Understanding the Dog Tapeworm Life Cycle
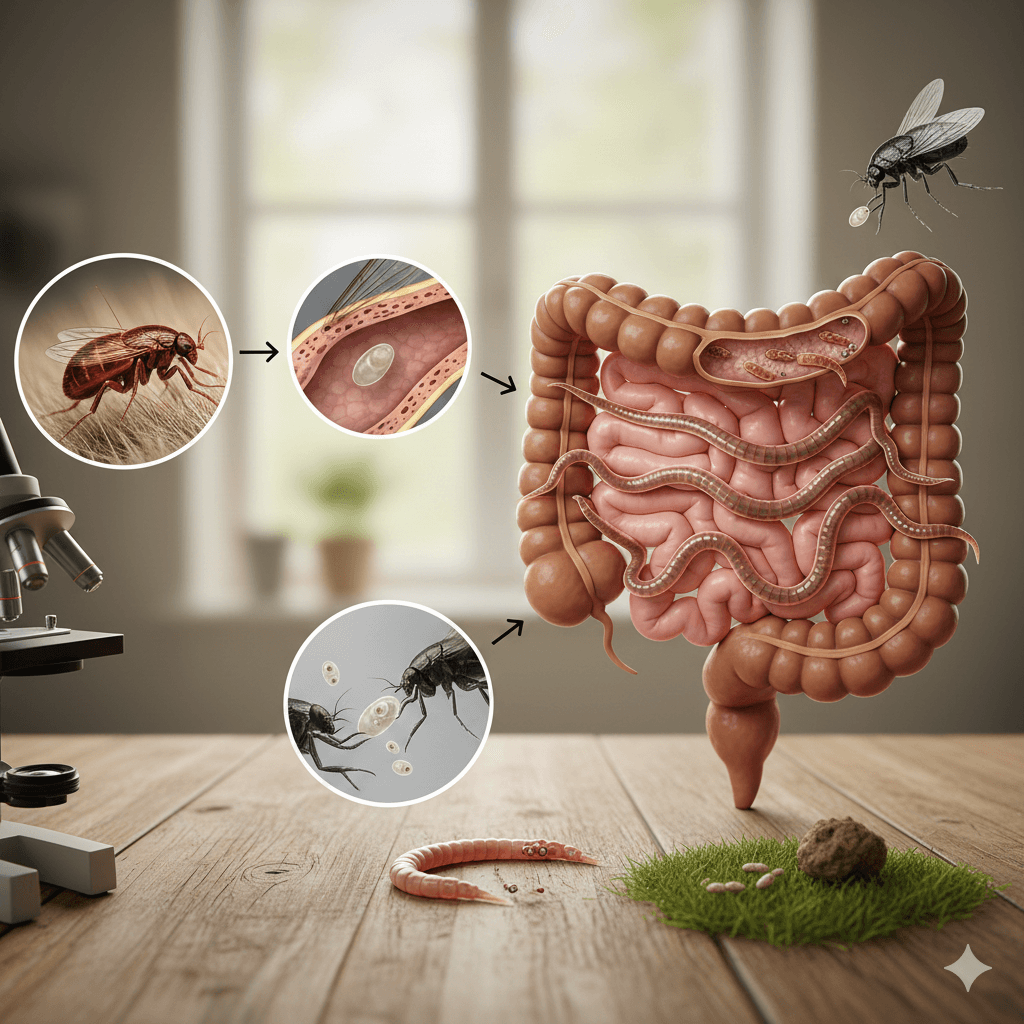
The Tapeworm Life Cycle: How It Begins
- Egg Stage:
Tapeworm eggs are released into the environment through an infected dog’s feces. These microscopic eggs are contained within segments of the tapeworm’s body, which break off and are shed during defecation. - Intermediate Host Ingestion:
Fleas or other small animals, such as rodents, ingest the tapeworm eggs while feeding on contaminated feces or grooming themselves. Inside the intermediate host, the eggs hatch into larvae. - Larval Development:
Once inside the intermediate host, the tapeworm larvae migrate to specific tissues, such as muscles or organs, where they form cysts. These cysts protect the larvae until they are ingested by a definitive host, such as a dog. - Role of Fleas in Transmission:
Fleas are the most common intermediate hosts for dog tapeworms. When dogs groom themselves or bite at fleas, they may accidentally ingest an infected flea, allowing the tapeworm larvae to enter their digestive system. - Completion of the Cycle:
Inside the dog’s intestines, the larvae mature into adult tapeworms, attaching themselves to the intestinal lining. Adult tapeworms produce new egg-filled segments, which are shed in the dog’s feces, restarting the cycle.
Identifying Signs of Tapeworm Infestation in Dogs
- Visible Worm Segments:
Small, rice-like segments may be seen around your dog’s anus, in their feces, or on bedding. These segments are parts of the tapeworm’s body that break off as it grows. - Itching and Scooting:
Dogs with tapeworms often scoot their rear end across the floor due to irritation caused by worm segments or itching around the anal area. - Weight Loss Despite Normal Appetite:
Tapeworms absorb nutrients from the dog’s food, leading to unexplained weight loss even if your dog eats regularly. - Vomiting or Diarrhea:
In some cases, tapeworm infestations cause gastrointestinal upset, including vomiting or loose stools. Occasionally, entire worms may be expelled during vomiting. - General Lethargy:
A heavy tapeworm burden can drain your dog’s energy, leaving them less active or playful than usual.
Check this guide 👉Cat Worms Identify: Best 7 Health Tips!
Check this guide 👉Can I Get Hookworms from My Cat? Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉How to Know If Your Cat Has Tapeworm: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Stages of the Tapeworm Life Cycle | Key Facts and Prevention Tips |
|---|---|
Egg Stage | Eggs are shed in feces; regular cleaning prevents environmental contamination. |
Intermediate Host (Flea) | Fleas ingest eggs; flea control is crucial to breaking the cycle. |
Larval Development | Larvae form cysts in fleas; grooming increases ingestion risks. |
Ingestion by Definitive Host | Dogs ingest infected fleas; deworming treats existing infestations. |
Adult Tapeworm in Intestine | Adult worms produce new eggs; routine vet checks catch issues early. |
How Fleas Contribute to Tapeworm Infestations
- Flea Lifecycle Connection:
Fleas ingest tapeworm eggs during their larval stage when exposed to contaminated environments. Once inside the flea, the eggs develop into infectious larvae. - Accidental Ingestion by Dogs:
Dogs often ingest fleas while grooming themselves or chewing irritated skin. This accidental ingestion introduces tapeworm larvae into their digestive system. - Flea Infestations Increase Risk:
Homes with heavy flea populations pose a higher risk of tapeworm transmission. Controlling fleas is essential to reducing tapeworm exposure. - Environmental Factors:
Warm, humid climates create ideal conditions for flea breeding, indirectly increasing tapeworm risks. Proper sanitation and pest control are vital in such areas. - Integrated Prevention Strategies:
Combining flea treatments, regular grooming, and environmental cleaning minimizes both flea and tapeworm infestations. Consistency is key to long-term success.
Preventing Tapeworm Infestations in Dogs
- Regular Deworming Treatments:
Administer veterinarian-recommended deworming medications every 3–6 months, depending on your dog’s risk factors and lifestyle. - Effective Flea Control:
Use vet-approved flea preventatives, such as topical solutions, collars, or oral medications, to eliminate fleas and reduce tapeworm risks. - Routine Fecal Exams:
Schedule annual or biannual fecal tests with your vet to detect tapeworm eggs or segments before symptoms appear. - Maintain Clean Living Spaces:
Regularly clean your home, vacuum carpets, and wash bedding to remove flea eggs, larvae, and tapeworm segments from the environment. - Supervise Outdoor Activities:
Prevent your dog from hunting or eating rodents, which can serve as intermediate hosts for certain tapeworm species.
Treatment Options for Tapeworm Infestations
- Anthelmintic Medications:
Prescription dewormers like praziquantel target and kill adult tapeworms, causing them to disintegrate in the intestines and pass out in feces. - Over-the-Counter Solutions:
Some non-prescription products contain praziquantel or similar active ingredients, though veterinary guidance is recommended for safe use. - Follow-Up Treatments:
Repeat doses may be necessary to ensure all tapeworms are eradicated, especially in cases of severe infestations or reinfection risks. - Environmental Deep Cleaning:
Thoroughly clean your home and yard to remove flea eggs, larvae, and tapeworm segments that could lead to reinfestation. - Monitoring for Recurrence:
Watch for signs of tapeworms in the weeks following treatment. Persistent symptoms may indicate incomplete eradication or reinfection.
The Role of Hygiene in Breaking the Tapeworm Cycle
- Proper Waste Disposal:
Promptly pick up and dispose of your dog’s feces to prevent tapeworm eggs from contaminating the environment. - Washing Hands After Handling Pets:
Regular handwashing after grooming, feeding, or cleaning up after your dog minimizes the risk of accidental ingestion of tapeworm eggs. - Bathing Your Dog Regularly:
Frequent baths help remove fleas and tapeworm segments clinging to your dog’s fur, reducing the chance of reinfection. - Cleaning Food and Water Bowls:
Wash your dog’s bowls daily to prevent contamination from tapeworm eggs or flea debris. - Educating Family Members:
Ensure everyone in the household understands the importance of hygiene and flea control in preventing tapeworms.
Long-Term Management of Tapeworm Risks
- Annual Veterinary Check-Ups:
Routine exams allow your vet to assess your dog’s overall health and recommend preventive measures based on their lifestyle. - Customized Prevention Plans:
Tailor flea control and deworming schedules to your dog’s age, breed, and activity level for optimal protection. - Education on Zoonotic Risks:
Teach children and family members about zoonotic diseases, emphasizing the importance of avoiding contact with dog feces or infected fleas. - Environmental Modifications:
Reduce outdoor risks by keeping grass trimmed, sealing gaps to prevent rodent entry, and using pet-safe insecticides. - Emergency Preparedness:
Keep a supply of deworming medications and flea treatments on hand in case of unexpected infestations or exposures.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Dog Tapeworm Life Cycle
How do dogs get tapeworms?
Dogs typically get tapeworms by ingesting fleas infected with tapeworm larvae while grooming or chewing at their skin.
Can humans get tapeworms from dogs?
Yes, but it’s rare. Humans can contract tapeworms if they accidentally ingest fleas or contaminated fecal matter, so practicing good hygiene is essential.
How long does a tapeworm live inside a dog?
Adult tapeworms can live in a dog’s intestines for several weeks to months if left untreated.
Do over-the-counter dewormers work for tapeworms?
Some over-the-counter products containing praziquantel are effective, but veterinary guidance ensures safe and appropriate treatment.
What happens if tapeworms go untreated?
A Lifeline in Every Step of Prevention
Dog Tapeworm Life Cycle: Best 7 Expert Tips! – Learn how tapeworms infect dogs, spot symptoms, and break the cycle with expert prevention strategies.
Anxious Cat Body Language: Best 7 Expert Tips! – Learn to spot signs of stress, understand triggers, and help your cat feel safe and relaxed.
Anxious Dog Body Language: Best 7 Expert Tips! – Learn to spot signs of anxiety, respond effectively, and help your dog feel safe and secure.
Is Breeding Dogs Bad? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Explore the ethics, benefits, and risks of dog breeding to make informed decisions for a better future.



