Why Dog Bite Wounds Are Not Sutured: Understanding the Risks
Dog bites are a common yet often underestimated injury, affecting millions of people worldwide every year. While some wounds may appear minor on the surface, they carry significant risks that require careful medical attention. One surprising fact about dog bite wounds is that they are rarely sutured, even when they seem severe. This decision is not arbitrary but rather rooted in science and safety. In this blog post, we will explore why suturing dog bite wounds is generally avoided, the potential complications involved, and how proper wound care can make all the difference. Whether you’re a pet owner or simply curious about medical practices, understanding this topic can help you respond effectively in case of an emergency.
The Anatomy of a Dog Bite: Why Suturing Can Be Dangerous
Dog bites are unique compared to other types of wounds due to their complex nature. The damage caused by a dog’s teeth is not always visible on the surface, and closing such wounds prematurely can lead to serious complications. Below are key reasons why suturing dog bite wounds is often avoided:
High Risk of Infection :
Dog mouths contain a variety of bacteria, including Pasteurella multocida, which can cause rapid infections if trapped inside a closed wound.Crushing and Tearing Damage :
Unlike clean cuts from sharp objects, dog bites often crush and tear tissues, creating pockets where bacteria can thrive.Delayed Healing :
Closing a wound too soon can trap debris and bacteria, leading to delayed healing and potentially worsening the injury.Need for Drainage :
Open wounds allow for natural drainage of fluids, reducing the risk of abscess formation.Assessment of Deep Tissue Injury :
Suturing can obscure deeper damage, making it harder for doctors to assess and treat underlying issues.
Understanding these factors highlights why medical professionals prioritize leaving dog bite wounds open for observation and treatment before considering any form of closure. This cautious approach ensures better outcomes and reduces the likelihood of complications.
Key Characteristics of Dog Bite Wounds That Influence Treatment Decisions
Each dog bite wound is unique, and its characteristics play a crucial role in determining whether suturing is appropriate. Medical professionals evaluate several aspects before deciding on the best course of action. Here’s what they consider:
Location of the Wound :
Bites on highly vascularized areas like the face may heal better without sutures, as blood flow aids in natural healing.Depth and Severity :
Deeper wounds are more prone to infection and may require extensive cleaning rather than immediate closure.Time Since Injury :
Delayed treatment increases the risk of bacterial colonization, making suturing less advisable.Patient’s Health Condition :
Individuals with weakened immune systems are at higher risk of complications, so non-suturing methods are preferred.Type of Tissue Involved :
Muscle, tendon, or joint involvement requires specialized care beyond simple suturing techniques.
By carefully evaluating these factors, healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans to each patient’s needs. This personalized approach minimizes risks and promotes faster recovery.
Check this guide 👉Guide to Dog Wound Care: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉Top 5 Best Dog Bandages for Ultimate Wound Protection!
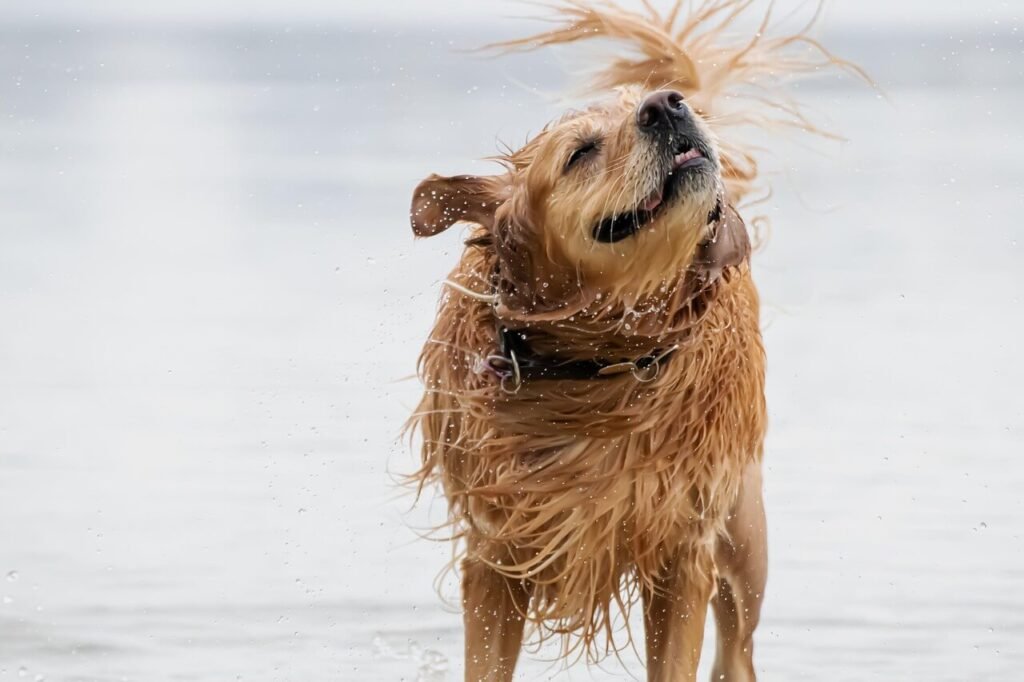

Factors Influencing Treatment | Reasons for Avoiding Sutures |
|---|---|
High bacterial load | Prevents trapping bacteria |
Crushing and tearing injuries | Reduces risk of abscess |
Location of the wound | Allows for proper drainage |
Time since injury occurred | Minimizes infection risks |
Patient’s overall health | Ensures safer healing process |
Alternative Treatments for Dog Bite Wounds
When suturing isn’t an option, medical professionals rely on alternative treatments to manage dog bite wounds effectively. These methods focus on reducing infection risks while promoting natural healing. Here’s what typically happens:
Thorough Cleaning :
Wounds are flushed with saline or antiseptic solutions to remove debris and bacteria.Antibiotic Therapy :
Oral or topical antibiotics are prescribed to combat potential infections.Tetanus Shots :
If the patient’s tetanus vaccination is not up-to-date, a booster shot is administered.Pain Management :
Pain relievers are provided to ensure comfort during the healing process.Regular Monitoring :
Follow-up visits allow doctors to track progress and address any signs of complications early.
These steps collectively ensure that the wound heals safely and efficiently, even without sutures. By prioritizing cleanliness and vigilance, patients can recover fully without unnecessary risks.
Preventing Complications After a Dog Bite
Proper aftercare is essential to prevent complications following a dog bite. Patients must adhere to specific guidelines to support healing and avoid setbacks. Here’s what you should know:
Keep the Wound Clean :
Regularly wash the area with mild soap and water to maintain hygiene.Avoid Scratching or Picking :
Touching the wound can introduce new bacteria and delay healing.Watch for Signs of Infection :
Symptoms like redness, swelling, or pus indicate possible complications.Follow Up with Your Doctor :
Scheduled check-ups help detect hidden issues before they worsen.Stay Updated on Vaccinations :
Ensure your vaccinations, especially rabies and tetanus, are current.
By following these recommendations, you can significantly reduce the chances of complications and promote a smooth recovery. Remember, prevention is always better than cure.
Risks of Suturing Dog Bite Wounds
Suturing dog bite wounds may seem like a quick solution to close an injury, but it carries significant risks that outweigh the benefits in most cases. Medical professionals prioritize patient safety over cosmetic outcomes when treating these types of wounds. Here are some of the primary risks associated with suturing dog bite wounds:
Increased Infection Rates :
Closing a wound too soon can trap bacteria inside, creating an ideal environment for infection.Delayed Detection of Complications :
Sutures can mask underlying tissue damage, making it harder to identify and address complications early.Abscess Formation :
Trapped bacteria and fluids can lead to painful abscesses, requiring additional surgical intervention.Poor Cosmetic Outcomes :
Infected or improperly healed wounds may result in more scarring than if left open initially.Need for Reopening :
If an infection develops, the sutures may need to be removed, causing further trauma to the wound.
These risks highlight why medical professionals exercise caution before deciding to suture dog bite wounds. By prioritizing open wound management, they ensure safer and more effective healing.
Benefits of Open Wound Management
Leaving dog bite wounds open is not just a precautionary measure; it also offers several practical benefits that contribute to better healing outcomes. This approach allows the body’s natural defenses to work effectively while minimizing external interference. Below are the key advantages of open wound management:
Natural Drainage :
Open wounds allow pus, blood, and other fluids to drain naturally, reducing the risk of abscess formation.Improved Monitoring :
Doctors can easily observe the wound for signs of infection or deeper tissue damage during follow-up visits.Reduced Antibiotic Dependency :
Proper drainage and cleaning often decrease the need for prolonged antibiotic use.Enhanced Healing Environment :
Oxygen exposure promotes faster healing of superficial tissues and reduces bacterial growth.Flexibility in Treatment :
Open wounds provide the option to suture later if the injury remains clean and free of complications.
By embracing open wound management, healthcare providers create a safer and more adaptable healing process for patients. This method ensures that any issues can be addressed promptly without compromising recovery.
Steps for At-Home Care After a Dog Bite
While professional medical treatment is essential after a dog bite, proper at-home care plays a crucial role in supporting the healing process. Patients must follow specific guidelines to prevent complications and promote optimal recovery. Here’s what you should do to care for a dog bite wound at home:
Clean the Wound Daily :
Gently wash the area with soap and water to remove dirt and bacteria.Apply Antiseptic Solutions :
Use an over-the-counter antiseptic to keep the wound disinfected and reduce infection risks.Keep the Area Covered :
Use a sterile bandage to protect the wound from external contaminants.Elevate the Affected Area :
Elevating the injured limb can reduce swelling and improve blood circulation.Avoid Strenuous Activities :
Refrain from activities that could strain the wound and delay healing.
Following these steps diligently ensures that your wound heals as quickly and safely as possible. Remember, consistent care at home complements professional treatment and significantly lowers the risk of complications.
Frequently Asked Questions About Dog Bite Wounds
Why do doctors leave dog bite wounds open?
Leaving wounds open allows for drainage, reduces infection risks, and enables doctors to monitor deeper tissue damage.
Can dog bite wounds ever be sutured?
Yes, but only under specific conditions, such as clean facial wounds treated promptly.
How long does it take for a dog bite wound to heal?
Healing times vary depending on the wound’s severity, location, and individual health factors, ranging from days to weeks.
Do I need antibiotics after a dog bite?
Antibiotics are commonly prescribed to prevent or treat infections, especially in deep or contaminated wounds.
What should I do immediately after a dog bite?
Wash the wound thoroughly, apply pressure to stop bleeding, and seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Final Thoughts: Prioritizing Safety Over Convenience
In conclusion, the decision to avoid suturing dog bite wounds is based on sound medical reasoning aimed at protecting patients from potentially life-threatening complications. By understanding the unique challenges posed by these injuries, we can appreciate the importance of allowing wounds to heal naturally whenever possible. Proper wound care, timely medical intervention, and adherence to aftercare guidelines are critical components of a successful recovery. Whether you’re a pet owner or someone who has experienced a dog bite, knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions and prioritize safety above all else.
Do Cats Have Taste Buds? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how cats experience flavors and why their taste is so unique.
Do Dogs Have Taste Buds? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how dogs experience taste, their preferences, and what it means for their diet and health.
Can Cats Taste Sweet? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover why cats can’t taste sweetness, how it affects their diet, and tips to keep them healthy and happy.
Can Dogs Taste Sweet? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how dogs perceive sweetness, which foods are safe, and tips to manage their sweet cravings responsibly.