Types of Dog Tumors: Understanding the Risks and Symptoms
Tumors in dogs are a common concern for pet owners, especially as their furry companions age. While some tumors are benign and pose little threat, others can be malignant and require immediate attention. Understanding the different types of dog tumors, their symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for ensuring your dog’s health and well-being. This blog post will guide you through the most common types of tumors, how to identify them, and what steps to take if you suspect your dog may have one. With early detection and proper care, many tumors can be managed effectively, giving your dog a better quality of life.
Common Types of Benign Tumors in Dogs
Benign tumors are non-cancerous growths that typically do not spread to other parts of the body. While they are generally less concerning than malignant tumors, they can still cause discomfort or complications if left untreated. Here are some of the most common benign tumors found in dogs.
Lipomas:
These soft, fatty lumps are often found under the skin and are usually harmless unless they grow large enough to interfere with movement.Papillomas (Warts):
Caused by the papillomavirus, these small, cauliflower-like growths are common on the skin or inside the mouth, especially in younger dogs.Sebaceous Adenomas:
These small, wart-like growths originate from oil glands in the skin and are typically found on older dogs.Histiocytomas:
Common in younger dogs, these round, raised tumors often appear on the head, ears, or limbs but usually resolve on their own.Perianal Adenomas:
Found near the anus, these tumors are more common in intact male dogs and are typically benign but should be monitored.
While benign tumors are rarely life-threatening, it’s important to have them evaluated by a veterinarian to rule out malignancy or complications.
Common Types of Malignant Tumors in Dogs
Malignant tumors, or cancers, are more serious and can spread to other parts of the body if not treated promptly. Early detection and intervention are key to improving outcomes for dogs with cancer. Below are some of the most common malignant tumors seen in dogs.
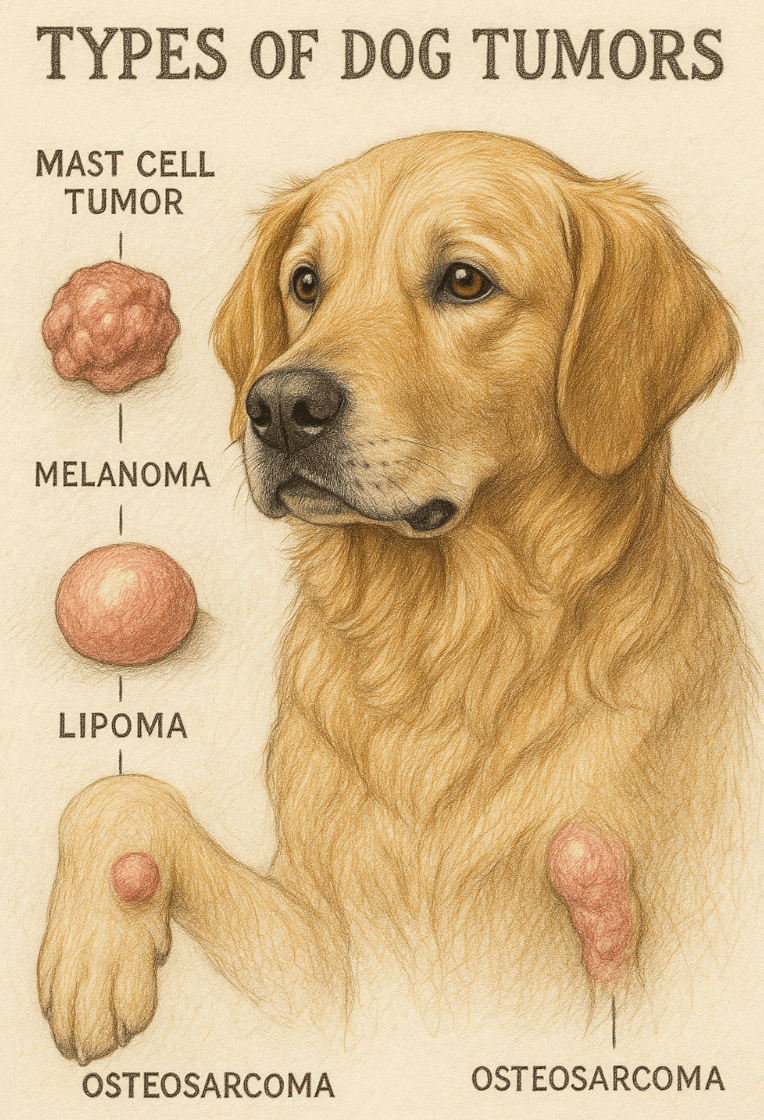
Mast Cell Tumors:
These tumors arise from mast cells, which play a role in allergic reactions, and can vary in severity depending on their grade.Melanomas:
Often found in the mouth or on the skin, melanomas can be aggressive and spread quickly if not addressed early.Lymphoma:
A cancer of the lymphatic system, lymphoma often presents as swollen lymph nodes and can affect multiple organs.Osteosarcoma (Bone Cancer):
This aggressive tumor typically affects large-breed dogs and causes lameness or swelling in the affected limb.Hemangiosarcoma:
Originating in blood vessels, this cancer commonly affects the spleen or heart and is often diagnosed at an advanced stage.
Malignant tumors require prompt veterinary attention, as timely treatment can significantly improve your dog’s prognosis.
Check this guide 👉Understanding Benign Tumors in Dogs: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉Nasal Tumors in Dogs: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉Signs of Brain Tumor in Dogs: Best 7 Health Tips!

Benign Tumors in Dogs | Malignant Tumors in Dogs |
|---|---|
Lipomas (fatty lumps) | Mast Cell Tumors |
Papillomas (warts) | Melanomas |
Sebaceous Adenomas | Lymphoma |
Histiocytomas | Osteosarcoma (bone cancer) |
Perianal Adenomas | Hemangiosarcoma |
Signs and Symptoms of Tumors in Dogs
Detecting tumors early is critical for effective treatment. Familiarizing yourself with the signs and symptoms can help you act quickly if something seems amiss.
Lumps or Bumps Under the Skin:
Any new or unusual growths should be examined by a veterinarian to determine their nature.Changes in Behavior:
Lethargy, loss of appetite, or unexplained weight loss can indicate an underlying health issue, including tumors.Swelling or Lameness:
Swollen areas or difficulty walking may signal bone tumors or other growths affecting mobility.Sores That Don’t Heal:
Persistent wounds or lesions could be a sign of skin cancer or other malignant conditions.Abnormal Bleeding or Discharge:
Unusual bleeding from the nose, mouth, or other areas may point to internal tumors requiring immediate attention.
Being vigilant about these symptoms ensures you can seek veterinary care promptly, improving your dog’s chances of recovery.
Treatment Options for Dog Tumors
The treatment plan for a dog with a tumor depends on the type, location, and severity of the growth. Here are some common approaches veterinarians use to manage and treat tumors in dogs.
Surgical Removal:
Surgery is often the first line of treatment for both benign and malignant tumors, especially if they are localized and accessible.Radiation Therapy:
This treatment targets cancer cells with high-energy beams and is particularly useful for tumors that cannot be fully removed surgically.Chemotherapy:
Used for systemic cancers like lymphoma, chemotherapy helps slow or stop the spread of malignant cells throughout the body.Cryosurgery:
Freezing and destroying abnormal tissue is an option for certain types of tumors, such as small skin growths.Palliative Care:
For advanced cases where curative treatment isn’t possible, palliative measures focus on improving the dog’s comfort and quality of life.
Consulting with your veterinarian will help determine the best course of action tailored to your dog’s specific needs.
Preventive Measures to Reduce Tumor Risks in Dogs
While not all tumors can be prevented, certain lifestyle choices and practices can lower the risk of developing tumors in dogs.
Regular Veterinary Check-Ups:
Routine exams allow vets to detect abnormalities early before they become serious issues.Maintaining a Healthy Weight:
Obesity has been linked to an increased risk of certain cancers; keeping your dog fit supports overall health.Avoiding Carcinogens:
Limit exposure to harmful chemicals, secondhand smoke, and pesticides that may contribute to cancer development.Spaying or Neutering:
Sterilization reduces the risk of reproductive cancers and certain hormonal imbalances.Providing Mental and Physical Stimulation:
A balanced lifestyle with regular exercise and mental challenges boosts immune function and reduces stress-related risks.
Taking preventive steps minimizes potential risks and promotes longevity for your beloved pet.
Emotional Support for Owners Dealing with Dog Tumors
A cancer diagnosis for your dog can be emotionally overwhelming. Finding ways to cope and seek support is vital during this challenging time.
Joining Support Groups:
Connecting with other pet owners facing similar situations provides comfort and shared experiences.Educating Yourself:
Learning about your dog’s condition helps you make informed decisions and feel more in control.Seeking Professional Guidance:
Veterinarians and oncologists offer valuable advice and reassurance throughout the treatment process.Practicing Self-Care:
Caring for yourself emotionally and physically ensures you’re strong enough to care for your dog.Celebrating Small Wins:
Acknowledge milestones and progress, no matter how small, to maintain hope and positivity.
Finding emotional strength enables you to provide the best care for your dog while navigating difficult times.
Alternative Therapies for Managing Dog Tumors
In addition to conventional treatments, some pet owners explore complementary therapies to enhance their dog’s recovery and well-being.
Acupuncture:
This ancient practice may help alleviate pain and improve circulation in dogs undergoing cancer treatment.Herbal Supplements:
Certain herbs, like turmeric or milk thistle, are believed to support immune function and reduce inflammation.Dietary Adjustments:
Adding omega-3 fatty acids or antioxidant-rich foods can complement traditional treatments and boost overall health.Massage Therapy:
Gentle massage promotes relaxation, reduces muscle tension, and improves circulation in dogs with limited mobility.Hydrotherapy:
Swimming or water-based exercises strengthen muscles and joints without putting strain on the body.
While alternative therapies should never replace veterinary care, they can serve as valuable additions to your dog’s treatment plan.
Frequently Asked Questions About Dog Tumors
Are all tumors in dogs cancerous?
No, many tumors are benign and do not pose a significant threat, though they should still be evaluated by a vet.
What should I do if I find a lump on my dog?
Schedule a veterinary appointment to have the lump examined and possibly biopsied for diagnosis.
Can diet prevent tumors in dogs?
While no diet can guarantee prevention, a balanced diet rich in antioxidants may support overall health and reduce risks.
How long can dogs live with cancer?
Prognosis varies widely depending on the type and stage of cancer; early detection and treatment can extend lifespan significantly.
Is treatment expensive for dog tumors?
Costs depend on the type of tumor and treatment required, but financial assistance programs or pet insurance may help offset expenses.
Staying Informed and Proactive About Dog Tumors
Understanding the types of tumors that can affect dogs empowers pet owners to take charge of their furry friend’s health. Whether dealing with benign growths or more serious malignant conditions, early detection and appropriate treatment are essential for managing tumors effectively. By staying informed, observing your dog closely, and partnering with your veterinarian, you can ensure your companion enjoys a happy, healthy life. Remember, your vigilance and care make all the difference in safeguarding your dog against the challenges posed by tumors.
Do Cats Have Taste Buds? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how cats experience flavors and why their taste is so unique.
Do Dogs Have Taste Buds? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how dogs experience taste, their preferences, and what it means for their diet and health.
Can Cats Taste Sweet? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover why cats can’t taste sweetness, how it affects their diet, and tips to keep them healthy and happy.
Can Dogs Taste Sweet? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how dogs perceive sweetness, which foods are safe, and tips to manage their sweet cravings responsibly.