Glaucoma in Cats: What Every Cat Owner Should Know
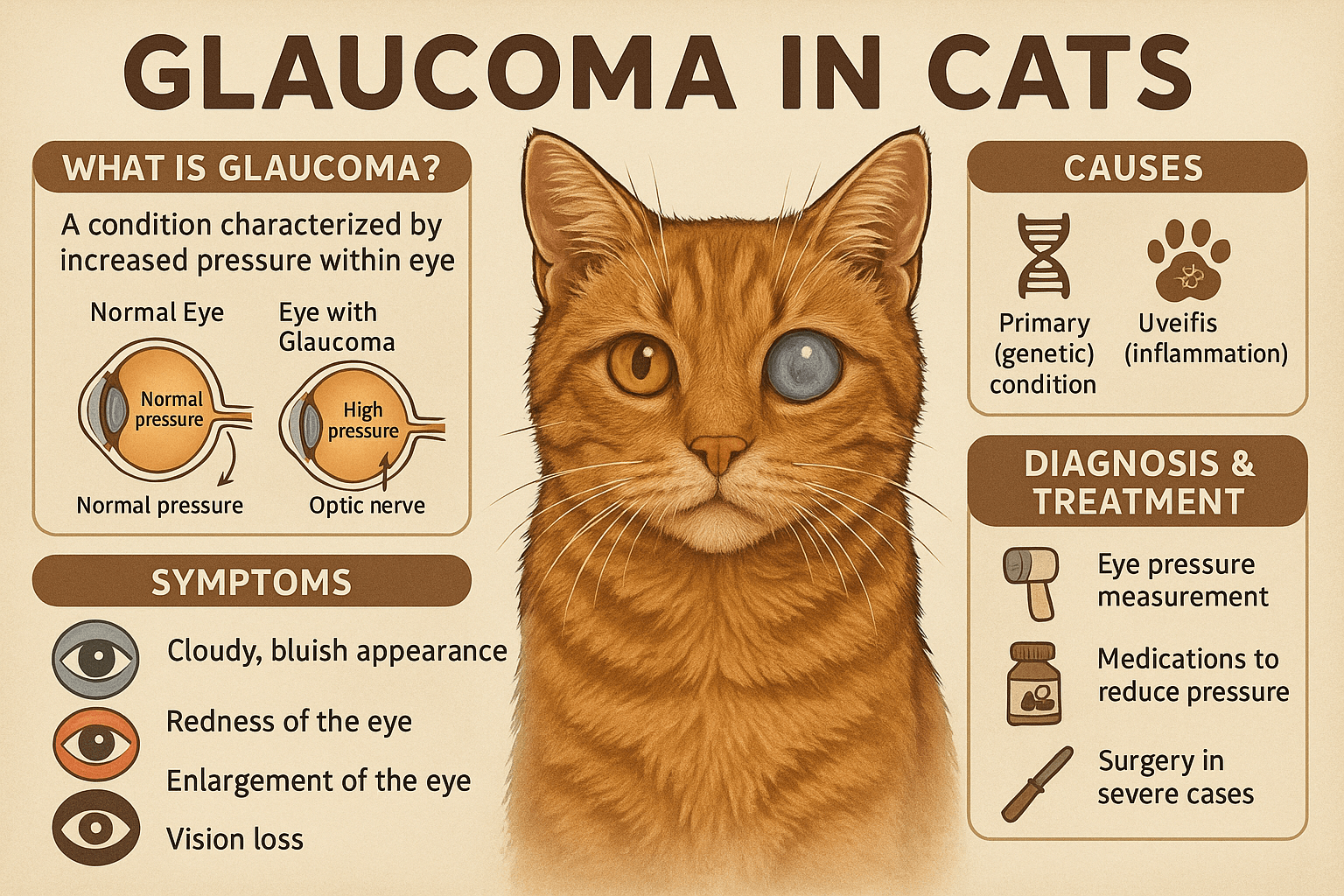
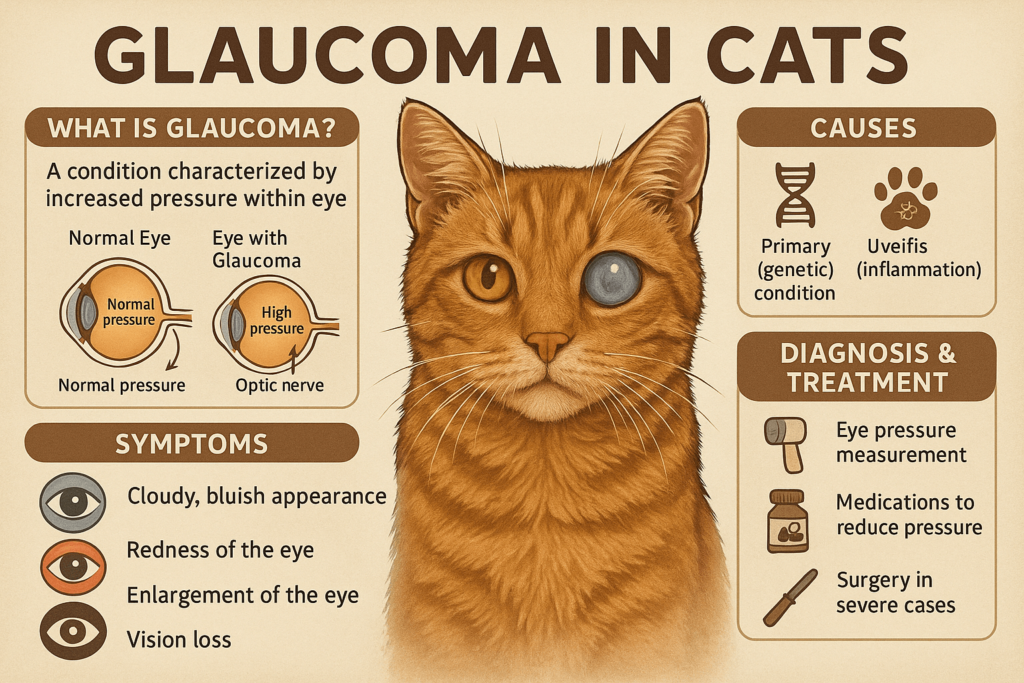
Glaucoma in cats is a serious eye condition that can lead to vision loss if left untreated. It occurs when there is an abnormal increase in pressure within the eye, known as intraocular pressure (IOP). While glaucoma is less common in cats than in dogs, it remains a significant health concern for feline companions. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for early detection and management. In this blog post, we’ll explore everything you need to know about glaucoma in cats, from recognizing warning signs to providing the best care for your furry friend.
Signs and Symptoms of Glaucoma in Cats
Detecting glaucoma early is essential for preventing irreversible damage to your cat’s eyesight. Keep an eye out for these common symptoms, which may indicate a problem with your cat’s ocular health.
Cloudy or Bluish Eye Appearance:
A noticeable change in the clarity or color of your cat’s eye could signal elevated intraocular pressure.Redness or Inflammation:
Bloodshot eyes or visible irritation around the eye may suggest discomfort or an underlying issue.Squinting or Excessive Blinking:
If your cat frequently squints or blinks excessively, they may be experiencing pain or sensitivity.Dilated Pupils:
Pupils that remain unusually large even in normal lighting conditions can be a sign of glaucoma.Vision Loss or Disorientation:
Cats with advanced glaucoma may bump into objects or appear confused due to reduced eyesight.
Recognizing these symptoms early allows for prompt veterinary intervention, improving the chances of preserving your cat’s vision.
Causes and Risk Factors for Feline Glaucoma
While glaucoma can affect any cat, certain factors increase the likelihood of its development. Understanding these causes helps cat owners take preventive measures and seek timely treatment.
Primary Glaucoma (Genetic Predisposition):
Some cats are born with structural abnormalities in their eyes, making them more prone to developing glaucoma.Secondary Glaucoma (Underlying Conditions):
Diseases like uveitis, lens luxation, or tumors can block drainage pathways, leading to increased eye pressure.Age and Breed Susceptibility:
Older cats and certain breeds, such as Siamese or Burmese, are at higher risk of developing glaucoma.Trauma or Injury to the Eye:
Physical damage to the eye can disrupt fluid drainage, resulting in elevated intraocular pressure.Systemic Health Issues:
Conditions like diabetes or hypertension may indirectly contribute to glaucoma by affecting eye health.
By identifying potential risk factors, cat owners can work closely with veterinarians to monitor and manage their pet’s ocular well-being.
Check this guide 👉Understanding Cat Eye Cataracts: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉How to Clean a Cat Eye Infection: Best 7 Health Tips!
Check this guide 👉Understanding Cat Eye Mucus: Best 7 Health Tips!
Preventive Measures for Glaucoma | Treatment Options for Glaucoma |
|---|---|
Regular veterinary eye exams | Medications to reduce intraocular pressure |
Monitoring high-risk breeds | Surgical interventions to improve drainage |
Managing underlying health conditions | Pain management for affected eyes |
Protecting eyes from injuries | Laser therapy for advanced cases |
Early detection of symptoms | Enucleation (eye removal) in severe cases |
How Glaucoma Is Diagnosed in Cats
Diagnosing glaucoma requires a thorough evaluation by a veterinarian. Understanding the diagnostic process ensures your cat receives accurate and timely care.
Tonometry Testing:
This non-invasive procedure measures intraocular pressure using specialized instruments to detect elevated levels.Ophthalmoscopic Examination:
A detailed inspection of the eye’s interior helps identify structural abnormalities or signs of damage.Slit-Lamp Biomicroscopy:
This technique provides a magnified view of the eye, allowing vets to assess corneal health and fluid drainage.Gonioscopy:
Used to examine the drainage angle of the eye, gonioscopy determines whether glaucoma is primary or secondary.Blood Tests and Imaging:
Additional diagnostics may be performed to rule out systemic diseases contributing to glaucoma.
Accurate diagnosis is the first step toward effective treatment, ensuring your cat’s comfort and quality of life.
Caring for a Cat with Glaucoma
Managing glaucoma in cats requires ongoing care and attention. These tips can help you support your feline companion and minimize discomfort.
Administer Medications as Directed:
Follow your vet’s instructions carefully when applying eye drops or oral medications to control intraocular pressure.Create a Safe Environment:
Remove obstacles and hazards to prevent accidents, especially if your cat has impaired vision.Schedule Regular Vet Visits:
Frequent check-ups allow your veterinarian to monitor your cat’s condition and adjust treatment plans as needed.Provide Comfort and Reassurance:
Offer extra affection and gentle handling to help your cat feel secure during this challenging time.Consider Lifestyle Adjustments:
Modify your home environment to accommodate any changes in your cat’s mobility or behavior due to vision loss.
With proper care and compassion, you can ensure your cat lives comfortably despite their condition.
Complications of Untreated Glaucoma
If left untreated, glaucoma can lead to severe complications that impact your cat’s overall well-being. Recognizing these risks underscores the importance of early intervention.
Permanent Vision Loss:
Prolonged elevated intraocular pressure damages the optic nerve, leading to irreversible blindness.Chronic Pain and Discomfort:
Untreated glaucoma often results in persistent pain, affecting your cat’s behavior and mood.Corneal Ulcers:
Increased eye pressure can cause corneal damage, increasing the risk of ulcers and infections.Shrinkage of the Eye (Phthisis Bulbi):
Advanced glaucoma may cause the affected eye to shrink and lose functionality entirely.Impact on Quality of Life:
Without treatment, glaucoma significantly diminishes your cat’s ability to enjoy daily activities.
Addressing glaucoma promptly minimizes these risks and preserves your cat’s comfort and happiness.
Breeds Most Prone to Glaucoma
Certain cat breeds are genetically predisposed to glaucoma, making them more susceptible to this condition. Owners of these breeds should remain vigilant about their pets’ eye health.
Siamese Cats:
Known for their striking blue eyes, Siamese cats are at higher risk due to inherited anatomical traits.Burmese Cats:
Burmese cats often experience structural issues in the eye drainage system, contributing to glaucoma.Persian Cats:
Their flat facial structure can lead to drainage problems, increasing the likelihood of glaucoma.Maine Coons:
Larger breeds like Maine Coons may face genetic predispositions to ocular conditions, including glaucoma.Abyssinians:
Abyssinians are prone to various eye disorders, making regular screenings essential for early detection.
Understanding breed-specific risks allows owners to take proactive steps in monitoring and managing their cat’s health.
Emotional Support for Owners
Caring for a cat with glaucoma can be emotionally challenging for pet owners. These strategies can help you cope and stay positive throughout the journey.
Educate Yourself About the Condition:
Learning about glaucoma empowers you to make informed decisions and reduces feelings of helplessness.Seek Support from Veterinary Professionals:
Rely on your vet’s expertise and guidance to navigate treatment options and manage expectations.Connect with Other Pet Owners:
Join online forums or local groups where you can share experiences and advice with others facing similar challenges.Celebrate Small Victories:
Acknowledge milestones, such as successful treatments or improved comfort, to maintain a positive outlook.Focus on Strengthening Your Bond:
Spend quality time with your cat, reinforcing your connection and reminding yourself why their care matters so deeply.
By prioritizing emotional well-being, you can better support your cat while nurturing your own resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions About Glaucoma in Cats
Can glaucoma in cats be cured?
Unfortunately, glaucoma cannot be cured, but early treatment can slow its progression and preserve vision.
Is glaucoma painful for cats?
Yes, glaucoma can cause significant discomfort or pain, particularly as intraocular pressure increases.
How quickly does glaucoma progress in cats?
Progression varies depending on the type and severity of glaucoma; some cases worsen rapidly, while others develop slowly.
What should I do if I suspect my cat has glaucoma?
Contact your veterinarian immediately for a thorough examination and appropriate testing.
Can diet or supplements help prevent glaucoma?
While no specific diet prevents glaucoma, maintaining overall health supports optimal eye function.
Prioritizing Your Cat’s Eye Health
Glaucoma in cats is a complex and potentially devastating condition, but awareness and vigilance can make all the difference. By understanding the symptoms, seeking timely veterinary care, and committing to ongoing management, you can provide your cat with the best possible quality of life. Remember, your feline friend relies on you to advocate for their health—regular check-ups and attentive care are key to protecting their precious vision. With love and dedication, you can navigate the challenges of glaucoma together and ensure your cat continues to thrive.
Cerenia Cat Side Effects: Best 7 Expert Tips! Discover expert advice on managing Cerenia side effects, ensuring your cat’s safety, and promoting a smooth recovery with practical tips.
Why Is My Cats Nose Dry? Best 7 Expert Tips! Discover expert advice on causes of dry cat noses, signs of concern, and how to keep your feline healthy and comfortable.
Can Cats Eat Raw Meat? Best 7 Expert Tips! Discover the benefits, risks, and expert advice on feeding raw meat to cats safely and nutritiously.
Cat Spraying vs. Peeing: Best 7 Expert Tips! Learn to identify the differences, understand causes, and stop unwanted behaviors with proven strategies for a cleaner, stress-free home.