Unlocking the Language of Police Dog Commands
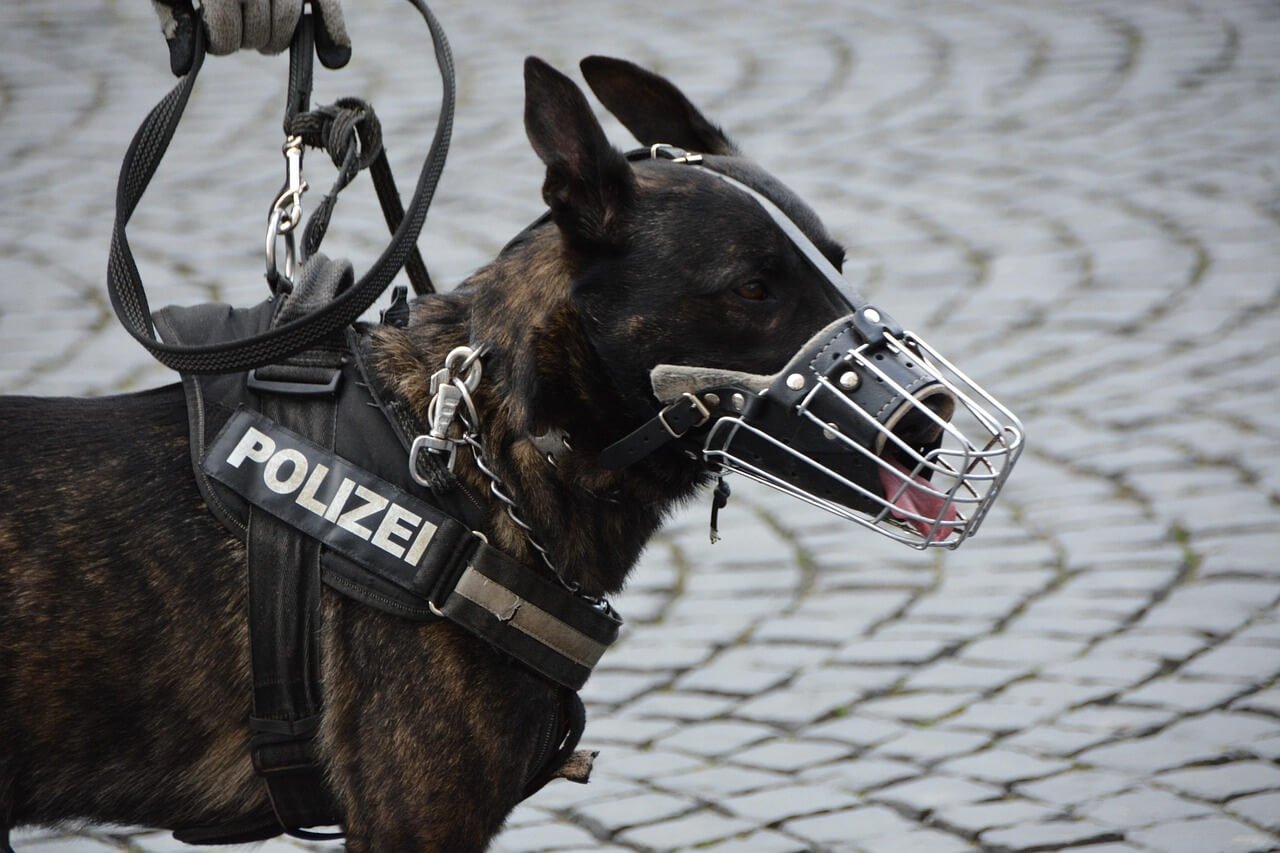
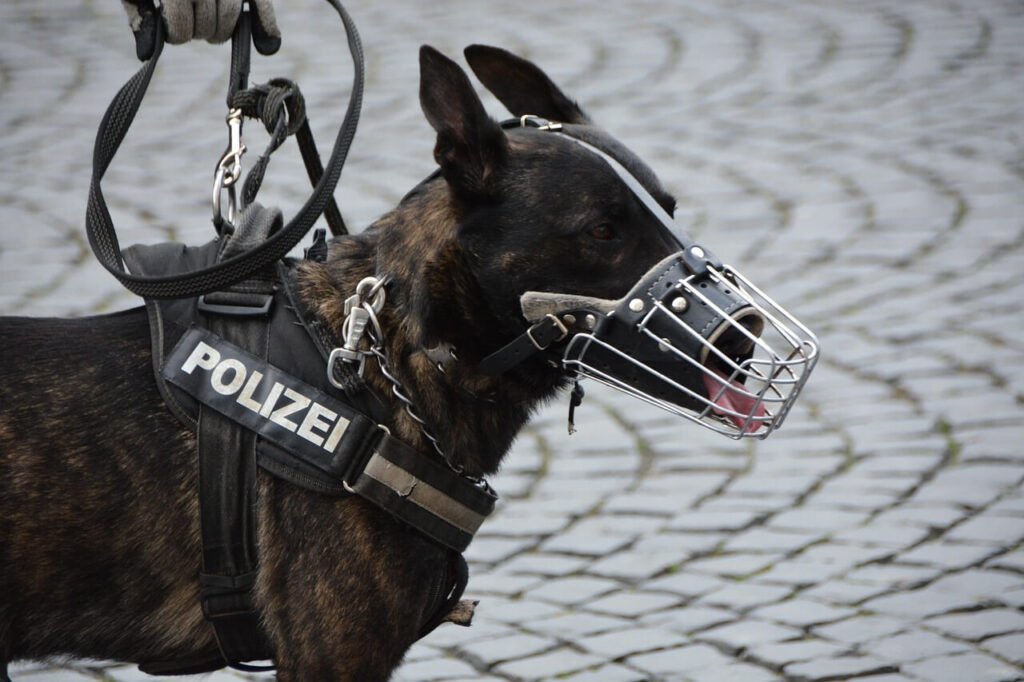
Police dogs, often referred to as K-9 units, play a vital role in law enforcement. These highly trained animals are not just pets but skilled partners who assist officers in various tasks, from tracking suspects to detecting illegal substances. Central to their success is the system of commands they respond to—a unique language that bridges the gap between humans and canines. Understanding police dog commands offers insight into the intricate bond between handler and dog, as well as the precision required for their demanding work. Whether you’re a dog enthusiast or simply curious about the world of K-9 units, this blog post will guide you through the fascinating realm of police dog communication.
The Foundation of Police Dog Commands
Before diving into specific commands, it’s essential to understand the core principles behind police dog training. These commands are designed to be clear, concise, and consistent, ensuring the dog responds accurately even in high-pressure situations.
Clarity : Commands must be easy for the dog to recognize and interpret. This often involves using short, one-word instructions.
Consistency : Handlers use the same words and tones every time to avoid confusing the dog.
Repetition : Training involves countless repetitions to reinforce the connection between the command and the desired action.
Positive Reinforcement : Rewards like treats or praise are used to encourage correct behavior during training sessions.
Adaptability : While basic commands remain constant, handlers may adjust their approach based on the dog’s individual personality and strengths.
These foundational elements ensure that police dogs can perform reliably in diverse scenarios, making them invaluable assets to law enforcement teams.
Common Police Dog Commands Every Handler Knows
Police dog training revolves around a set of universal commands that form the basis of their operational duties. These commands are taught early in the dog’s training and refined over time to suit specialized tasks.
Sit : A fundamental command used to keep the dog calm and focused during brief pauses in activity.
Stay : Ensures the dog remains in place until given further instructions, crucial for maintaining discipline at crime scenes.
Come : Calls the dog back to the handler, often used when the dog has been sent ahead to investigate an area.
Heel : Instructs the dog to walk closely beside the handler, maintaining control during patrols or public interactions.
Search : Directs the dog to actively look for suspects, evidence, or specific scents, depending on the situation.
Mastering these commands allows police dogs to transition seamlessly between roles, whether they’re conducting searches, apprehending suspects, or providing security. The precision with which they execute these instructions is a testament to their rigorous training.
Check this guide 👉Understanding Military Dog Commands: Best 7 Expert Tips!
Check this guide 👉The Role of German Shepherd Police Dogs: Best 7 Expert Tips!

Command Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
Sit | Maintains focus and control |
Stay | Keeps the dog stationary |
Come | Recalls the dog to the handler |
Heel | Ensures close proximity |
Search | Initiates scent detection |
Advanced Commands for Specialized Tasks
Beyond basic obedience, police dogs are trained in advanced commands tailored to their specific roles. These instructions allow them to tackle complex challenges, such as detecting explosives or tracking fleeing suspects.
Track : Guides the dog to follow a scent trail left by a person or object.
Bite and Hold : Used sparingly, this command instructs the dog to apprehend a suspect without causing excessive harm.
Find It : Focuses the dog’s attention on locating hidden items or substances.
Alert : Signals the dog to notify the handler upon discovering something significant, such as drugs or weapons.
Release : Orders the dog to let go of an item or person it has secured.
These advanced commands demonstrate the incredible adaptability of police dogs, enabling them to excel in high-stakes environments. Their ability to execute such precise actions under pressure is a testament to their rigorous training and unwavering loyalty.
Training Techniques Behind Effective Commands
The effectiveness of police dog commands hinges on the methods used during training. Handlers employ a variety of techniques to ensure their dogs respond reliably in real-world scenarios.
Clicker Training : Uses a clicking sound paired with rewards to mark desired behaviors instantly.
Scent Association : Teaches the dog to link specific scents with positive outcomes, enhancing its detection abilities.
Scenario-Based Drills : Simulates real-life situations to prepare the dog for unpredictable challenges.
Handler Bonding : Strengthens the relationship between dog and handler, improving communication and trust.
Progressive Difficulty : Gradually increases the complexity of tasks to build confidence and competence.
Through these techniques, police dogs develop the skills and discipline needed to perform their duties effectively. The success of their training reflects the dedication of both the handler and the animal.
The Role of Non-Verbal Commands
While verbal commands are essential, non-verbal signals also play a critical role in police dog communication. These silent cues allow handlers to direct their dogs discreetly, especially in situations where silence is paramount.
Hand Signals : Gestures like pointing or raising a hand can direct the dog to move in specific directions without alerting others nearby.
Body Language : Handlers use posture and movement to convey urgency or calmness, helping the dog gauge the situation’s intensity.
Eye Contact : Maintaining or breaking eye contact can signal when the dog should focus or relax, reinforcing trust between handler and canine.
Tactical Cues : Subtle touches or taps on the dog’s body guide it during close-quarters operations, ensuring precision in confined spaces.
Silent Whistles : High-pitched whistles audible only to dogs provide a discreet way to issue commands over short distances.
Non-verbal commands highlight the versatility of police dog training, enabling seamless communication even in the most challenging environments. This silent language underscores the depth of the bond between handler and dog.
Challenges in Training Police Dogs
Training a police dog is no small feat, as it requires overcoming numerous challenges to ensure the animal is prepared for real-world scenarios. Both physical and mental obstacles must be addressed to create a reliable K-9 partner.
Distraction Management : Dogs must learn to ignore loud noises, crowds, or other distractions while focusing on their handler’s commands.
Stamina Building : Physical endurance is crucial, as police dogs often work long hours in demanding conditions.
Behavioral Consistency : Ensuring the dog responds reliably every time, regardless of stress or fatigue, is a key training goal.
Adapting to New Environments : Dogs must perform equally well in urban settings, wooded areas, or open fields, adapting quickly to unfamiliar terrain.
Handler Dependency : Over-reliance on a single handler can hinder performance, so dogs are trained to respond to multiple team members if needed.
Overcoming these challenges requires patience, expertise, and a deep understanding of canine behavior. The result is a highly skilled partner capable of excelling in diverse law enforcement roles.
Benefits of Police Dog Commands Beyond Law Enforcement
The principles behind police dog commands extend far beyond their application in law enforcement. These techniques have influenced various fields, demonstrating the broader impact of effective canine training.
Search and Rescue Operations : Commands like “search” and “track” are invaluable for locating missing persons in disaster zones or wilderness areas.
Service Dog Training : Techniques used for police dogs are adapted to train service animals that assist individuals with disabilities, enhancing their quality of life.
Military Applications : Military working dogs benefit from similar command structures, aiding in tasks like bomb detection and patrol duties.
Pet Obedience Programs : Basic commands such as “sit,” “stay,” and “heel” are derived from police dog training, helping everyday pet owners manage their dogs more effectively.
Therapy Animal Work : Commands that promote calm and focused behavior are essential for therapy dogs working in hospitals, schools, and nursing homes.
The influence of police dog commands reaches into countless areas, proving that the methods developed for law enforcement have universal value. This shared knowledge strengthens the human-canine bond across different contexts.
Frequently Asked Questions About Police Dog Commands
What languages are police dog commands given in?
While English is commonly used, some handlers may use their native language or even code words for added security.
How long does it take to train a police dog?
Training typically lasts 12 to 16 weeks, followed by ongoing practice throughout the dog’s career.
Can any dog become a police dog?
No, only certain breeds with the right temperament, intelligence, and physical attributes are selected for police work.
Do police dogs understand multiple commands?
Yes, they are trained to recognize dozens of commands, both verbal and non-verbal.
What happens if a police dog disobeys a command?
Disobedience is rare due to extensive training, but handlers address it through reinforcement exercises.
The Enduring Partnership Between Humans and Police Dogs
The world of police dog commands reveals the depth of collaboration between humans and animals. These remarkable canines undergo years of training to master a language that bridges species, enabling them to serve alongside officers with unparalleled skill and dedication. From basic obedience to advanced detection, their ability to interpret and execute commands showcases the power of teamwork and trust. As we reflect on their contributions to law enforcement, it’s clear that police dogs are more than just tools—they are loyal partners whose impact resonates far beyond the field. With their unique talents and unwavering commitment, they continue to inspire admiration and respect worldwide.
Do Cats Have Taste Buds? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how cats experience flavors and why their taste is so unique.
Do Dogs Have Taste Buds? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how dogs experience taste, their preferences, and what it means for their diet and health.
Can Cats Taste Sweet? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover why cats can’t taste sweetness, how it affects their diet, and tips to keep them healthy and happy.
Can Dogs Taste Sweet? Best 7 Expert Tips! – Discover how dogs perceive sweetness, which foods are safe, and tips to manage their sweet cravings responsibly.