Can Cat Chlamydia Be Passed to Humans? Understanding the Risks
Cat chlamydia, a bacterial infection that primarily affects a cat’s eyes, can raise concerns among pet owners about its potential transmission to humans. While this condition is common in cats, especially those living in multi-cat households or shelters, it’s important to understand whether it poses any risk to human health. In this blog post, we’ll explore what cat chlamydia is, how it spreads, and whether it can be transmitted to humans. By gaining clarity on this topic, you can take the necessary precautions to protect both your feline companion and your family. Let’s dive into the facts and dispel any myths surrounding cat chlamydia and its impact on humans.
What Is Cat Chlamydia and How Does It Spread?
Cat chlamydia, also known as Chlamydophila felis , is a bacterial infection that primarily affects a cat’s respiratory and ocular systems. Here’s what you need to know about this condition:
Symptoms in Cats
Infected cats often exhibit signs like red, swollen eyes, excessive tearing, and discharge from the eyes or nose.Highly Contagious Among Cats
The bacteria spread easily through direct contact, such as grooming or sharing food bowls, especially in crowded environments.Common in Kittens
Young kittens are more vulnerable to infection due to their weaker immune systems.Environmental Transmission
The bacteria can survive briefly on surfaces, making shared bedding or toys potential sources of infection.Diagnosis by Veterinarians
A vet can confirm chlamydia through tests like swabs or blood work, ensuring accurate treatment.
Understanding how cat chlamydia spreads among cats helps explain why it’s essential to maintain hygiene and monitor your pet’s health closely.
Can Cat Chlamydia Be Passed to Humans? Key Facts
While cat chlamydia primarily affects felines, there are rare instances where humans may be impacted. Here’s what experts say about zoonotic risks:
Limited Zoonotic Potential
Chlamydophila felis rarely infects humans, but immunocompromised individuals may face a slightly higher risk.Mild Conjunctivitis in Humans
If transmission occurs, humans may develop mild eye irritation or conjunctivitis, which is treatable with antibiotics.Direct Contact Required
Human infection typically happens through close contact with an infected cat’s eye discharge.Low Risk for Healthy Individuals
Most healthy people are unlikely to contract the bacteria, as their immune systems can fend off the infection.Proper Hygiene Reduces Risk
Washing hands after handling an infected cat minimizes the chances of bacterial transfer.
While the risk of transmission is minimal, taking precautions ensures the safety of both humans and cats.
Check this guide 👉Understanding the FVRCP Cat Vaccine: Best 7 Health Tips!

Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Primary Affected Species | Cats |
Common Symptoms in Cats | Eye discharge, redness, sneezing |
Risk to Humans | Rare, mostly affects immunocompromised people |
Transmission Method | Direct contact with infected secretions |
Prevention Measures | Hygiene, vet care, and isolation of sick cats |
How to Prevent and Manage Cat Chlamydia
Preventing and managing cat chlamydia involves a combination of veterinary care, hygiene practices, and environmental control. Here’s how you can protect your cat and household:
Regular Vet Check-Ups
Schedule routine visits to monitor your cat’s health and catch infections early.Isolate Infected Cats
Keep infected cats away from other pets to prevent the spread of bacteria.Clean Living Spaces
Disinfect shared items like food bowls, bedding, and toys regularly to reduce contamination.Administer Prescribed Medications
Follow your vet’s instructions for antibiotics to ensure complete recovery.Practice Good Hygiene
Wash your hands thoroughly after handling an infected cat or cleaning their belongings.
By taking these steps, you can minimize the risk of cat chlamydia spreading and keep your household safe.
Signs You Should Consult a Veterinarian
If you suspect your cat has chlamydia or notice unusual symptoms, seeking veterinary advice is crucial. Here’s when to act:
Persistent Eye Discharge
If your cat’s eye discharge doesn’t improve within a few days, it could indicate an infection.Redness or Swelling
Severe inflammation around the eyes requires professional evaluation.Lethargy or Loss of Appetite
These signs may suggest a more serious underlying issue beyond chlamydia.Sneezing or Nasal Discharge
Respiratory symptoms accompanying eye issues warrant immediate attention.Exposure to Infected Cats
If your cat has been in contact with an infected animal, schedule a check-up promptly.
Early intervention ensures your cat receives the care they need and prevents complications.
Understanding the Role of Hygiene in Preventing Transmission
Maintaining proper hygiene is one of the most effective ways to minimize the risk of cat chlamydia spreading to humans or other pets. Here’s how you can incorporate hygiene practices into your daily routine:
Wash Hands After Handling Cats
Always wash your hands with soap and water after touching an infected cat or cleaning their belongings.Avoid Touching Your Face
Refrain from touching your eyes, nose, or mouth after interacting with an infected cat to prevent bacterial transfer.Disinfect Surfaces Regularly
Clean surfaces like countertops, floors, and furniture that may come into contact with your cat’s secretions.Use Disposable Gloves
Wear gloves when administering medication or cleaning up after an infected cat to reduce direct exposure.Launder Bedding and Toys
Wash your cat’s bedding, blankets, and toys in hot water to eliminate any lingering bacteria.
By prioritizing hygiene, you can significantly reduce the chances of transmission and keep your household safe.
How to Strengthen Your Cat’s Immune System
A strong immune system helps your cat fight off infections like chlamydia more effectively. Here are some ways to boost your cat’s immunity:
Provide a Balanced Diet
Feed your cat high-quality food rich in essential nutrients like vitamins A, C, and E to support their immune system.Ensure Proper Hydration
Encourage your cat to drink plenty of water to flush out toxins and maintain overall health.Minimize Stress
Create a calm and stable environment to reduce stress, which can weaken your cat’s immune response.Regular Exercise
Engage your cat in playtime to keep them physically active and promote a healthy immune system.Schedule Routine Vaccinations
Keep your cat up-to-date on vaccinations to protect them from other infections that could compromise their immunity.
Strengthening your cat’s immune system not only helps them recover faster but also prevents future health issues.
Recognizing the Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of cat chlamydia is crucial for preventing its spread and ensuring prompt treatment. Here’s why acting quickly matters:
Prevents Outbreaks in Multi-Cat Households
Identifying and isolating an infected cat early can stop the bacteria from spreading to other pets.Reduces Recovery Time
Starting treatment as soon as symptoms appear ensures a quicker and smoother recovery process.Minimizes Human Exposure
Addressing the infection promptly lowers the risk of accidental transmission to humans.Avoids Complications
Untreated chlamydia can lead to secondary infections or chronic eye problems in cats.Saves on Veterinary Costs
Early intervention often requires less intensive and costly treatments compared to advanced cases.
By staying alert to the signs of chlamydia, you can act swiftly to protect both your cat and your household.
Frequently Asked Questions About Cat Chlamydia
Can I get chlamydia from my cat?
While rare, humans with weakened immune systems may develop mild conjunctivitis from Chlamydophila felis .
How is cat chlamydia treated?
Antibiotics prescribed by a veterinarian are the primary treatment for infected cats.
Is cat chlamydia contagious to other pets?
Yes, it spreads easily among cats, especially in close quarters like shelters.
Can I prevent my cat from getting chlamydia?
Maintaining hygiene, isolating sick cats, and regular vet visits help reduce the risk.
How long does treatment take?
Treatment typically lasts 2-4 weeks, depending on the severity of the infection.
Protecting Your Cat and Family from Chlamydia
While cat chlamydia is not a significant threat to human health, understanding its potential risks and taking preventive measures is essential for maintaining a healthy household. By staying vigilant about your cat’s well-being, practicing good hygiene, and consulting a veterinarian when needed, you can ensure both your feline friend and your family remain safe and happy. Remember, knowledge is power—armed with the right information, you can tackle any health concern that comes your way. After all, a healthy cat means a joyful home!
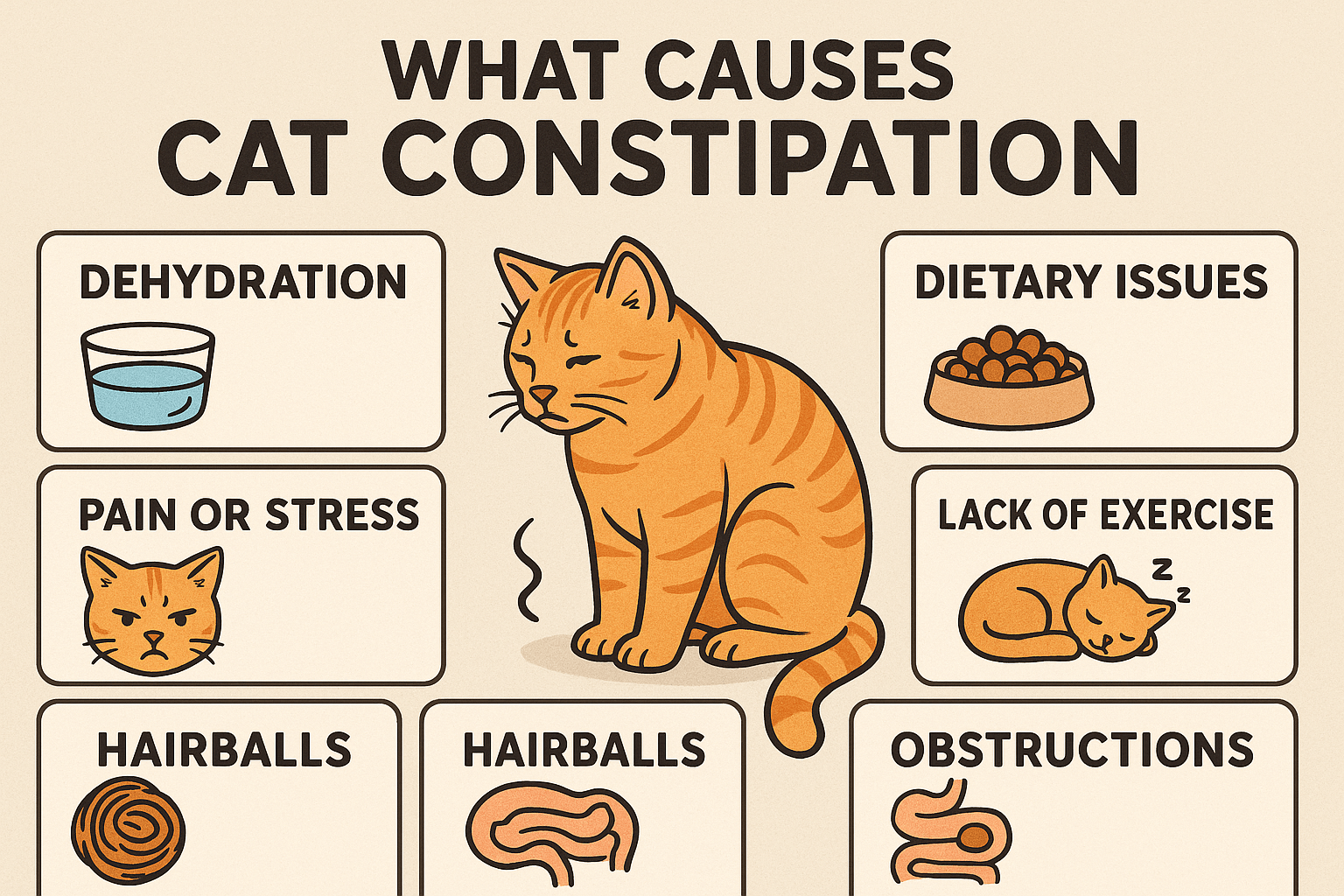
What Causes Cat Constipation? Best 7 Expert Tips! Discover common causes, symptoms, and solutions for cat constipation to keep your feline healthy and comfortable.
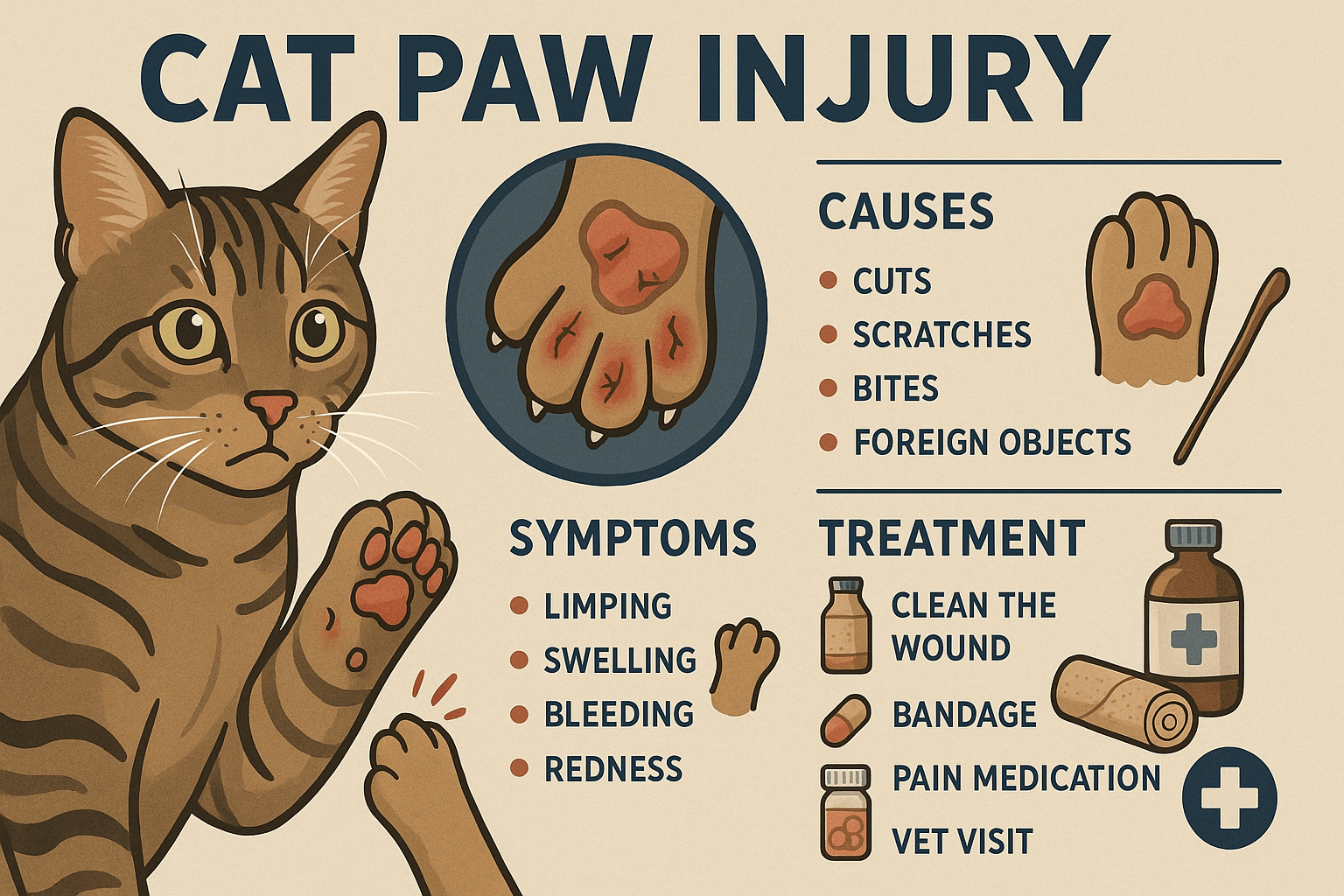
Cat Paw Injury: Best 7 Expert Tips! Discover essential advice on identifying, treating, and preventing cat paw injuries to keep your feline friend healthy and happy.
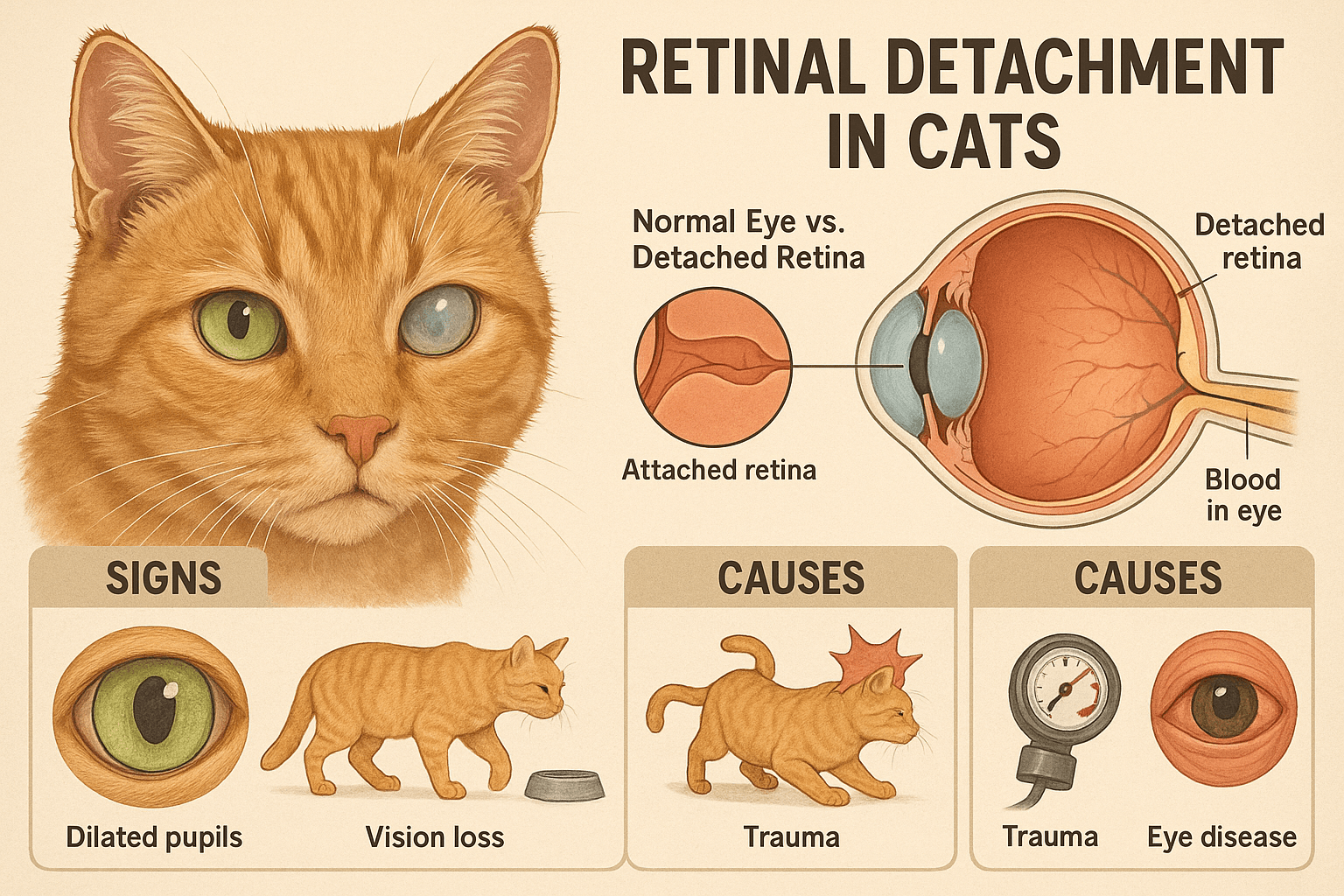
Retinal Detachment in Cats: Best 7 Expert Tips! Learn to identify symptoms, understand causes, and explore treatment options to protect your cat’s vision effectively.
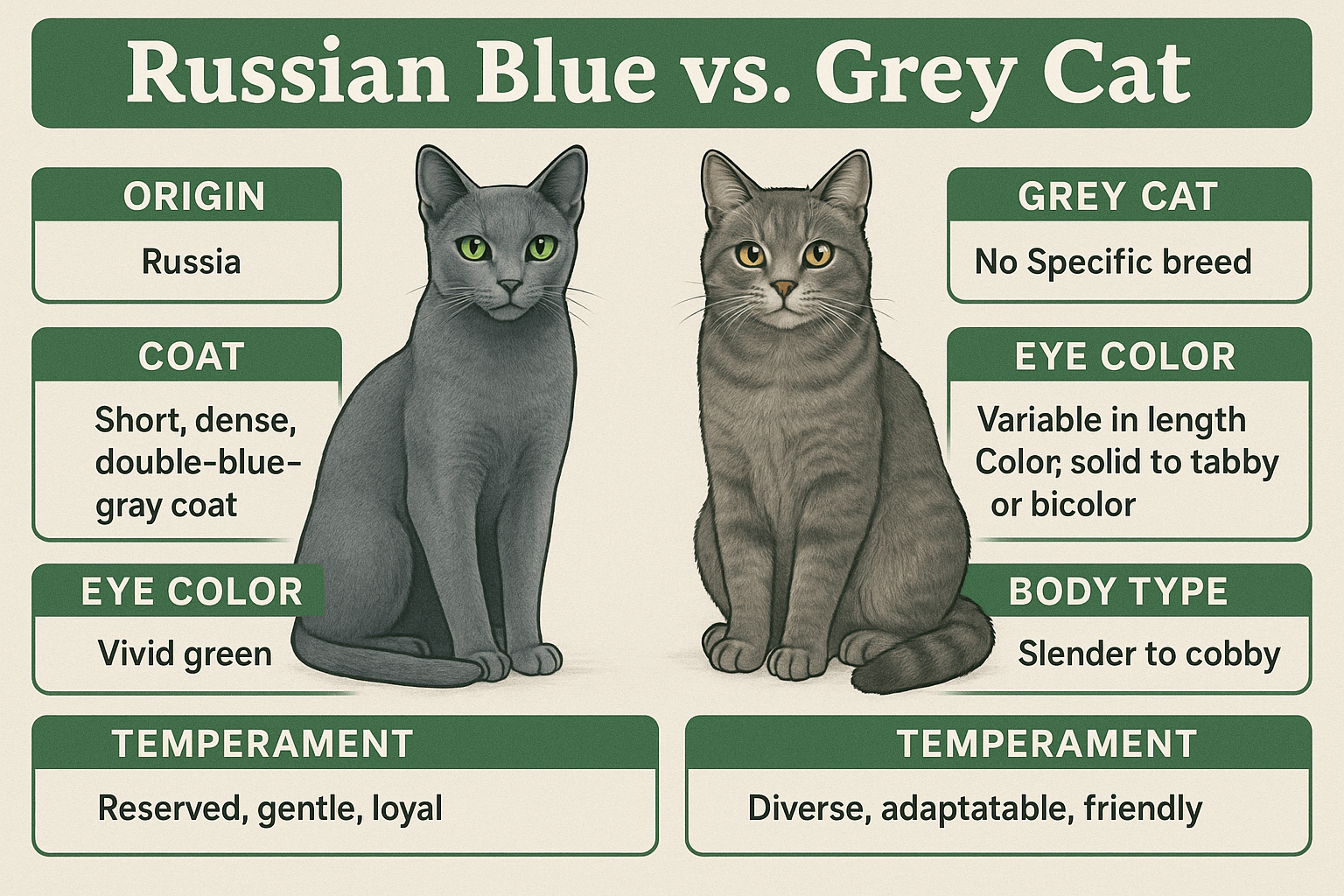
Russian Blue vs Grey Cat: Best 7 Expert Tips! Discover key differences, unique traits, and expert advice to help you choose between a Russian Blue and a generic grey cat for your perfect feline companion.