Understanding Anal Gland Cancer in Dogs
Anal gland cancer, also known as anal sac adenocarcinoma, is a rare but serious condition that affects dogs. While many pet owners are familiar with the occasional discomfort caused by impacted or infected anal glands, cancer of these glands presents a more complex and potentially life-threatening challenge. This type of cancer originates in the anal sacs, small glands located on either side of a dog’s anus, which produce scent-marking fluids. Early detection and proper treatment are crucial to managing this disease effectively. In this blog post, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options for anal gland cancer in dogs, helping you become better informed and prepared to support your furry friend.
Signs and Symptoms of Anal Gland Cancer in Dogs
Recognizing the signs of anal gland cancer early can make a significant difference in your dog’s prognosis. While some symptoms may overlap with less severe conditions like anal gland infections, it’s important to consult your veterinarian if you notice any of the following:
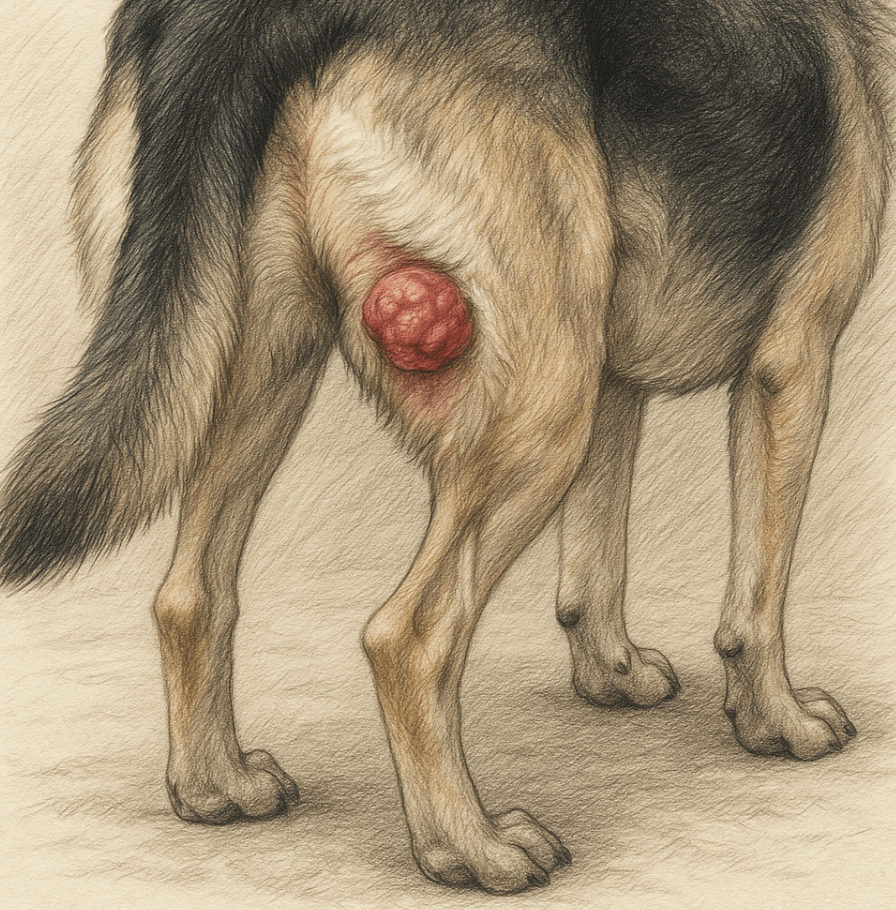
Swelling Around the Anal Area:
A noticeable lump or swelling near the anus may indicate an abnormal growth in the anal glands.Difficulty Defecating:
Tumors can press against the rectum, causing discomfort or pain during bowel movements.Blood in Stool or Around the Anus:
Bleeding may occur due to irritation or ulceration caused by the tumor.Excessive Licking or Chewing at the Rear End:
Dogs often lick or chew excessively when they experience discomfort or pain in the anal area.Changes in Behavior or Appetite:
Advanced stages of cancer may lead to lethargy, weight loss, or a decreased appetite as the disease progresses.
If your dog exhibits any of these symptoms, seeking veterinary care promptly is essential for accurate diagnosis and timely intervention.
Diagnosing Anal Gland Cancer in Dogs
Diagnosing anal gland cancer requires a thorough veterinary examination and specific tests to confirm the presence of a tumor. Understanding the diagnostic process can help you prepare for what to expect and ensure your dog receives the best care possible.
Physical Examination:
Your veterinarian will palpate the anal area to check for lumps, swelling, or abnormalities.Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA):
A small sample of cells is extracted from the tumor using a needle to determine whether it is cancerous.Biopsy:
If FNA results are inconclusive, a biopsy may be performed to analyze tissue samples under a microscope.Imaging Tests:
X-rays, ultrasounds, or CT scans help identify the size of the tumor, its location, and whether it has metastasized to other organs.Blood Work and Urinalysis:
These tests assess your dog’s overall health and detect any underlying conditions that could complicate treatment.
Accurate diagnosis is critical to developing an effective treatment plan tailored to your dog’s needs.
Check this guide 👉Dog Colon Cancer Symptoms: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉Kidney Cancer in Dogs: Best 7 Health Tips!
Check this guide 👉Dog Cancer Diet: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Treatment Options for Anal Gland Cancer | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|
Surgical Removal of the Tumor | Risk of infection, temporary incontinence |
Radiation Therapy | Skin irritation, fatigue |
Chemotherapy | Nausea, vomiting, weakened immune system |
Pain Management Medications | Drowsiness, digestive upset |
Hormonal Therapy (if applicable) | Weight gain, changes in appetite |
Treatment Options for Anal Gland Cancer in Dogs
Once diagnosed, several treatment options are available to manage anal gland cancer in dogs. The choice of treatment depends on factors such as the tumor’s size, stage, and whether it has spread.
Surgical Removal:
Surgery is often the first line of treatment, especially if the tumor is localized and hasn’t metastasized.Radiation Therapy:
Radiation can shrink tumors that cannot be fully removed surgically or target remaining cancer cells after surgery.Chemotherapy:
Used in cases where cancer has spread to other parts of the body, chemotherapy aims to slow progression and improve quality of life.Pain Management:
Controlling pain is essential to keeping your dog comfortable, especially in advanced stages of the disease.Hormonal Therapy:
In some cases, hormonal treatments may be recommended to address specific types of tumors.
Each treatment option comes with its own benefits and challenges, so working closely with your vet is key to making the best decision for your dog.
How to Support Your Dog During Treatment
Supporting your dog emotionally and physically throughout their cancer journey can significantly impact their well-being. Here are some ways to provide comfort and care during this challenging time.
Maintain a Nutritious Diet:
A balanced diet rich in protein and essential nutrients helps strengthen your dog’s immune system and aids recovery.Provide Mental Stimulation:
Engage your dog in light play or interactive activities to keep their spirits up and reduce stress.Monitor for Side Effects:
Keep an eye on your dog’s behavior and physical condition to catch any adverse reactions to treatment early.Create a Comfortable Environment:
Ensure your dog has a cozy, quiet space to rest and recover away from noise and disturbances.Offer Plenty of Affection:
Spending quality time with your dog reassures them and strengthens your bond during a difficult period.
By focusing on your dog’s emotional and physical needs, you can help them navigate treatment with greater ease and resilience.
Preventive Measures to Reduce the Risk of Anal Gland Issues
While anal gland cancer cannot always be prevented, there are steps you can take to minimize the risk of related issues and promote your dog’s overall health.
Regular Vet Check-Ups:
Routine examinations allow your vet to detect early warning signs of anal gland problems before they escalate.Proper Diet and Hydration:
A high-fiber diet promotes healthy digestion and regular bowel movements, reducing strain on the anal glands.Exercise and Weight Management:
Maintaining a healthy weight prevents excess pressure on the anal area, lowering the risk of gland complications.Monitor for Behavioral Changes:
Be alert to excessive licking, scooting, or signs of discomfort, as these may indicate anal gland issues requiring attention.Gland Expression When Necessary:
If your dog frequently experiences impacted glands, professional expression by a vet can prevent infections or abscesses.
Taking preventive measures ensures your dog stays healthy and reduces the likelihood of serious complications.
Common Misconceptions About Anal Gland Cancer
Misunderstandings about anal gland cancer can lead to unnecessary fear or delays in seeking treatment. Clearing up these misconceptions helps pet owners make informed decisions.
Myth: All Anal Gland Problems Are Cancerous:
Many anal gland issues, such as infections or impactions, are benign and treatable without surgery.Myth: Only Older Dogs Get Anal Gland Cancer:
While older dogs are at higher risk, younger dogs can also develop this type of cancer.Myth: Surgery Always Cures the Disease:
While surgery is effective for localized tumors, cancer that has spread requires additional treatments like radiation or chemotherapy.Myth: Anal Gland Cancer Is Always Fatal:
With early detection and appropriate care, many dogs can live comfortably for years after diagnosis.Myth: There Are No Symptoms Until It’s Too Late:
Early signs like swelling or difficulty defecating can alert owners to seek help before the disease progresses.
Dispelling these myths encourages proactive care and realistic expectations for treatment outcomes.
The Emotional Impact of a Cancer Diagnosis on Pet Owners
A cancer diagnosis doesn’t just affect your dog—it can also take an emotional toll on pet owners. Acknowledging these feelings and finding ways to cope is an important part of the journey.
Feelings of Guilt or Helplessness:
Many owners blame themselves for not noticing symptoms sooner, but remember that early signs can be subtle.Financial Stress:
The cost of cancer treatment can add financial strain, but payment plans or pet insurance may alleviate some burdens.Fear of Losing Your Companion:
Facing the possibility of losing a beloved pet is heart-wrenching, but cherishing each moment together can bring comfort.Seeking Support from Others:
Connecting with online communities or local groups of pet owners facing similar challenges can provide encouragement.Celebrating Small Victories:
Focus on milestones, such as successful treatments or happy days, to maintain hope and positivity throughout the process.
Acknowledging your emotions and seeking support can help you navigate this difficult chapter with strength and resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions About Anal Gland Cancer in Dogs
What causes anal gland cancer in dogs?
The exact cause is unknown, but genetics, age, and breed predisposition may play a role.
Is anal gland cancer curable?
Early-stage tumors can often be cured with surgery, but advanced cases require ongoing management.
Which breeds are most at risk?
Certain breeds, such as Cocker Spaniels and German Shepherds, have a higher incidence of anal gland cancer.
Can anal gland cancer spread to other organs?
Yes, cancer can metastasize to nearby lymph nodes or distant organs like the lungs or liver.
How long can a dog live with anal gland cancer?
Prognosis varies depending on the stage of cancer and treatment success, but early intervention improves survival rates.
Empowering Yourself to Help Your Dog Through Anal Gland Cancer
While a diagnosis of anal gland cancer in dogs can feel overwhelming, understanding the disease and exploring available treatment options empowers you to take action. With advancements in veterinary medicine and a proactive approach to care, many dogs can enjoy a good quality of life despite their diagnosis. By staying vigilant, advocating for your dog’s needs, and providing unwavering love and support, you can make a meaningful difference in their journey. Remember, you’re not alone—your veterinarian and support networks are here to guide you every step of the way.
Do Cats Have Taste Buds? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how cats experience flavors and why their taste is so unique.
Do Dogs Have Taste Buds? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how dogs experience taste, their preferences, and what it means for their diet and health.
Can Cats Taste Sweet? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover why cats can’t taste sweetness, how it affects their diet, and tips to keep them healthy and happy.
Can Dogs Taste Sweet? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how dogs perceive sweetness, which foods are safe, and tips to manage their sweet cravings responsibly.