Recognizing Dog Seizure Symptoms: What Every Owner Should Know
Seizures in dogs can be alarming, but understanding the signs helps you respond effectively and seek timely care. Whether caused by epilepsy, toxins, or underlying health issues, recognizing symptoms early is crucial for your dog’s well-being. By staying informed, you can provide the support and treatment your furry companion needs to manage this challenging condition.
Common Symptoms of Seizures in Dogs
Seizures in dogs can manifest in various ways, ranging from subtle behavioral changes to full-body convulsions. Recognizing these symptoms early allows you to act quickly and minimize potential harm. While every dog’s experience is unique, certain signs are commonly observed during or before a seizure episode. Familiarizing yourself with these indicators ensures you’re prepared to respond effectively if your dog experiences one.
- Pre-Seizure Signs (Aura Phase):
Before a seizure, many dogs exhibit unusual behaviors such as restlessness, pacing, or seeking attention. This phase, known as the aura, may last minutes or hours and serves as a warning sign for impending episodes. - Loss of Consciousness:
During a seizure, some dogs lose consciousness entirely, appearing unresponsive to touch or sound. They may collapse suddenly, which can be distressing for owners witnessing the event. - Muscle Spasms or Convulsions:
Generalized seizures often involve uncontrollable muscle twitching, paddling motions with their legs, or rigid body postures. These physical symptoms are among the most recognizable signs of a seizure. - Excessive Drooling or Foaming at the Mouth:
Drooling or foaming occurs due to increased salivation and involuntary jaw movements during a seizure. This symptom is often mistaken for poisoning or choking, so context matters when identifying the cause. - Temporary Blindness or Confusion Afterward:
Following a seizure, dogs may seem disoriented, stumble around, or appear temporarily blind. This post-seizure phase, called the recovery period, can last from minutes to hours depending on the severity.
Understanding these symptoms helps differentiate seizures from other medical emergencies and guides appropriate next steps for your dog’s care.

Causes of Seizures in Dogs
Seizures don’t occur without reason—they’re typically triggered by underlying conditions or external factors that affect brain activity. Identifying the root cause is essential for managing and treating recurrent episodes effectively. While some causes are treatable, others require long-term management strategies tailored to your dog’s needs.
- Epilepsy:
Idiopathic epilepsy, a genetic condition with no identifiable cause, is one of the most common reasons for seizures in dogs. It usually begins between ages 1 and 5 and requires lifelong monitoring. - Toxin Exposure:
Ingesting harmful substances like antifreeze, chocolate, or certain plants can lead to seizures. Immediate veterinary intervention is critical to prevent further complications. - Brain Tumors or Injuries:
Tumors, trauma, or infections affecting the brain disrupt normal electrical activity, potentially triggering seizure episodes. Diagnostic imaging often reveals these issues. - Liver Disease:
The liver filters toxins from the blood; impaired function allows harmful substances to reach the brain, causing hepatic encephalopathy and seizures. - Low Blood Sugar Levels:
Hypoglycemia, especially in small breeds or diabetic dogs, deprives the brain of energy, leading to seizures. Regular feeding schedules help mitigate this risk.
Pinpointing the exact cause enables targeted treatment plans, improving your dog’s quality of life while reducing seizure frequency.
Check this guide 👉Dog Focal Seizure Symptoms: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉How to Stop Seizures in Dogs Immediately: Best 7 Tips!
Check this guide 👉Gabapentin for Dog Seizures: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Types of Seizures in Dogs
Not all seizures look the same—different types vary in intensity, duration, and impact on your dog’s behavior. Understanding these distinctions aids in accurate communication with veterinarians and ensures proper care. Each type presents unique challenges that require specific approaches to diagnosis and treatment.
- Generalized (Grand Mal) Seizures:
These involve the entire body, characterized by loss of consciousness, violent muscle contractions, and involuntary urination or defecation. They’re the most dramatic and easily recognized form. - Focal Seizures:
Limited to one part of the brain, focal seizures cause localized symptoms like twitching in a limb or facial muscles. Some progress to generalized seizures over time. - Psychomotor Seizures:
These result in sudden, unusual behaviors such as chasing imaginary objects, biting at the air, or hiding for no apparent reason. Behaviors last only a few minutes but recur consistently. - Cluster Seizures:
Multiple seizures occurring within a short timeframe (hours to days) indicate cluster seizures, which pose significant health risks if untreated. - Status Epilepticus:
A life-threatening emergency, status epilepticus involves continuous seizure activity lasting more than five minutes. Immediate medical attention is required to prevent brain damage or death.
Knowing the type of seizure your dog experiences assists veterinarians in tailoring treatment protocols effectively.
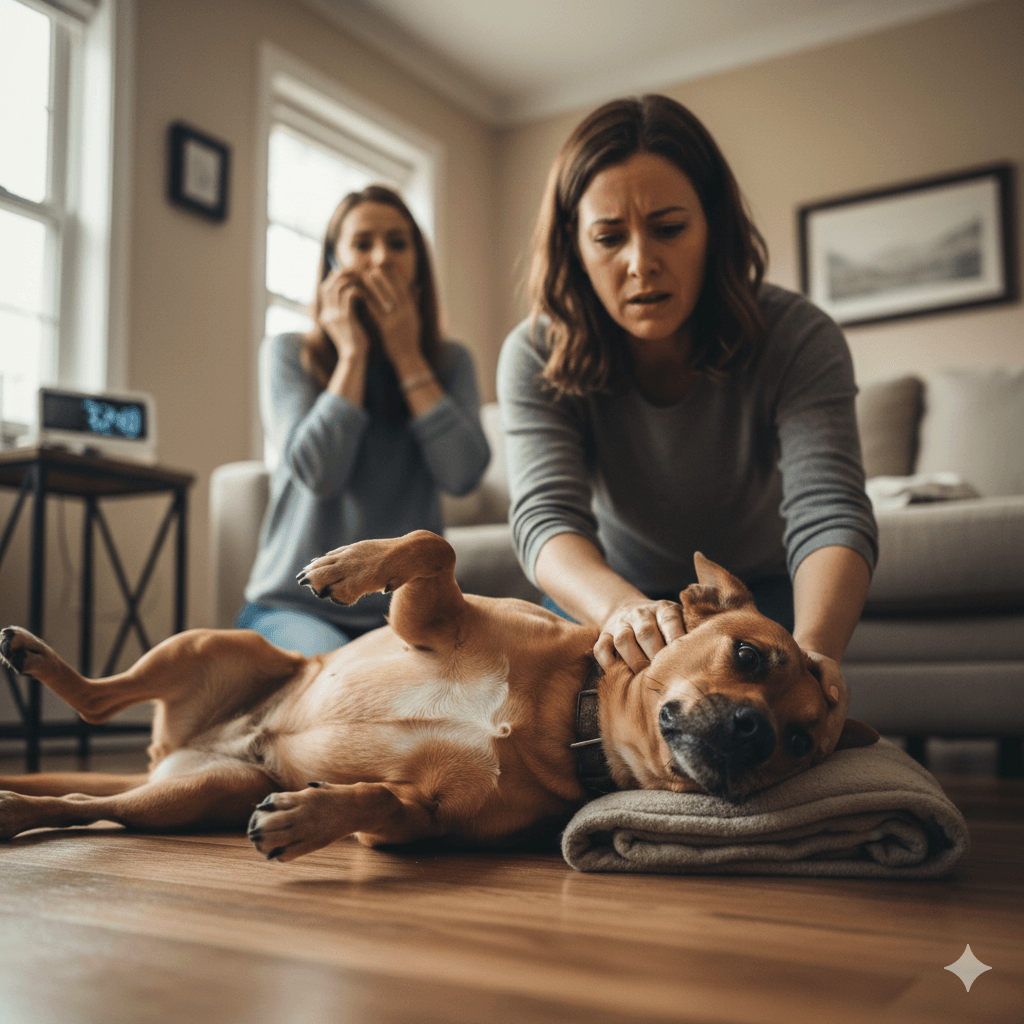
First Aid Steps During a Seizure
Witnessing your dog have a seizure is frightening, but staying calm and acting decisively minimizes harm and ensures their safety. Following these first aid steps provides comfort until professional help arrives. Never attempt aggressive interventions that could worsen the situation.
- Move Objects Away from Your Dog:
Clear the area of furniture, toys, or sharp objects to prevent injury during involuntary movements. Keep hands away from their mouth to avoid accidental bites. - Time the Seizure Duration:
Use a timer to track how long the seizure lasts. Episodes under two minutes are less urgent, but prolonged seizures require immediate vet attention. - Stay Calm and Reassuring:
Speak softly and remain nearby to comfort your dog once they regain consciousness. Avoid restraining them during the seizure itself. - Cool Their Body Temperature:
If the seizure persists for several minutes, apply cool (not cold) water or damp cloths to their paws to prevent overheating. - Contact Your Veterinarian Immediately:
Even if the seizure resolves quickly, schedule an appointment to investigate potential underlying causes and discuss ongoing management strategies.
Quick, informed responses protect your dog’s well-being and reduce stress for both of you during a seizure episode.
Long-Term Management of Canine Seizures
Managing seizures in dogs involves a combination of medication, lifestyle adjustments, and regular veterinary check-ups. Consistent care minimizes seizure frequency and improves overall quality of life. While complete elimination isn’t always possible, effective management reduces the burden on both pets and owners.
- Anticonvulsant Medications:
Drugs like phenobarbital or potassium bromide stabilize brain activity, significantly decreasing seizure frequency in most cases. Compliance with prescribed doses is crucial for success. - Regular Vet Visits:
Frequent blood tests monitor drug levels and detect side effects early, ensuring safe and effective treatment over time. - Stress Reduction Techniques:
Minimizing environmental triggers such as loud noises, travel, or abrupt routine changes lowers the likelihood of seizure episodes. - Balanced Diet and Hydration:
Nutritious meals support brain health, while avoiding allergens or toxins prevents additional strain on the nervous system. - Emergency Preparedness:
Keep a seizure diary to track patterns and share insights with your vet. Always have contact info for emergency clinics readily available.
Commitment to long-term management fosters resilience and stability for dogs prone to seizures.
Potential Complications of Untreated Seizures
Ignoring or inadequately addressing seizures poses serious risks to your dog’s health and longevity. Recurrent episodes left untreated can lead to irreversible damage or even life-threatening complications. Awareness of these dangers underscores the importance of timely veterinary care and adherence to treatment plans.
- Brain Damage:
Prolonged or frequent seizures starve the brain of oxygen, resulting in permanent cognitive decline or neurological deficits. - Increased Risk of Status Epilepticus:
Unmanaged seizures elevate the likelihood of entering status epilepticus, a fatal condition requiring intensive medical intervention. - Behavioral Changes:
Post-seizure confusion, anxiety, or aggression may develop, altering your dog’s personality and straining the human-animal bond. - Organ Strain:
Repeated seizures place immense stress on vital organs like the heart and kidneys, increasing susceptibility to secondary diseases. - Reduced Lifespan:
Without proper care, dogs with chronic seizure disorders face shorter lifespans compared to those receiving consistent treatment.
Addressing seizures promptly safeguards not only your dog’s immediate health but also their long-term vitality.
Preventing Future Seizure Episodes
While not all seizures are preventable, proactive measures significantly reduce the risk of future episodes. Combining preventive strategies with vigilant monitoring creates a safer environment for your dog. Small changes in daily routines can yield substantial benefits over time.
- Avoid Known Triggers:
Identify and eliminate exposure to substances or situations that provoke seizures, such as specific foods, chemicals, or stressful events. - Maintain Consistent Routines:
Predictable feeding, exercise, and sleep schedules promote stability and reduce seizure susceptibility. - Monitor Weight and Health:
Obesity and underlying illnesses exacerbate seizure risks; regular vet visits ensure optimal physical condition. - Use Protective Gear Outdoors:
Dog-safe bug repellents or protective clothing minimize insect encounters that could trigger allergic reactions or toxin exposure. - Educate Family Members:
Ensure everyone caring for your dog knows how to recognize symptoms and respond appropriately during emergencies.
Preventive efforts empower you to take control of your dog’s health, fostering a happier, seizure-free life whenever possible.
Frequently Asked Questions About Dog Seizure Symptoms
What should I do if my dog has a seizure?
Stay calm, move objects away from your dog, time the seizure, and contact your veterinarian immediately after it ends.
How long do dog seizures usually last?
Most seizures last between 30 seconds to 2 minutes; anything longer than 5 minutes requires emergency veterinary care.
Can seizures be cured in dogs?
While some causes of seizures can be treated or managed, others like epilepsy require lifelong medication to control symptoms.
Are certain dog breeds more prone to seizures?
Yes—breeds like Border Collies, Belgian Tervurens, and Labrador Retrievers are genetically predisposed to idiopathic epilepsy.
What triggers seizures in dogs?
Common triggers include stress, toxins, low blood sugar, liver disease, or brain injuries, though some seizures have no identifiable cause.
Supporting Your Dog Through Seizure Challenges
Managing seizures in dogs is a journey that requires patience, dedication, and teamwork with your veterinarian. While witnessing a seizure is undoubtedly frightening, understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options empowers you to provide the best possible care for your furry companion. By staying proactive with preventive measures, adhering to prescribed medications, and maintaining open communication with your vet, you can minimize seizure frequency and improve your dog’s quality of life. Remember, your unwavering love and support are the foundation of their resilience—and every step you take brings them closer to comfort and stability.
Dog Seizure Symptoms: Best 7 Expert Tips! – Learn to spot signs, respond effectively, and manage seizures in dogs for a healthier, happier life.
Carprofen Dosage for Cats: Best 7 Expert Tips! – Learn safe dosing, risks, and alternatives to manage pain and inflammation in cats effectively.
Africanis Dog Breed: Best 7 Expert Tips! – Explore the resilience, loyalty, and adaptability of this ancient African breed, perfect for diverse lifestyles.
Cruciate Ligament Injury Symptoms in Dogs: Best 7 Tips! – Discover key signs like limping, swelling, and joint instability to ensure prompt treatment.