Understanding the Dog Tympanic Membrane: A Key to Ear Health
Functions of the Dog Tympanic Membrane
- Sound Transmission:
The tympanic membrane vibrates in response to sound waves, transferring these vibrations to the ossicles (tiny bones) in the middle ear for processing by the brain. - Barrier Against Infections:
By sealing off the middle ear, the tympanic membrane prevents bacteria, fungi, and foreign particles from reaching sensitive inner ear structures. - Pressure Regulation:
The eardrum helps equalize pressure between the outer and middle ear, ensuring optimal auditory function and preventing discomfort. - Role in Balance and Orientation:
While primarily an auditory structure, the tympanic membrane indirectly supports balance by facilitating proper middle ear function. - Indicator of Ear Health:
Changes in the appearance or integrity of the tympanic membrane often signal underlying issues like infections, trauma, or chronic ear disease.
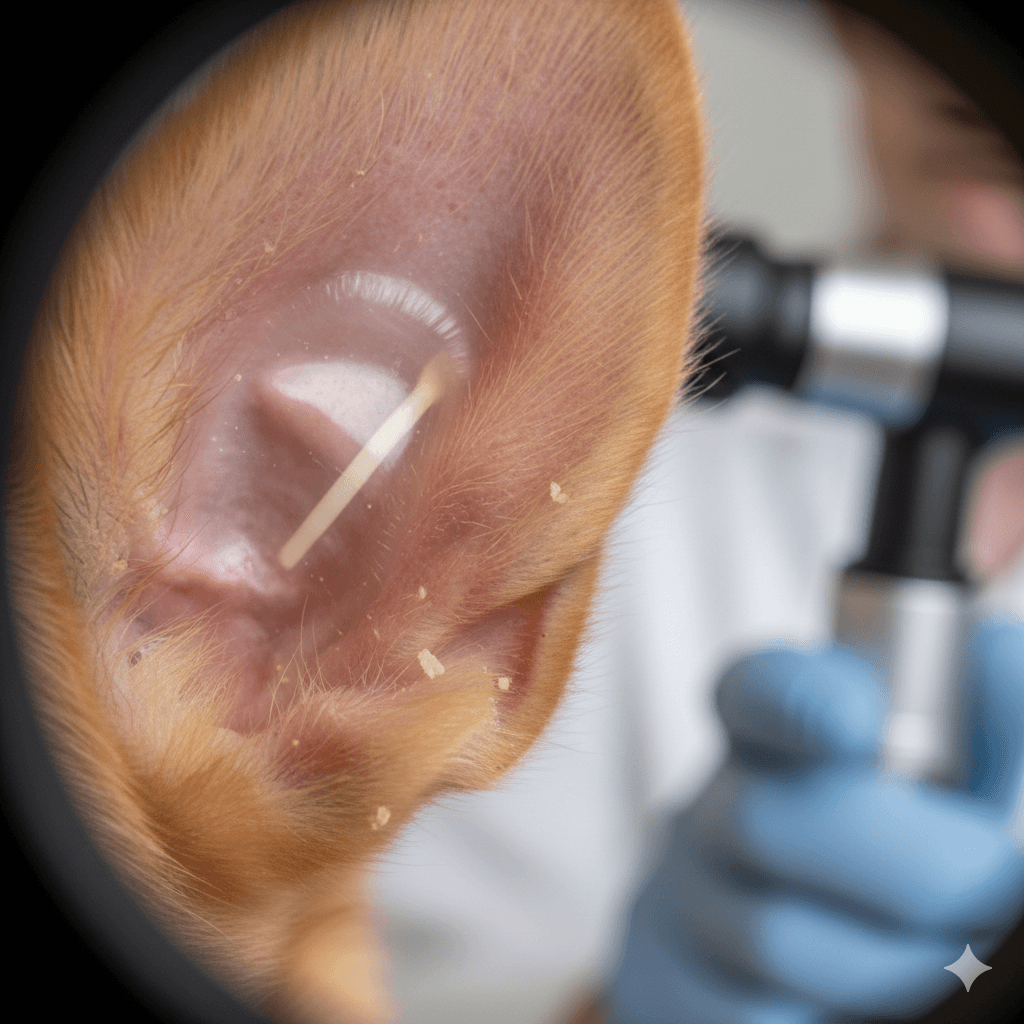
Common Causes of Tympanic Membrane Damage in Dogs
- Ear Infections (Otitis Media):
Chronic or untreated ear infections can spread to the middle ear, causing inflammation and perforation of the tympanic membrane. - Foreign Objects:
Dogs often insert objects like grass seeds or twigs into their ears, which can puncture or irritate the delicate eardrum. - Trauma or Injury:
Aggressive cleaning with cotton swabs or improper use of ear medications may accidentally rupture the tympanic membrane. - Loud Noises:
Exposure to extremely loud sounds, such as fireworks or machinery, can damage the eardrum through excessive vibration. - Congenital Abnormalities:
Some dogs are born with structural defects in the tympanic membrane, making them more prone to complications.
Check this guide 👉Dog Ear Infection Spread to Brain: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉Dog Ear Infection vs Yeast Infection: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉Dog Ear Hematoma Popped: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Symptoms of Tympanic Membrane Issues in Dogs
- Hearing Loss:
Partial or complete hearing impairment occurs if the tympanic membrane is perforated or inflamed, disrupting sound transmission. - Head Shaking or Tilting:
Dogs may shake their heads vigorously or tilt them to one side due to discomfort or pain originating from the affected ear. - Ear Discharge:
Pus, blood, or fluid leaking from the ear indicates potential tympanic membrane rupture or infection. - Odor from the Ear:
A foul smell emanating from the ear canal suggests bacterial or fungal infections affecting the tympanic membrane. - Behavioral Changes:
Increased irritability, reluctance to engage in play, or sensitivity to touch around the ears signals underlying ear issues.
Diagnosis of Tympanic Membrane Problems
- Otoscopic Examination:
An otoscope allows vets to visually inspect the tympanic membrane for tears, swelling, or abnormalities in color and texture. - Imaging Techniques:
X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs provide detailed images of the middle ear, helping identify structural damage or infections. - Tympanometry:
This non-invasive test measures the eardrum’s response to sound waves, assessing its flexibility and integrity. - Cytology and Culture Tests:
Samples from the ear canal are analyzed to detect bacteria, fungi, or parasites contributing to tympanic membrane issues. - Blood Tests:
Systemic infections or inflammatory conditions may be identified through blood work, providing additional diagnostic insights.
Treatment Options for Tympanic Membrane Damage
- Antibiotics or Antifungals:
Medications target infections causing inflammation or perforation of the tympanic membrane, administered orally or topically. - Anti-Inflammatory Drugs:
Steroids or NSAIDs reduce swelling and pain, promoting faster healing of the eardrum. - Surgical Intervention:
Severe cases may require procedures like myringotomy (incision in the eardrum) to drain fluid or repair damage. - Protective Measures:
Elizabethan collars prevent further trauma by stopping dogs from scratching or pawing at their ears during recovery. - Follow-Up Care:
Regular rechecks ensure proper healing and prevent recurrence of tympanic membrane issues.
Preventing Tympanic Membrane Issues in Dogs
- Routine Ear Cleaning:
Use vet-approved solutions and gentle techniques to clean your dog’s ears without injuring the tympanic membrane. - Avoid Foreign Objects:
Keep small items like grass seeds, toys, or cotton swabs away from your dog’s ears to prevent accidental injury. - Monitor for Ear Infections:
Early detection and treatment of outer ear infections prevent them from spreading to the middle ear. - Limit Exposure to Loud Noises:
Protect your dog’s hearing by avoiding prolonged exposure to high-decibel sounds like fireworks or construction noise. - Regular Veterinary Check-Ups:
Scheduled exams help identify and address potential ear issues before they escalate into serious problems.
Long-Term Effects of Tympanic Membrane Damage
- Chronic Hearing Loss:
Permanent damage to the tympanic membrane may lead to partial or complete deafness, impacting communication and quality of life. - Recurrent Ear Infections:
Scar tissue or structural changes increase susceptibility to future infections, necessitating vigilant monitoring and care. - Balance and Coordination Issues:
Damage to the middle ear affects vestibular function, potentially causing dizziness, disorientation, or difficulty walking. - Behavioral Changes:
Hearing loss or chronic pain may alter your dog’s temperament, making them more anxious or withdrawn. - Increased Veterinary Costs:
Long-term management of tympanic membrane damage involves regular check-ups, medications, and possible surgeries, adding financial strain.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Dog Tympanic Membrane
What causes a perforated tympanic membrane in dogs?
Perforations often result from chronic ear infections, trauma, or improper cleaning techniques that damage the delicate eardrum.
Can a dog’s tympanic membrane heal on its own?
Minor tears may heal naturally with time and proper care, but severe damage or infections require veterinary intervention to prevent complications.
How can I tell if my dog has a damaged tympanic membrane?
Signs include hearing loss, head shaking, ear discharge, foul odors, or behavioral changes like irritability or sensitivity around the ears.
Is surgery always needed for tympanic membrane issues?
Not always—mild cases respond well to medications, but severe damage or recurring infections may necessitate surgical repair.
Can loud noises damage a dog’s tympanic membrane?
Yes, prolonged exposure to extremely loud sounds can harm the eardrum, leading to temporary or permanent hearing loss.
Protecting Your Dog’s Ears for a Lifetime of Health
Pemphigus Erythematosus in Cats: Best 7 Expert Tips! – Learn to recognize symptoms, manage flare-ups, and improve your cat’s quality of life.
Pemphigus Erythematosus in Dogs: Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover causes, symptoms, and treatment options to manage this autoimmune skin condition effectively.
Cat Tympanic Membrane: Best 7 Expert Tips! – Learn how to protect your cat’s eardrum, spot issues early, and ensure lifelong auditory health.
Dog Tympanic Membrane: Best 7 Expert Tips! – Learn how to protect your dog’s eardrum, spot issues early, and ensure lifelong ear health with expert advice.