Luxated Lens in Dogs: What Every Pet Owner Needs to Know
A luxated lens, also known as a dislocated lens, is a serious eye condition that can affect dogs of all breeds and ages. This occurs when the lens of the eye shifts out of its normal position, potentially leading to vision problems or even blindness if left untreated. While some dogs are genetically predisposed to this condition, others may develop it due to trauma or underlying health issues. Recognizing the signs early and seeking prompt veterinary care is crucial for preserving your dog’s vision and overall quality of life. In this blog post, we’ll explore everything you need to know about a luxated lens in dogs, from causes and symptoms to treatment options and prevention strategies.
Expert Insight on Lens Luxation
“Lens luxation either can be the primary problem in the eye (called primary lens luxation), or it may occur secondary to another condition inside the eye (called secondary lens luxation).
The lens can either fall forward or backward out of its normal position. When the lens falls forward, it is called anterior luxation. When it falls backward, it is called posterior luxation.”
Common Causes of a Luxated Lens in Dogs
Understanding the causes of a luxated lens can help pet owners take proactive steps to prevent or manage this condition. Here are some of the most common factors that contribute to lens dislocation in dogs.
Genetic Predisposition:
Certain breeds, such as terriers, spaniels, and German Shepherds, are more prone to inherited conditions like lens luxation due to weak zonular fibers.Trauma or Injury:
Blunt force trauma to the eye, such as from an accident or fight, can cause the lens to shift out of place.Glaucoma:
Increased intraocular pressure associated with glaucoma can weaken the structures supporting the lens, leading to dislocation.Underlying Health Conditions:
Diseases like diabetes or Cushing’s syndrome may indirectly contribute to lens instability by affecting the eye’s structure.Age-Related Changes:
As dogs age, the ligaments holding the lens in place may weaken, increasing the risk of luxation.
Identifying the root cause of a luxated lens is essential for determining the appropriate treatment plan and preventing further complications.
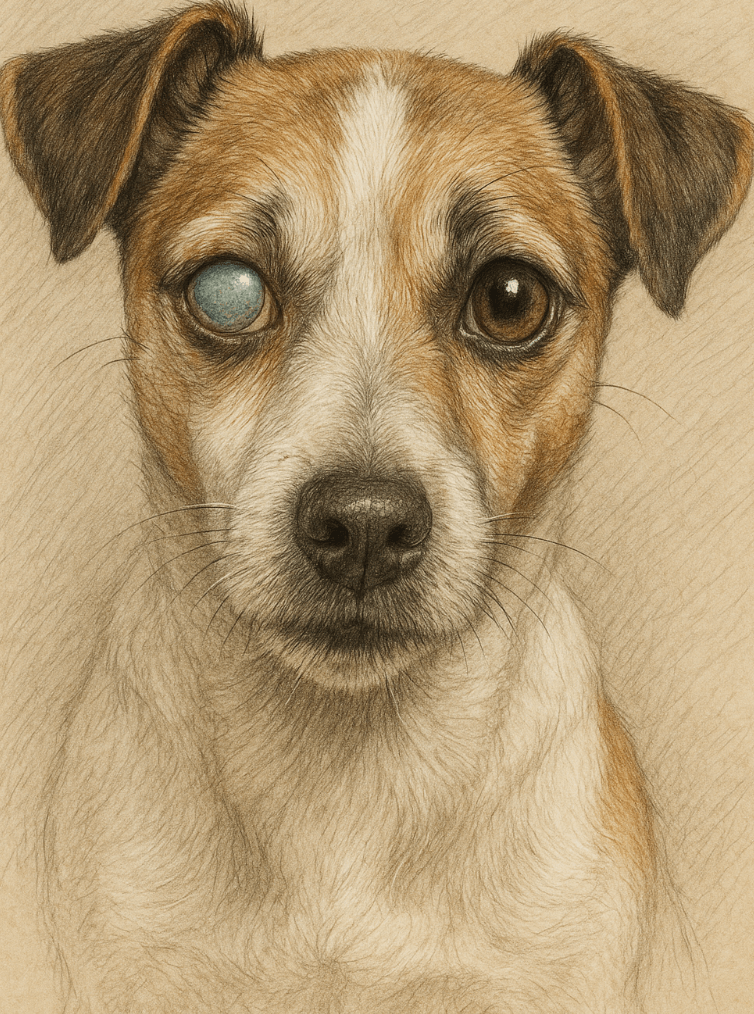

Signs and Symptoms of a Luxated Lens in Dogs
Recognizing the signs of a luxated lens early can make a significant difference in your dog’s prognosis. Keep an eye out for these common symptoms, which indicate that immediate veterinary attention may be necessary.
Visible Abnormalities in the Eye:
A dislocated lens may cause the pupil to appear irregular or cloudy compared to the unaffected eye.Squinting or Pawing at the Eye:
Dogs may squint or paw at their eyes in response to discomfort or pain caused by the displaced lens.Redness or Inflammation:
The affected eye may appear red or swollen due to irritation or secondary infections.Changes in Vision:
Sudden vision loss or difficulty navigating familiar spaces can signal a luxated lens disrupting normal eye function.Behavioral Changes:
Dogs may become lethargic, anxious, or reluctant to engage in activities they once enjoyed due to discomfort or impaired vision.
If you notice any of these symptoms, consult your veterinarian promptly to prevent further damage to your dog’s eye.
Check this guide 👉Dog Eye Injury Treatment: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉Dog Eye Blood Vessel Burst: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉Dog Eye Watering: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Treatment Options for Luxated Lens | Preventive Measures for Dog Owners |
|---|---|
Surgical removal of the lens | Regular eye exams for at-risk breeds |
Medications to reduce intraocular pressure | Avoiding activities that risk eye trauma |
Anti-inflammatory drugs for pain relief | Monitoring for early signs of glaucoma |
Corneal sutures to stabilize the lens | Managing underlying health conditions |
Enucleation (eye removal) in severe cases | Providing a safe environment for your dog |
Treatment Options for a Luxated Lens in Dogs
The treatment for a luxated lens depends on the severity of the condition and whether it is causing additional complications. Here are some common approaches veterinarians may recommend.
Medical Management:
In mild cases, medications such as anti-inflammatories or pressure-reducing drugs may help alleviate symptoms temporarily.Lens Removal Surgery:
Surgically removing the dislocated lens is often necessary to prevent further damage to the eye and restore comfort.Intraocular Lens Implants:
After lens removal, artificial lenses can sometimes be implanted to improve vision in the affected eye.Corneal Sutures:
In partial luxations, sutures may be used to reposition and stabilize the lens in its correct location.Enucleation (Eye Removal):
In severe cases where the eye is irreparably damaged, removing the eye may be the best option to relieve pain.
Each treatment option has its pros and cons, and your veterinarian will guide you toward the best choice based on your dog’s specific needs.
How to Support Your Dog After a Luxated Lens Diagnosis
Caring for a dog with a luxated lens requires patience, dedication, and ongoing support. Here are some ways you can help your furry friend adjust and thrive after diagnosis.
Follow Veterinary Instructions Carefully:
Adhere to all prescribed medications and follow-up appointments to ensure proper healing and recovery.Create a Safe Environment:
Remove obstacles and hazards in your home to prevent accidents, especially if your dog’s vision is impaired.Monitor for Complications:
Watch for signs of infection, increased pain, or worsening vision, and report them to your vet immediately.Provide Emotional Comfort:
Offer extra love and reassurance to help your dog cope with stress or anxiety related to their condition.Adjust Their Routine:
Modify activities like walks or playtime to accommodate any changes in mobility or behavior caused by vision loss.
By providing attentive care and making necessary adjustments, you can ensure your dog remains happy and comfortable despite their condition.
Tips for Preventing Lens Luxation in At-Risk Breeds
For dog owners with breeds prone to lens luxation, taking preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of this condition developing.
Schedule Regular Eye Exams:
Routine check-ups allow veterinarians to detect early signs of lens instability before it progresses.Manage Underlying Health Issues:
Conditions like diabetes or hypertension can increase the risk of lens luxation, so keeping them under control is vital.Avoid Activities That Risk Trauma:
Discourage rough play or situations where your dog’s eyes could be injured.Be Aware of Genetic Risks:
Research your dog’s breed history to understand their predisposition to eye-related conditions.Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle:
Proper nutrition and exercise support overall health, including eye function and resilience.
By implementing these strategies, you can minimize the likelihood of lens luxation in susceptible breeds.
Post-Surgical Care Tips for Dogs Recovering from Lens Removal
After surgery to treat a luxated lens, careful post-operative care is essential for ensuring a smooth recovery. Here are some tips to aid your dog’s healing process.
Administer Medications as Directed:
Follow your vet’s instructions for antibiotics, anti-inflammatories, and pain relievers to promote healing.Use an Elizabethan Collar:
Prevent your dog from scratching or rubbing their eyes by using a protective collar during recovery.Limit Physical Activity:
Restrict running, jumping, and vigorous play to avoid straining the surgical site.Keep the Eye Clean:
Gently clean around the eye area as instructed to prevent infections and irritation.Attend Follow-Up Appointments:
Regular check-ins with your vet ensure the eye is healing properly and address any concerns early.
Proper post-surgical care maximizes the chances of a successful outcome for your dog.
Alternative Ways to Support Dogs with Vision Loss
If your dog experiences vision loss due to a luxated lens, there are several ways to enhance their quality of life and adapt to their new reality.
Use Scent Markers:
Place scented items near furniture or doorways to help your dog navigate their surroundings more easily.Stick to Familiar Routines:
Maintain consistent daily routines to provide stability and reduce anxiety for your visually impaired dog.Teach Verbal Cues:
Train your dog to respond to verbal commands instead of visual signals to improve communication.Provide Mental Stimulation:
Engage your dog with scent-based games or toys that don’t rely on sight for enjoyment.Consider Mobility Aids:
Specialized harnesses or vests can assist dogs with limited vision during walks or outdoor adventures.
With creativity and compassion, you can help your dog adapt to vision loss and continue living a joyful life.
How to Support Your Dog After a Luxated Lens Diagnosis
What is a luxated lens?
A luxated lens occurs when the lens of a dog’s eye becomes dislodged from its normal position, potentially affecting vision.
Can a luxated lens be cured?
While the condition itself cannot be reversed, treatments like surgery can address the issue and preserve vision in many cases.
Is a luxated lens painful for dogs?
Yes, a luxated lens can cause significant discomfort or pain, especially if it leads to secondary complications like glaucoma.
Are certain breeds more prone to lens luxation?
Yes, breeds like terriers, spaniels, and German Shepherds have a higher genetic predisposition to this condition.
How much does treatment cost?
Treatment costs vary depending on the severity of the case and the chosen procedure, ranging from hundreds to thousands of dollars.
Prioritizing Your Dog’s Eye Health
A luxated lens is a serious but manageable condition that requires prompt attention and ongoing care. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring available treatment options, you can take proactive steps to safeguard your dog’s vision and well-being. Remember, your veterinarian is your greatest ally in navigating this challenging condition, so don’t hesitate to seek their guidance whenever needed. With proper care and compassion, you can ensure your beloved companion continues to lead a happy, fulfilling life despite this diagnosis.
Do Cats Have Taste Buds? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how cats experience flavors and why their taste is so unique.
Do Dogs Have Taste Buds? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how dogs experience taste, their preferences, and what it means for their diet and health.
Can Cats Taste Sweet? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover why cats can’t taste sweetness, how it affects their diet, and tips to keep them healthy and happy.
Can Dogs Taste Sweet? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how dogs perceive sweetness, which foods are safe, and tips to manage their sweet cravings responsibly.