Understanding Dry Eye in Dogs
Dry eye, also known as keratoconjunctivitis sicca (KCS), is a common yet often misunderstood condition that affects many dogs. This condition occurs when the tear glands fail to produce enough tears to keep the eyes properly lubricated, leading to discomfort and potential damage to the cornea. While dry eye can affect any breed, certain dogs are more predisposed to developing this issue. Recognizing the symptoms early and seeking appropriate treatment is crucial for maintaining your dog’s eye health and overall well-being. In this blog post, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and management of dry eye in dogs to help you better care for your furry companion.
Common Symptoms of Dry Eye in Dogs
Identifying dry eye in its early stages can make a significant difference in your dog’s quality of life. Here are some telltale signs to watch for if you suspect your dog may be suffering from this condition.
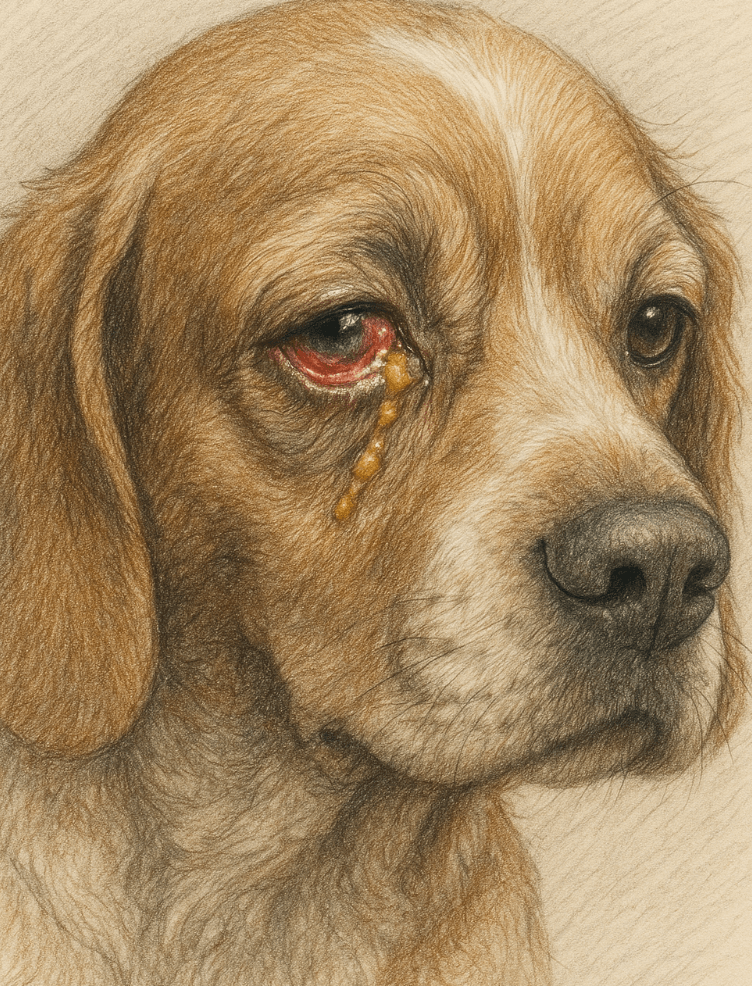
Red or Inflamed Eyes:
The lack of tears can cause irritation, leading to redness and inflammation around the eyes.Excessive Blinking or Squinting:
Dogs with dry eye often blink frequently or squint due to discomfort caused by insufficient lubrication.Thick, Yellowish Discharge:
A noticeable increase in mucus-like discharge is a common symptom of dry eye, often mistaken for an infection.Cloudy or Dull Appearance of the Eyes:
Without proper tear production, the cornea can become cloudy, giving the eyes a dull or hazy look.Sensitivity to Light:
Dogs with dry eye may avoid bright lights or appear uncomfortable in well-lit environments.
Recognizing these symptoms early allows you to seek veterinary care promptly, preventing further complications and ensuring your dog’s comfort.
Causes of Dry Eye in Dogs
Dry eye in dogs can stem from a variety of factors, ranging from genetic predispositions to environmental influences. Understanding the underlying causes can help you take preventive measures and manage the condition effectively.
Autoimmune Disorders:
The immune system mistakenly attacks the tear glands, reducing tear production—a leading cause of dry eye in dogs.Breed Predisposition:
Certain breeds, such as Bulldogs, Shih Tzus, and Cocker Spaniels, are genetically more prone to developing dry eye.Medications or Treatments:
Some medications, particularly those affecting the immune system, can lead to reduced tear production as a side effect.Infections or Trauma:
Eye infections or injuries can damage the tear glands, resulting in chronic dry eye.Age-Related Changes:
Older dogs are more susceptible to dry eye due to the natural decline in gland function over time.
By identifying the root cause of dry eye, veterinarians can tailor treatment plans to address your dog’s specific needs and improve their quality of life.
Check this guide 👉Dog Eye Injury Treatment: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉Dog Eye Blood Vessel Burst: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉Dog Eye Watering: Best 7 Expert Tips!

Preventive Measures for Dry Eye | Treatment Options for Dry Eye |
|---|---|
Regular eye check-ups with the vet | Artificial tear drops or ointments |
Avoiding exposure to irritants like smoke | Anti-inflammatory medications |
Providing a balanced diet rich in omega-3 | Immunosuppressive drugs like cyclosporine |
Keeping the eyes clean and debris-free | Surgical intervention in severe cases |
Monitoring high-risk breeds closely | Regular follow-ups to monitor progress |
How to Manage Dry Eye at Home
While professional veterinary care is essential, there are several steps you can take at home to support your dog’s eye health and manage dry eye effectively.
Administer Prescribed Medications:
Follow your vet’s instructions carefully when applying eye drops or ointments to ensure consistent treatment.Clean the Eyes Daily:
Gently wipe away any discharge or debris using a soft, damp cloth to prevent further irritation.Use a Humidifier:
Adding moisture to your home environment can help reduce eye dryness, especially during winter months.Avoid Irritants:
Keep your dog away from smoke, strong winds, and other environmental factors that can exacerbate dry eye symptoms.Monitor Progress Regularly:
Track changes in your dog’s eye condition and report any concerns to your veterinarian promptly.
With proper care and attention, you can help your dog live comfortably despite their dry eye diagnosis.
When to Seek Veterinary Care for Dry Eye
While some symptoms of dry eye can be managed at home, certain situations require immediate veterinary attention to prevent complications.
Persistent Redness or Swelling:
If your dog’s eyes remain red and swollen despite treatment, it could indicate an underlying issue that needs addressing.Corneal Ulcers:
A cloudy or damaged cornea may signal the presence of ulcers, which require urgent medical intervention.Severe Pain or Discomfort:
Excessive pawing at the eyes or vocalizations of pain should never be ignored and warrant a vet visit.Vision Impairment:
Any signs of vision loss or difficulty navigating spaces should be evaluated immediately to rule out permanent damage.Unresponsive to Treatment:
If your dog’s condition does not improve with prescribed medications, consult your vet for alternative solutions.
Timely veterinary care ensures that your dog receives the necessary treatment to prevent long-term damage and maintain their quality of life.
Tips for Preventing Dry Eye in High-Risk Breeds
If your dog belongs to a breed predisposed to dry eye, taking preventive measures can significantly reduce their risk of developing the condition.
Schedule Routine Eye Exams:
Regular check-ups allow your vet to catch early signs of dry eye before it progresses.Provide Omega-3 Supplements:
Omega-3 fatty acids support tear production and reduce inflammation, promoting healthier eyes.Minimize Exposure to Allergens:
Pollen, dust, and other allergens can irritate the eyes, increasing the likelihood of dry eye.Encourage Proper Hydration:
Ensuring your dog drinks enough water supports overall eye health and tear production.Watch for Early Warning Signs:
Be alert to subtle changes in your dog’s eyes, such as redness or increased blinking, and act quickly.
Proactive prevention can make a world of difference for high-risk breeds.
Alternative Therapies for Managing Dry Eye
In addition to conventional treatments, some pet owners explore alternative therapies to complement their dog’s dry eye management plan.
Acupuncture:
Acupuncture may help stimulate tear production and reduce inflammation in some dogs.Herbal Remedies:
Certain herbs, like chamomile or calendula, have anti-inflammatory properties that can soothe irritated eyes.Warm Compresses:
Applying a warm, damp cloth to the eyes can provide temporary relief and loosen dried discharge.Massage Techniques:
Gentle massage around the tear glands may encourage improved tear flow in some cases.Dietary Adjustments:
Incorporating whole foods rich in antioxidants and vitamins can boost eye health naturally.
Always consult your vet before trying alternative therapies to ensure they’re safe for your dog.
The Emotional Impact of Dry Eye on Dogs
Dry eye doesn’t just affect your dog physically—it can also influence their emotional well-being. Understanding these effects helps you provide holistic care for your pet.
Increased Anxiety:
Chronic discomfort from dry eye can make dogs more anxious or irritable than usual.Reduced Playfulness:
Pain or vision issues may lead to decreased interest in activities they once enjoyed.Dependence on Owners:
Dogs with impaired vision may rely more heavily on their owners for guidance and reassurance.Behavioral Changes:
Frustration or stress from dry eye symptoms can manifest as unusual behaviors, such as excessive licking or whining.Strengthened Bond Through Care:
Providing attentive care and comfort fosters trust and deepens the bond between you and your dog.
Addressing both the physical and emotional aspects of dry eye ensures your dog feels supported and loved throughout their journey.
Frequently Asked Questions About Dry Eye in Dogs
What is dry eye in dogs?
Dry eye, or keratoconjunctivitis sicca (KCS), occurs when a dog’s tear glands fail to produce enough tears, leading to eye irritation and potential damage.
Can dry eye be cured?
While there is no definitive cure, most cases can be managed effectively with medications and lifestyle adjustments.
Is dry eye painful for dogs?
Yes, dry eye can cause significant discomfort, including irritation, itching, and sensitivity to light.
How is dry eye diagnosed?
Veterinarians use a Schirmer tear test to measure tear production and confirm a dry eye diagnosis.
Can diet help with dry eye?
A diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids can support eye health and reduce inflammation, though it should complement—not replace—medical treatment.
Prioritizing Your Dog’s Eye Health
Dry eye in dogs is a manageable condition when detected early and treated appropriately. By staying vigilant about symptoms, following your veterinarian’s guidance, and implementing preventive measures, you can ensure your dog enjoys a comfortable and happy life. Remember, your dog relies on you to advocate for their health—so don’t hesitate to seek professional advice if you notice any concerning changes in their eyes. With love, care, and proactive management, you can help your furry friend thrive despite the challenges of dry eye.
Rimadyl for Dogs: Best 7 Expert Tips! Discover expert advice on using Rimadyl safely, managing pain, and improving your dog’s mobility with trusted veterinary insights.
Can Dogs Have Tylenol for Pain? Best 7 Expert Tips! Discover the risks, safe alternatives, and expert advice on managing your dog’s pain effectively while avoiding harmful medications.
Understanding Hemophilia in Dogs: Best 7 Expert Tips! Discover expert advice on managing hemophilia, recognizing symptoms, and ensuring your dog’s well-being with practical care strategies.
Understanding Dog Sensitive Skin: Best 7 Expert Tips! Discover expert advice on managing dog sensitive skin, relieving irritation, and improving your pup’s comfort with practical solutions.