liver-related symptoms in cats require immediate veterinary attention. Knowing when to act quickly can save your cat’s life.
Severe Jaundice:
Pronounced yellowing of the skin, gums, or eyes signals advanced liver dysfunction needing urgent care.Persistent Vomiting or Diarrhea:
Uncontrolled digestive issues can lead to dehydration and worsening liver health.Sudden Collapse or Seizures:
These symptoms may indicate liver failure or toxin exposure, requiring emergency treatment.Refusal to Eat for More Than 24 Hours:
Prolonged anorexia increases the risk of hepatic lipidosis and must be addressed immediately.Difficulty Breathing:
Labored breathing could indicate fluid buildup or other complications related to liver disease.
Prompt action in these situations ensures your cat receives timely care and improves their chances of recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions About High Liver Enzymes in Cats
What does it mean if my cat has high liver enzymes?
Elevated liver enzymes indicate that your cat’s liver may be under stress or damaged, requiring further investigation to identify the cause.
Can high liver enzymes be cured?
Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Many conditions can be managed or resolved with proper care, but chronic issues may require lifelong management.
How is liver disease treated in cats?
Treatment varies based on the diagnosis and may include dietary changes, medications, surgery, or supportive therapies.
Is hepatic lipidosis life-threatening?
Yes, untreated hepatic lipidosis can be fatal, but early intervention and aggressive treatment often lead to recovery.
How can I tell if my cat’s liver is improving?
Improved appetite, energy levels, and normalized bloodwork results are positive indicators of progress.
Taking Action for Your Cat’s Liver Health
High liver enzymes in cats are a signal to investigate further, not a definitive diagnosis. By understanding the potential causes, recognizing symptoms, and working closely with your veterinarian, you can address underlying issues effectively. Whether through dietary adjustments, medical treatments, or lifestyle changes, there are many ways to support your cat’s liver health and improve their quality of life. Remember, early detection and proactive care are key to ensuring your feline companion remains happy and healthy for years to come.
Can I Give My Cat Midol? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Learn the risks, symptoms, and safe alternatives to keep your cat healthy and avoid toxic reactions.
Can I Give My Dog Midol? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover the risks, safe alternatives, and expert advice to keep your dog safe from accidental poisoning.
Maximum Weight for Cats on Planes: Best 7 Expert Tips! – Learn airline policies, tips to stay compliant, and ensure safe travels for your feline friend.
Max Weight for Dogs on Planes: Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover airline weight limits, safe travel tips, and solutions for flying with your dog stress-free.