Understanding Prognathism in Dogs: A Comprehensive Guide
Prognathism in dogs is a fascinating yet often misunderstood condition that affects the alignment of their jaws. Whether you’re a seasoned dog owner or considering bringing a furry friend into your life, understanding this trait can help you better care for your canine companion. Prognathism refers to an overbite or underbite, where the upper or lower jaw protrudes more than usual. While some breeds naturally exhibit this feature as part of their genetic makeup, others may develop it due to health issues or environmental factors. In this blog post, we’ll explore everything you need to know about prognathism in dogs, from its causes and types to how it impacts their daily lives.
Types of Prognathism in Dogs
Prognathism manifests in different forms, each with unique characteristics. Understanding these variations is crucial for identifying whether your dog’s jaw alignment falls within normal limits or requires veterinary attention. Below are the primary types of prognathism observed in dogs:
Mandibular Prognathism (Underbite)
This occurs when the lower jaw extends farther forward than the upper jaw. It’s commonly seen in brachycephalic breeds like Bulldogs and Pugs.Maxillary Prognathism (Overbite)
In this case, the upper jaw protrudes significantly beyond the lower jaw. This type is less common but can still occur naturally in certain breeds.Wry Mouth
A wry mouth happens when one side of the jaw grows faster than the other, resulting in a misaligned bite. This condition can lead to chewing difficulties if left untreated.Level Bite
While not technically prognathism, a level bite occurs when the upper and lower teeth meet evenly without overlap. Some breed standards consider this ideal, while others view it as a fault.Genetic Prognathism
Certain breeds are predisposed to prognathism due to their genetics. For example, Boxers and Shih Tzus often display mild forms of mandibular prognathism as part of their natural anatomy.
Understanding these distinctions helps owners recognize potential issues early on and seek appropriate care. By familiarizing yourself with these types, you can ensure your dog receives the best possible support.
Causes of Prognathism in Dogs
The development of prognathism in dogs can stem from various factors, ranging from genetics to environmental influences. Knowing what contributes to this condition allows pet parents to take preventive measures and make informed decisions about their dog’s health. Here’s a breakdown of the most common causes:
Genetic Predisposition
Certain breeds are genetically inclined toward prognathism. Breeds such as Bulldogs, Pugs, and Boston Terriers frequently exhibit this trait as part of their breed standard.Selective Breeding Practices
Intensive breeding programs aimed at achieving specific physical traits can inadvertently promote prognathism. Over time, exaggerated features may become more pronounced.Nutritional Deficiencies
Poor nutrition during puppyhood can hinder proper jaw development. Calcium and phosphorus imbalances, for instance, might affect bone growth.Trauma or Injury
Accidents involving the face or jaw can disrupt normal alignment, leading to prognathism later in life.Congenital Disorders
Some dogs are born with structural abnormalities that cause prognathism. These conditions often require veterinary intervention to manage effectively.
By addressing these underlying causes, owners can mitigate the risk of severe prognathism and improve their dog’s overall well-being. Early detection and proactive care play a vital role in managing this condition successfully.
Check this guide 👉Underbite Dog: Best 7 Tips for a Healthy, Happy Pup!
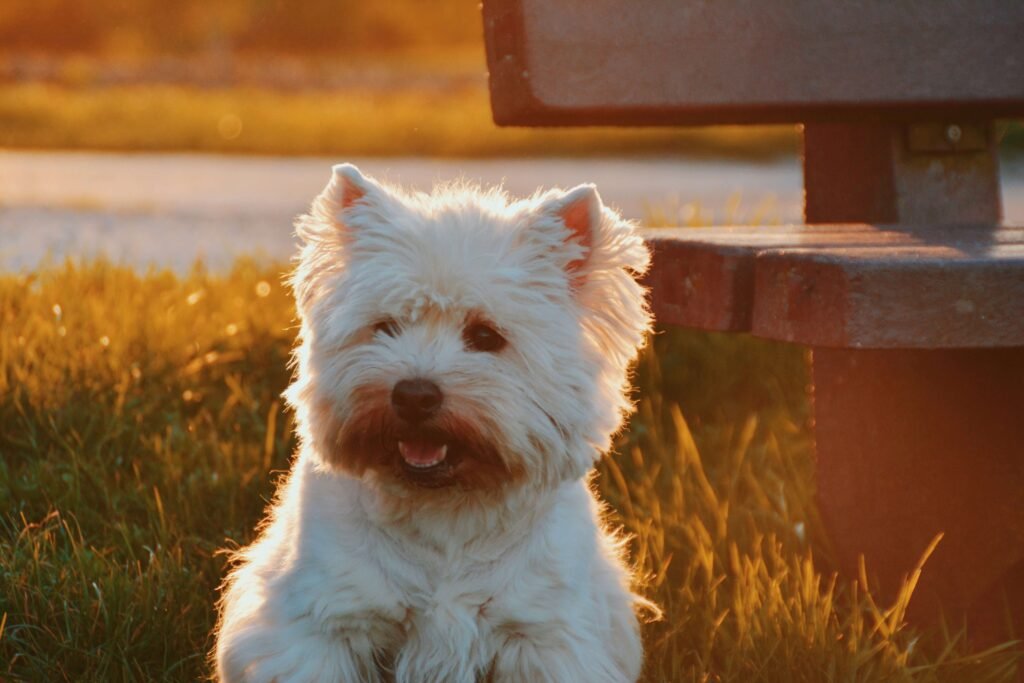

Type of Prognathism | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|
Mandibular Prognathism | Lower jaw protrudes forward; common in brachycephalic breeds. |
Maxillary Prognathism | Upper jaw protrudes forward; rare but noticeable. |
Wry Mouth | Uneven jaw growth causing asymmetry; affects chewing. |
Level Bite | Teeth meet evenly without overlap; varies by breed standards. |
Genetic Prognathism | Naturally occurring in specific breeds due to inherited traits. |
Impact of Prognathism on Daily Life
Prognathism doesn’t just affect a dog’s appearance—it can also influence their quality of life in significant ways. Depending on the severity of the condition, dogs may face challenges related to eating, grooming, and even social interactions. Let’s delve into the key impacts of prognathism:
Chewing Difficulties
Misaligned jaws can make it hard for dogs to chew food properly, potentially leading to malnutrition or digestive issues.Dental Problems
Teeth that don’t align correctly are prone to plaque buildup, gum disease, and tooth decay. Regular dental checkups are essential for affected dogs.Breathing Issues
In brachycephalic breeds, prognathism often coincides with respiratory problems, making breathing laborious during exercise or hot weather.Social Challenges
Other dogs may perceive prognathic traits as unusual, which could impact social dynamics during play or interactions.Grooming Limitations
Dogs with severe prognathism may struggle to groom themselves effectively, necessitating extra assistance from their owners.
While prognathism poses challenges, many dogs adapt remarkably well with proper care and attention. Owners who stay vigilant about their pet’s needs can minimize discomfort and enhance their dog’s happiness.
Managing Prognathism in Dogs
If your dog has been diagnosed with prognathism, there are several steps you can take to ensure they live comfortably and thrive despite the condition. With the right approach, most dogs with prognathism lead fulfilling lives. Consider the following management strategies:
Regular Veterinary Checkups
Frequent visits to the vet help monitor jaw alignment and address any emerging issues promptly.Specialized Diet Plans
Soft or specially formulated foods can ease chewing difficulties and provide adequate nutrition.Orthodontic Interventions
In severe cases, orthodontic devices or surgery may be recommended to correct misalignment.Behavioral Training
Training sessions focused on positive reinforcement can boost confidence and reduce anxiety stemming from social challenges.Routine Dental Care
Brushing your dog’s teeth regularly and scheduling professional cleanings prevents dental complications associated with prognathism.
By implementing these practices, you can create a supportive environment that caters to your dog’s unique needs. Remember, patience and consistency are key to successful management.
Breeds Prone to Prognathism
Prognathism is more prevalent in certain dog breeds due to their genetic predisposition and physical characteristics. Recognizing which breeds are more likely to exhibit this trait can help owners anticipate potential challenges and provide tailored care. Here’s a list of breeds commonly associated with prognathism:
Bulldogs
Known for their distinctive underbites, Bulldogs often display mandibular prognathism as part of their breed standard.Pugs
These charming companions frequently have brachycephalic features, including an underbite that enhances their unique appearance.Boxers
Boxers may exhibit mild forms of prognathism, particularly mandibular prognathism, which aligns with their robust jaw structure.Shih Tzus
This small breed occasionally shows signs of prognathism, contributing to their adorable, flat-faced look.Boston Terriers
With their compact size and brachycephalic traits, Boston Terriers are prone to both overbites and underbites.
Understanding the breeds most affected by prognathism allows owners to prepare for any related health or lifestyle considerations. By focusing on proactive care, you can ensure your dog thrives regardless of their jaw alignment.
Preventive Measures for Prognathism
While some cases of prognathism are unavoidable due to genetics, there are steps owners can take to minimize its impact or prevent secondary issues. Early intervention and consistent care play a critical role in maintaining your dog’s overall health. Below are actionable preventive measures:
Balanced Nutrition
Providing a diet rich in essential nutrients supports proper jaw and bone development during puppyhood.Avoid Overbreeding
Responsible breeding practices reduce the likelihood of exaggerated physical traits that contribute to prognathism.Regular Dental Hygiene
Brushing your dog’s teeth daily and scheduling professional cleanings prevents dental complications linked to misaligned jaws.Monitor Growth Patterns
Keep an eye on your puppy’s jaw alignment as they grow, consulting a vet if abnormalities arise.Minimize Trauma Risks
Protect your dog from injuries to the face or jaw that could exacerbate prognathism later in life.
By incorporating these preventive strategies into your routine, you can safeguard your dog’s well-being and reduce the risk of complications associated with prognathism. Prevention is always better than cure when it comes to your pet’s health.
Signs Your Dog May Have Prognathism
Identifying prognathism early can make a significant difference in managing the condition effectively. While some signs are subtle, others are more noticeable. Being aware of these indicators helps you seek timely veterinary advice and implement appropriate care. Here are common signs to watch for:
Misaligned Teeth
Noticeable gaps or overlaps between the upper and lower teeth may indicate prognathism.Difficulty Eating
If your dog struggles to pick up food or chews awkwardly, it could be a sign of jaw misalignment.Excessive Drooling
Dogs with prognathism may drool more than usual due to difficulties closing their mouths properly.Abnormal Jaw Shape
A visibly protruding upper or lower jaw is a clear indicator of prognathism.Behavioral Changes
Reluctance to eat, play, or engage in activities involving the mouth might signal discomfort caused by prognathism.
Recognizing these signs empowers you to take swift action and address any underlying issues. Early detection not only improves your dog’s comfort but also enhances their long-term quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions About Prognathism in Dogs
What is prognathism in dogs?
Prognathism refers to a misalignment of the jaws, where either the upper or lower jaw protrudes abnormally.
Is prognathism painful for dogs?
Most dogs experience no pain unless the condition leads to secondary issues like dental problems or breathing difficulties.
Can prognathism be corrected?
Mild cases often don’t require treatment, but severe cases may benefit from orthodontics or surgical intervention.
Are certain breeds more prone to prognathism?
Yes, brachycephalic breeds like Bulldogs, Pugs, and Boxers are more likely to exhibit prognathism.
How can I tell if my dog has prognathism?
Look for signs of misaligned jaws, difficulty chewing, or uneven tooth placement. A veterinarian can confirm the diagnosis.
Embracing Prognathism: Celebrating Our Unique Canine Companions
Prognathism in dogs is far more than a mere physical trait—it’s a testament to the diversity and resilience of our beloved pets. Whether your dog was born with a slight underbite or developed a more pronounced overbite, understanding and accepting this characteristic is the first step toward providing them with the care they deserve. By staying informed about the causes, impacts, and management options, you empower yourself to nurture a happy, healthy relationship with your furry friend. After all, every wagging tail tells a story, and embracing their quirks makes the bond between human and dog even stronger.
Do Cats Have Taste Buds? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how cats experience flavors and why their taste is so unique.
Do Dogs Have Taste Buds? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how dogs experience taste, their preferences, and what it means for their diet and health.
Can Cats Taste Sweet? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover why cats can’t taste sweetness, how it affects their diet, and tips to keep them healthy and happy.
Can Dogs Taste Sweet? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how dogs perceive sweetness, which foods are safe, and tips to manage their sweet cravings responsibly.