Cat Mange Symptoms: What Every Cat Owner Should Know
Mange is a skin condition caused by parasitic mites that can affect cats of all ages and breeds. While mange is less common in cats than in dogs, it can still pose serious health risks if left untreated. Recognizing the symptoms early is crucial to ensuring your feline friend receives prompt care and relief. From excessive scratching to patchy fur, mange manifests in various ways, making it essential for cat owners to stay informed. In this guide, we’ll explore the signs of mange, how it affects cats, and what steps you can take to address this uncomfortable condition.
Common Symptoms of Cat Mange
Identifying mange symptoms in cats can be challenging, as they often mimic other skin conditions. However, understanding the key signs can help you seek veterinary care sooner rather than later.
Excessive Scratching or Licking:
Cats with mange often scratch or lick their skin excessively in an attempt to relieve itching caused by mites.Hair Loss or Bald Patches:
Patchy fur or bald spots, especially around the ears, face, or legs, are common indicators of mange infestation.Red, Irritated Skin:
Mange can cause redness, inflammation, and sores due to constant scratching and irritation from mites.Thickened or Crusty Skin:
Infected areas may develop scabs, crusts, or thickened skin as the condition progresses.Behavioral Changes:
Cats may become irritable, lethargic, or withdrawn due to discomfort and stress caused by mange.
Recognizing these symptoms early allows you to intervene promptly, reducing your cat’s suffering and preventing further complications.
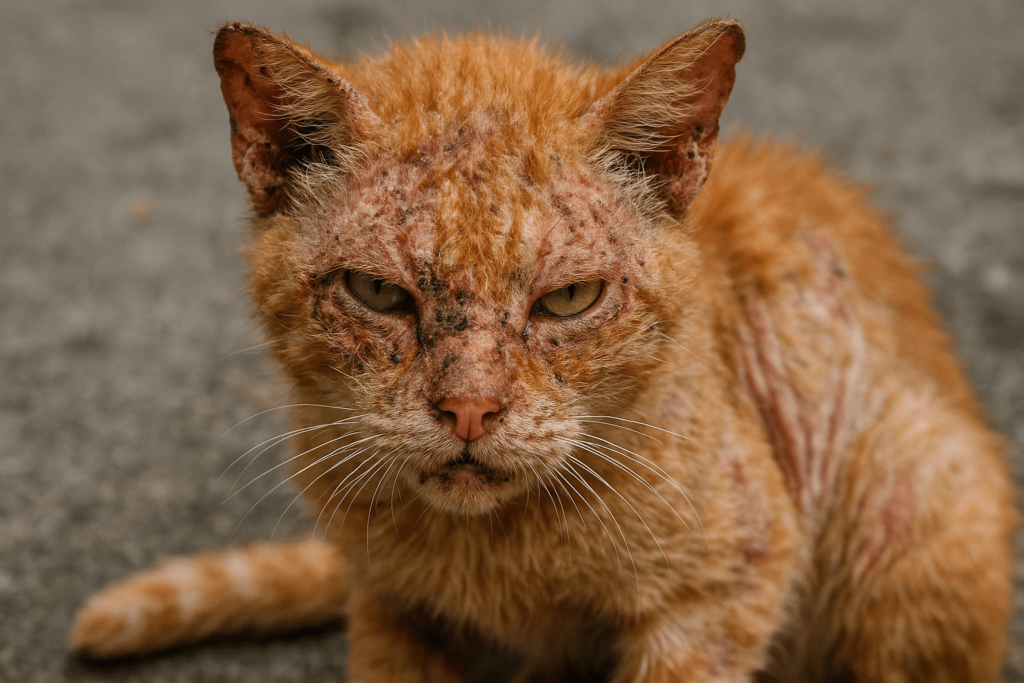

Types of Mange in Cats and Their Characteristics
There are several types of mange that can affect cats, each caused by different mites and presenting unique symptoms. Understanding these variations helps ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Notoedric Mange (Feline Scabies):
Caused by Notoedres cati, this highly contagious form of mange leads to intense itching and crusting, primarily on the head and neck.Demodectic Mange:
Triggered by Demodex cati mites, this type is less common and typically affects cats with weakened immune systems. Symptoms include localized hair loss and mild irritation.Otodectic Mange (Ear Mites):
Ear mites (Otodectes cynotis) cause itching, head shaking, and dark, waxy discharge inside the ears.Sarcoptic Mange (Rare in Cats):
Though uncommon, sarcoptic mange (Sarcoptes scabiei) can occur in cats, causing severe itching and widespread skin lesions.Cheyletiellosis (Walking Dandruff):
Caused by Cheyletiella mites, this condition results in flaky skin that appears to “move” due to mite activity.
Each type of mange requires specific treatment, underscoring the importance of consulting a veterinarian for proper diagnosis and care.
Check this guide 👉Understanding Cat Skin Cancer: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉Understanding Cat Skin Conditions: Best 7 Health Tips!
Check this guide 👉Cat Dry Skin Treatment: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Symptoms of Cat Mange | Possible Causes |
|---|---|
Excessive scratching or licking | Mite infestations irritating the skin |
Hair loss or bald patches | Mites damaging hair follicles |
Red, inflamed skin | Allergic reactions to mite bites |
Thickened or crusty skin | Secondary infections from scratching |
Behavioral changes like irritability | Discomfort and stress from mange |
How to Prevent Mange in Cats
Preventing mange involves maintaining good hygiene and minimizing exposure to mites. These proactive measures can help protect your cat from this uncomfortable condition.
Regular Grooming:
Brushing your cat’s fur regularly removes dirt, debris, and potential parasites, reducing the risk of mange.Clean Living Environment:
Wash bedding, toys, and litter boxes frequently to eliminate mites and other contaminants.Avoid Contact with Infected Animals:
Keep your cat away from stray animals or pets showing signs of mange to prevent transmission.Veterinary Check-Ups:
Schedule routine vet visits to monitor your cat’s skin and overall health, catching issues early.Strengthen Your Cat’s Immune System:
Provide a balanced diet and reduce stress to support your cat’s natural defenses against mites.
By taking these preventive steps, you can significantly lower your cat’s risk of developing mange.
Treating Cat Mange Effectively
Once diagnosed, treating mange requires a combination of veterinary guidance and at-home care. These strategies can help restore your cat’s comfort and health.
Topical Treatments:
Medicated shampoos, ointments, or spot-on treatments kill mites and soothe irritated skin.Oral Medications:
Prescription medications target mites internally, providing faster relief for severe cases.Anti-Parasitic Injections:
Veterinarians may administer injections to eliminate mites and reduce symptoms quickly.Environmental Cleaning:
Thoroughly clean your home to remove mites and prevent reinfestation after treatment begins.Follow-Up Care:
Monitor your cat’s progress and attend follow-up appointments to ensure complete recovery.
With timely intervention and proper care, mange can be successfully treated, restoring your cat’s well-being.
Common Misconceptions About Cat Mange
Misinformation about mange can lead to confusion and delayed treatment. Clearing up these misconceptions helps cat owners make informed decisions.
Myth: Mange Only Affects Dirty Cats:
Mange can affect any cat, regardless of cleanliness, though poor hygiene may increase the risk.Myth: All Mange Is Highly Contagious:
While some types are contagious, others, like demodectic mange, are not easily transmitted.Myth: Over-the-Counter Products Cure Mange:
Many over-the-counter treatments are ineffective against mange and may worsen the condition.Myth: Mange Always Causes Severe Symptoms:
Mild cases of mange may present subtle signs, making them harder to detect without professional help.Myth: Indoor Cats Can’t Get Mange:
Indoor cats can still contract mange through contact with contaminated objects or visiting animals.
Understanding the truth behind these myths ensures better prevention and treatment outcomes.
Signs That Your Cat’s Mange Is Improving
Monitoring your cat’s recovery is essential to gauge the effectiveness of treatment. Look for these positive signs indicating improvement.
Reduced Scratching:
A decrease in scratching or licking suggests that the mites are being eradicated.New Hair Growth:
Regrowth of fur in previously bald areas indicates healing and recovery.Clearer Skin:
Redness, scabs, and crusts should gradually fade as the skin heals.Improved Mood:
As discomfort subsides, your cat will likely become more playful and relaxed.No New Lesions:
The absence of new irritated areas signals that the treatment is working effectively.
Tracking these improvements reassures you that your cat is on the path to full recovery.
Supporting Your Cat During Mange Treatment
Caring for a cat with mange involves more than just medical treatment—it requires emotional support and environmental adjustments. These tips can enhance your cat’s recovery experience.
Provide Comfortable Resting Areas:
Soft bedding and quiet spaces help your cat rest and heal without additional stress.Offer Nutritious Food:
A high-quality diet supports immune function and promotes faster healing of the skin.Minimize Stressors:
Reduce noise and disruptions in the home to create a calming atmosphere for your cat.Use Gentle Handling:
Be cautious when touching affected areas to avoid causing further discomfort or pain.Reward Positive Behavior:
Encourage cooperation during treatment by rewarding your cat with treats or affection.
By combining medical care with compassionate support, you can help your cat recover fully and comfortably.
Frequently Asked Questions About Cat Mange
Can humans catch mange from cats?
Some types of mange, like notoedric mange, can temporarily affect humans but usually resolve on their own.
Is mange contagious between pets?
Yes, mange is highly contagious, especially among cats and dogs sharing close quarters.
How long does it take to treat mange?
Treatment typically lasts several weeks, depending on the severity and type of mange.
Can mange recur after treatment?
Recurrence is possible if preventative measures aren’t taken, such as maintaining cleanliness and monitoring your cat’s health.
What should I do if I suspect my cat has mange?
Contact your veterinarian immediately for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Prioritizing Your Cat’s Skin Health
Mange is a distressing condition for both cats and their owners, but with vigilance and proper care, it can be managed and cured. By recognizing the symptoms, understanding the types of mange, and following preventive measures, you can safeguard your cat’s skin health and overall well-being. Early detection and veterinary intervention are key to ensuring your feline companion remains happy, healthy, and free from discomfort. Remember, a little attention and care go a long way in keeping your furry friend thriving.
How Do I Know If My Cat Died Peacefully? Best 7 Expert Tips! Discover the quiet signs of a peaceful feline passing and find comfort in their final moments.
How Do I Know If My Cat Died Peacefully? A Gentle Guide for Heartbroken Owners Losing a cat is not just …
Why Do Abyssinian Cat Colors Matter? Best 7 Expert Tips! Discover the genetics, rare hues, and care secrets behind Abyssinian coat colors for a healthier, happier cat.
Cat Enrichment Activities: Best 7 Expert Tips! Unlock your cat’s natural instincts with proven strategies for mental stimulation, physical health, and lasting happiness.